













Hassle free, 2-Year Warranty
Fast, Free Shipping on Orders $35+
Lifetime Technical Support
30-Day Money Back Guarantee
Plugable USB-C Triple 4K Monitor Docking Station with 100W Laptop Charging
$239.95 USD
SKU: UD-ULTC4KAmazon Rating : (1564 Reviews)
Features
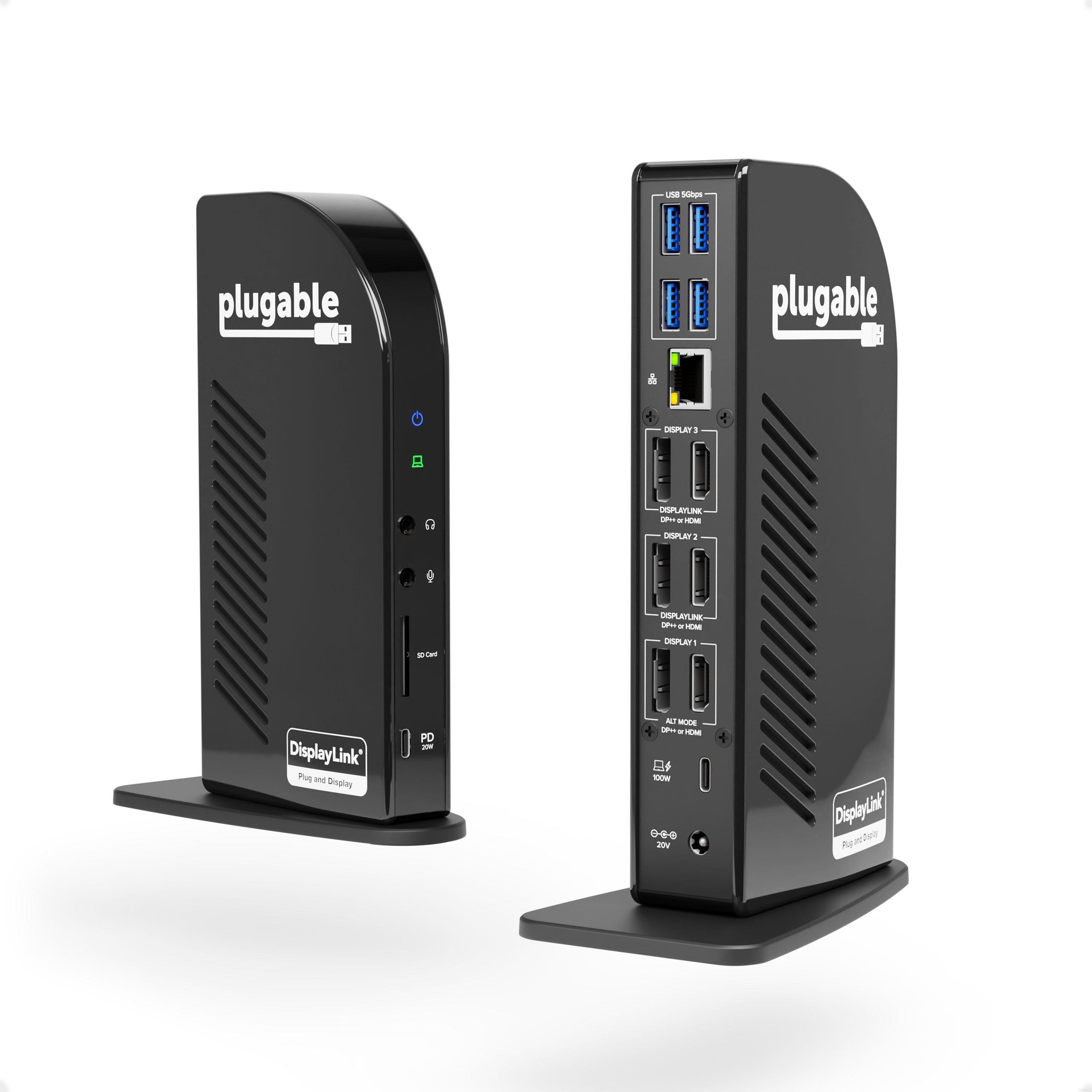
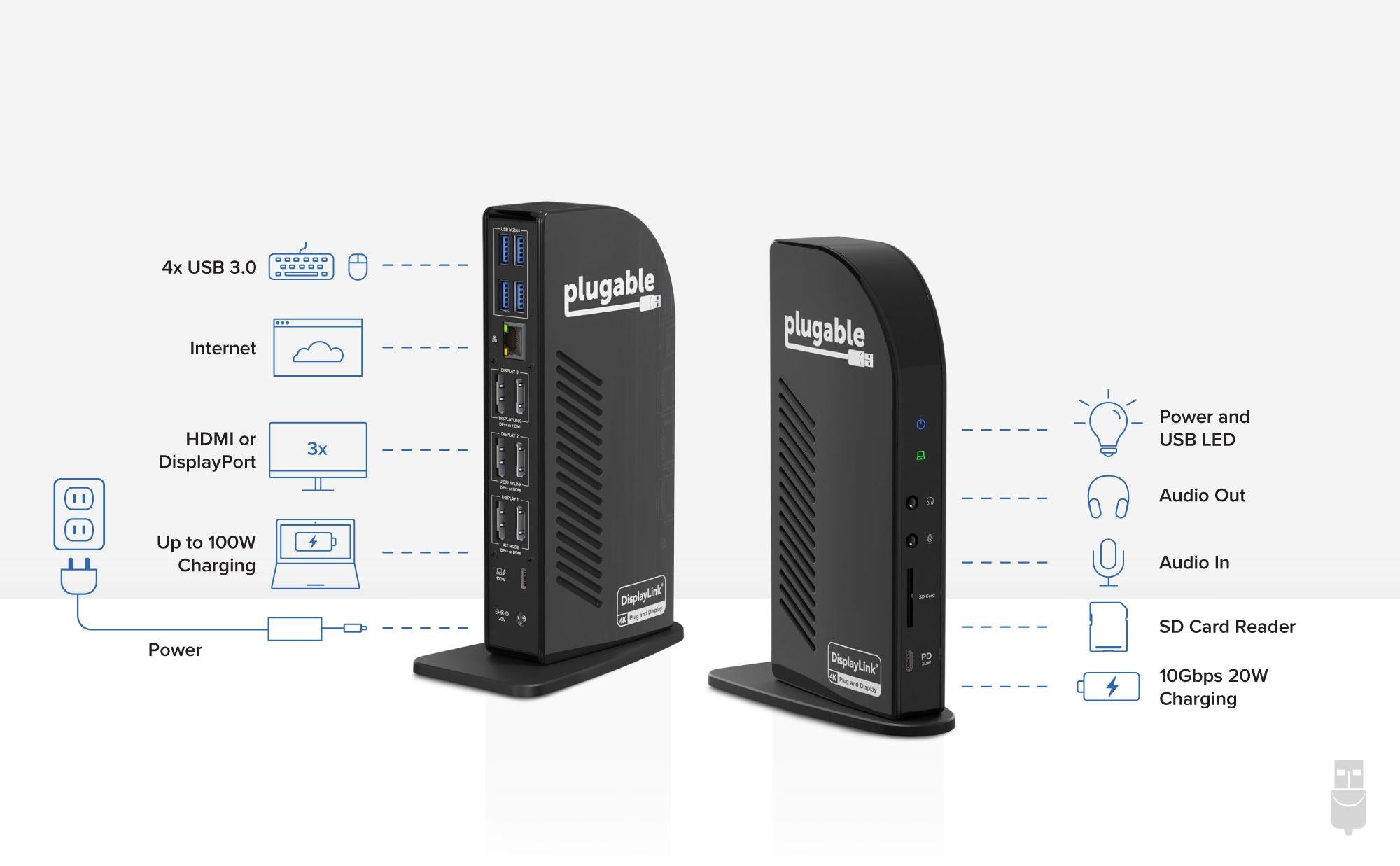
- Powerful Ports—13 ports and power delivery to keep your laptop running all day, this USB-C docking station with Power Delivery extends across three screens with room for all of your peripherals. All through a single 10Gbps USB-C cord back to the computer
- Triple 4K—Featuring 3x DisplayPort ports, and 3x HDMI ports — standardize on one or use a mix of both to extend your desktop across three 4K monitors @ 60Hz with USB4 / Thunderbolt 4 hosts via Alt Mode and this laptop docking station — no dongles required
- 100W Power Delivery—Power your laptop with up to 100W (96W certified) directly through the DisplayLink docking station, so you can leave your laptop power adapter in your travel bag.
- Compatibility—USB-C dock is compatible with Windows 10 or later, ChromeOS 100.x or later, and macOS 11+ systems with Thunderbolt 4, Thunderbolt 3, USB4, and USB-C. Requires installation of DisplayLink Drivers. HDCP not supported
- Connection Options—Triple display docking station let’s you connect your phone or other devices with 1x USB-C (10Gbps, 20W PD), and keep expanding with 4x USB 3.0 (5Gbps), an SD card reader, Gigabit Ethernet, and audio in and out ports
Free 3-Day Shipping When Buying Direct!

Plugable's flagship DisplayLink docking station has gotten a big upgrade. The Plugable USB-C Triple 4K Display Docking Station (UD-ULTC4K) was designed from the ground up based on five years of collected user feedback to include improved charging capabilities, more flexible display options, an SD card reader, and a front-facing 10Gbps, 20W USB-C port to fast charge your phone and other devices.
This second-generation dock provides a better customer experience with 3x DisplayPort ports and 3x HDMI ports to match your monitors. And of course, whichever you choose—HDMI or DisplayPort—you’ll get resolutions up to 4K @ 60Hz on all three monitors with USB4 / Thunderbolt 4 hosts via Alt Mode. But monitor ports weren’t the only thing to get a boost. The UD-ULTC4K comes with 100W charging to better accommodate larger laptops. This docking station is a one-stop shop for all peripherals users may need, connecting all 13 ports to the laptop with a powerful 10Gbps USB-C cable.
Note: New and innovative products aren't without compatibility concerns, it is important to read the information below for details regarding display output types and system requirements.
Not all USB-C ports offer Alt Mode or PD charging. Having a fully compatible USB-C, USB4, Thunderbolt 3, or Thunderbolt 4 port is required for this docking station, it will not work properly when adapted to USB 3.0. The UD-ULTC4K supports Windows 11, 10, 8.x, and 7, ChromeOS 100+, and macOS 10.14+. Linux, and some older macOS versions are not supported.

4K Your Way
Compatible with Windows, ChromeOS, and Mac, the Plugable USB-C Triple 4K Display Docking Station (UD-ULTC4K) is the computer docking station built for adding monitors.
Featuring 3x DisplayPort ports, and 3x HDMI ports, now you can standardize on one or use a mix of both. And HDMI or DisplayPort will give you resolutions up to 4K @ 60Hz on all three monitors when connected to a compatible host computer with USB4 / Thunderbolt 4 hosts via Alt Mode.
Ports a Plenty
This Displaylink docking station has a front-facing USB-C port for 10Gbps data transfer and 20W charging to accommodate your phone or other devices.
Speaking of peripherals, the UD-ULTC4K also has 4x USB 3.0 ports for 5Gbps data transfer rates, an SD Card Reader, a Gigabit Ethernet port, and separate audio in and audio out ports.

Power Delivered
Power Delivery—charging your laptop through a USB-C port—can get confusing. How much power is enough? How much is too much?
The UD-ULTC4K has you covered. With 100W charging (96W certified), you have enough power to charge just about any laptop—even under a heavy workload. And if your laptop needs less power, the dock communicates with your computer to negotiate the perfect charge level.
To strictly comply with 100W regulatory limits with margin, certification limits to charging to 96W.

The Breakdown
- 1x USB-C (10Gbps, 20W PD)
- 1x SD Card Reader
- 1x Audio In (3.5mm) and 1x Audio Out (3.5mm)
- 2x DisplayPort 1.2 or HDMI 2.0 (DisplayLink)
- 1x DisplayPort 1.2 or HDMI 2.0 (Alt Mode)
- 4x USB 3.0 (5Gbps)
- 1x Gigabit Ethernet
- 1x 10Gbps USB-C connection to host with 100W Power Delivery
Display Compatibility and Supported Resolutions
- 3x 4K @ 60Hz via DisplayPort or HDMI with USB4, Thunderbolt 4 / 3, USB-C hosts that support DP 1.4
- On hosts that support DP 1.2, get 1x 4K @ 30Hz via DisplayPort or HDMI and 2x 4K @ 60Hz via DisplayPort or HDMI
In The Box
| Item and Quantity | Item Notes |
|---|---|
| 1x Plugable USB-C 4K Triple Display Docking Station | |
| 1x 10Gbps USB-C to USB-C Cable | |
| 1x 135W Power Adapter | |
| 1x Quick Start Guide |
Included Cables
| Port Type (Side 1) | Cable Specification | Port Type (Side 2) | Cable Length | External Power for Cable |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male USB-C | USB 3.2 Gen 2 (10Gbps) | USB-C | 1.0m/3.28ft | No |
| Male IEC Type B | IEC C5/C6 | 1.88m/6.17ft | No |
Video
| Port | Placement | Specification | Max Resolution and Refresh Rate | HDCP | Chipset |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1x HDMI 4K or
DisplayPort (Output) |
Rear | DisplayPort 1.2 or HDMI 2.0 | 3440x1440 @ 60Hz 3840x2160 @ 60Hz2560x1440 @ 60Hz 2560x1080 @ 60Hz 1920x1200 @ 60Hz 1920x1080 @ 60Hz 1600x900 @ 60Hz 1280x1024 @ 60Hz 1280x800 @ 60Hz 1280x720 @ 60Hz 1152x864 @ 60Hz 1024x768 @ 60Hz 800x600 @ 60Hz 640x480 @ 60Hz |
Host Dependent | |
| 2x HDMI 4K or
DisplayPort (Output) |
Rear | DisplayPort 1.2 or HDMI 2.0 | 3440x1440 @ 60Hz 3840x2160 @ 60Hz2560x1440 @ 60Hz 2560x1080 @ 60Hz 1920x1200 @ 60Hz 1920x1080 @ 60Hz 1600x900 @ 60Hz 1280x1024 @ 60Hz 1280x800 @ 60Hz 1280x720 @ 60Hz 1152x864 @ 60Hz 1024x768 @ 60Hz 800x600 @ 60Hz 640x480 @ 60Hz |
Not Supported | DL-6950 DisplayLink |
Video Output Modes
| Host Stream Specification | Host Port Type | Number of Displays Used | Max Resolution at Display Count |
|---|---|---|---|
| DisplayPort 1.2 or HDMI 2.0 | Thunderbolt™ 3 or USB-C | 1, 2, or 3 | 3840x2160 @ 60Hz 3840x2160 @ 60Hz3840x1600 @ 60Hz 3440x1440 @ 60Hz 2560x1440 @ 60Hz 2560x1080 @ 60Hz 1920x1080 @ 60Hz 1600x900 @ 60Hz 1280x1024 @ 60Hz 1280x800 @ 60Hz 1280x720 @ 60Hz 1152x864 @ 60Hz 1024x768 @ 60Hz 800x600 @ 60Hz 640x480 @ 60Hz |
Audio
| Port | Placement | Connection | Max Bit Depth and Sample Rate | Signal Output | Channels | Chipset |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Headphone Jack Line Out |
Front | 3.5mm (TRS) | 16-bit 48KHz | Analog | 2 | DL-6950 DisplayLink |
| Microphone Jack Line In |
Front | 3.5mm (TRS) | 16-bit 48KHz | Analog | 2 | DL-6950 DisplayLink |
| DisplayPort Output |
Rear | DisplayPort | Host Dependent | Digital | Host Dependent | |
| DisplayPort Output |
Rear | DisplayLink DisplayPort | 16-bit 48KHz | Digital | 6* | DL-6950 DisplayLink |
| DisplayPort Output |
Rear | DisplayLink DisplayPort | 16-bit 48KHz | Digital | 6* | DL-6950 DisplayLink |
| HDMI 4K Output |
Rear | HDMI | Host Dependent | Digital | Host Dependent | |
| HDMI 4K Output |
Rear | DisplayLink HDMI | 16-bit 48KHz | Digital | 6* | DL-6950 DisplayLink |
| HDMI 4K Output |
Rear | DisplayLink HDMI | 16-bit 48KHz | Digital | 6* | DL-6950 DisplayLink |
Power
| Port | Placement | Power Host / Device | Connection Type | Notes | Voltage | Amperage | Wattage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power Supply | Rear | Device | Region-specific Power Adapter | 20.0V | 6.75A | 135.0W | |
| USB-C to Host | Rear | Host | USB-C Power Delivery | Check Compatibility Table | 20.0V | 5.0A | 100.0W |
USB To Devices
| Port | Placement | Version and Link Rate | Features | Voltage | Amperage | Wattage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4x USB-A | Rear | USB 3.0 (5Gbps) | 5V | 900mA | 4.5W | |
| 1x USB-C | Front | USB 3.2 Gen 2 (10Gbps) | USB Power Delivery | 9V | 2200mA | 19.8W |
Connection To Host
| Port | Placement | Version and Link Rate | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1x USB-C | Rear | USB 3.2 Gen 2 (10Gbps) | USB Power Delivery |
Wired Network
| Port | Placement | Version and Link Rate | Features | Chipset |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DisplayLink Gigabit Ethernet | Rear | 1000BASE-T | DL-6950 DisplayLink |
Physical Stats
| Item | Size (H x W x D) or Length | Weight | SKU or Part Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| USB-C Docking Station | 20 x 7.3 x 13.6 centimeters 7.9 x 2.9 x 5.4 inches |
624 grams 22 ounces |
UD-ULTC4K |
Card Reader
| Media Interface | Bus Interface | Bus Speed | Chipset |
|---|---|---|---|
| SD or SDHC or SDXC or MMC | Ultra-High Speed II (UHS-II) | 312 MB/s | Genesys Logic GL3232S |
LEDs
| LED Number | Shape | Color | Status | Definition | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Power Symbol | Blue | Solid | Powered on | |
| 2 | Laptop Icon | Green | Solid | Active host connection |
Operating Systems:
- Windows 11 and 10, Home or Pro
- Recommended with all updates installed
- Administrative permissions are required for DisplayLink software installation
- Chrome OS 100+
- macOS 10.15.5->10.15.6 (Catalina), macOS 11 (Big Sur), and macOS 12 (Monterey)
- Recommended fully updated to the latest version of the operating system
- DisplayLink Manager App installation requires administrative permissions
- MacOS users, please click here for additional compatibility notes with DisplayLink and macOS.
CPU/APU:
- Intel Core i5 or i7 6th Generation (6xxx series ) 2.4+GHz
- AMD Ryzen 2.4GHz or better
- Apple M1 / M2 / M3 (M1 Pro/Max, M2 Pro/Max, M3 Pro/Max)
Graphics Controller (with fully updated drivers):
- Intel HD 620 or better
- AMD Vega or newer ( except Vega 3 )
- NVIDIA GeForce 900 series or newer
- Apple M1 / M2 / M3 graphics
Connectivity and Ports:
- USB-C, Thunderbolt 3, Thunderbolt 4, or USB4 with DisplayPort Alternate Mode (DP Alt-Mode) and USB-C Power Delivery (PD)
- USB-C Port with Power Delivery (PD), this docking station can replace a power supply rated up to 96W
Charging Support:
Supported Displays:
- 3x 4K @ 60Hz via DisplayPort or HDMI with USB4, Thunderbolt 4 / 3, USB-C hosts that support DP 1.4 Alternate Mode
- On hosts that support DP 1.2 Alternate Mode, get 1x 4K @ 30Hz via DisplayPort or HDMI and 2x 4K @ 60Hz via DisplayPort or HDMI
- 1366x768 resolution is not supported on either DisplayLink based DisplayPort or HDMI outputs
Not all computers with USB-C ports support both USB-C DisplayPort Alternate Mode and USB-C Power Delivery, most desktop computers will not support DisplayPort Alternate Mode. Many notebooks (laptops) do not support both DP Alt-Mode or PD, or may not support either. Please feel free to contact our support team and we will be happy to help determine if your laptop is compatible with our UD-ULTC4K docking station.
Windows Installation and Setup
- Download and install the DisplayLink software.
- Connect the power supply to your wall socket or power strip, and then to the docking station.
- Connect the displays to the docking station.
- Connect the docking station to the computer using the USB cable provided with the docking station.
macOS Installation and Setup
- Download and install the DisplayLink Manager for macOS.
- Detailed installation and configuration instructions can be found by clicking on the "INFO" button, or in the next step.
- Please follow the detailed instructions below to install and configure the DisplayLink software for your version of macOS:
- Connect the power supply to your wall socket or power strip, and then to the docking station.
- Connect the displays to the docking station.
- Connect the docking station to the computer using the USB cable provided with the docking station.
ChromeOS Installation and Setup
- No driver download is necessary, through ChromeOS version 100 or later is required.
- Connect the power supply to your wall socket or power strip, and then to the docking station.
- Connect the displays to the docking station.
- Connect the docking station to the computer using the USB cable provided with the docking station.
macOS users, please click the 'INFO' button in the table below for important installation instructions.
| Platform | Important Notes | Date | Version and Download |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 11 and 10 | Drivers will typically install automatically through Windows Update. See the following article for more information about installing the DisplayLink driver. |
June 12, 2024 | DisplayLink Software 11.4 M0 |
| macOS 11, 12, 13, and 14 | macOS 13 and 14 installation instructions for the DisplayLink Manager App available on our knowledge base. macOS 11 and 12 installation instructions for the DisplayLink Manager App available on our knowledge base. |
July 16, 2023 | DisplayLink Manager App version 1.9 |
| ChromeOS | ChromeOS supported with latest software updates installed (version 100 or later) See the following article for more information on using DisplayLink products on ChromeOS. |
No driver installation needed |
Legacy Drivers for Older Systems
| Platform | Important Notes | Date | Version and Download |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 8.x and 7 | Drivers often install automatically through Windows Update. See the following article for more details about installing the DisplayLink driver. |
September 22, 2022 | DisplayLink Software 10.3 M0 |
| Windows Vista | January 7, 2015 | DisplayLink Software 7.7 M3 | |
| Windows XP | July 18, 2014 | DisplayLink Software 7.6 M2 | |
| macOS 10.15 | DisplayLink Manager App Installation Instructions See the following article for more information about the macOS DisplayLink Manager app. |
September 8, 2021 | DisplayLink Manager App version 1.5 |
| macOS 10.14 | It is highly recommended to follow along our instructions on installing the legacy driver to ensure the driver loads properly. See the following article for more information about the macOS Legacy driver. |
August 13, 2020 | DisplayLink Software 5.2.5 |
Filter Help Articles and Frequent Questions by Category
Choose one or more filters within each category to narrow down the articles. Each selection will result in only displaying articles that include all of your choices.
Articles
Well how about that, it looks like we don't have any articles matching your filters! Try removing one of your choices or clear the filters to show all articles.
You can always contact support if you need help too!
USB Port Types
USB-A
pietz, CC BY-SA 3.0 , via Wikimedia Commons
This is the standard USB connection that most computers offered prior to the introduction of USB Type-C (USB-C). Even after the introduction of USB Type-C, this is still quite common.
It can provide data transfer rates up to the USB 3.1 Gen 2 (10 gbps) specification depending on the host and device, but does not directly support video in the way that USB-C Alternate Mode does. This limitation makes DisplayLink USB graphics adapters and docking stations ideal on systems that do not have USB-C, or in instances where more displays are needed beyond available video outputs of a PC.
USB-B
Fred the Oyster, CC BY-SA 4.0 , via Wikimedia Commons
IngenieroLoco, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
This type of connection comes in a couple different styles depending on whether USB 3.0 and higher transfer rates are supported (bottom graphic). Usually this type of connection is used to plug into USB devices that do not have a fixed cable connected, such as USB docking stations, USB hubs, printers, and others.
USB Mini-B
Fred the Oyster, CC BY-SA 4.0 , via Wikimedia Commons
One of the first connectors for charging a smartphone, wireless game controller (such as the Sixaxis and DualShock 3), and other small devices such as external hard drives. Not commonly used today, but is still used in some cases. Most devices using USB Mini B are using USB 2.0, though a USB 3.0 variant does exist. This specification also added USB On-The-Go (OTG) functionality, though it is more commonly implemented with Micro USB.
USB Micro-B
Fred the Oyster, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
IngenieroLoco, CC BY-SA 4.0 , via Wikimedia Commons
A smaller connector that serves many of the same uses as the Mini B connector, with added optional features such as Mobile High-Definition Link (MHL) to allow devices like smartphones to output video to larger displays without requiring a dedicated port for video output.
The larger variant of USB-B is most commonly used for external hard drives for higher 5Gbps transfer rates.
USB-C, Thunderbolt™ 3, and Thunderbolt™ 4
Niridya , CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
The most recent USB connection, USB Type-C (USB-C), represents a major change in what USB can do. The connector is smaller, can be connected in two orientations, is able to carry substantially more power and data, and can directly carry video signals of multiple types (HDMI, DisplayPort, etc.) Intel has also adapted the USB-C connector for use with Thunderbolt 3 and Thunderbolt 4.
It is important to note that while all Thunderbolt 3 and Thunderbolt 4 connections are USB-C, not all USB-C connections can be used with Thunderbolt 3 or Thunderbolt 4 devices.
More details regarding physical USB connections can be found on Wikipedia . The graphics depicted here are adapted from Wikimedia Commons by various artists under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license.
My Plugable DisplayLink USB Docking Station or USB Video Adapter Is Not Working As Expected On Mac. Why is this happening?
This document covers steps to resolve the most common issues enabling video from Plugable products with DisplayLink technology on Mac. In order to use a Plugable DisplayLink device on Mac, the following actions are necessary:
1. The DisplayLink Manager Application must be installed on the host Mac
The DisplayLink Manager Application is available to download here
We have detailed installation instructions available at the links below:
macOS Sonoma version 14 and macOS Ventura version 13 installation instructions
macOS Monterey version 12 and macOS Big Sur version 11 installation instructions
2. The DisplayLink Manager Application must be granted the proper security permissions in order to function properly
The DisplayLink Manager application must be granted ‘Screen Recording’ permissions within the macOS ‘Privacy & Security’ settings in order to function. If these permissions are not granted, then the product will not function.
To be clear, no information is actually being recorded. The DisplayLink Application only needs this permission in order to generate the image shown within the displays connected to the product.
More information for granting these permissions for the various supported versions of macOS is available at the links below:
macOS Sonoma 14: Screen Recording Permission
macOS Ventura 13: Screen Recording permission
macOS Monterey 12: Screen Recording permission
macOS Big Sur 11: Screen Recording permission
3. The DisplayLink Manager Application must be actively running
The DisplayLink Manager Application must be running in order for the product’s video outputs to function.
When the DisplayLink Manager Application is running, there will be a small DisplayLink icon (which looks like two interlocking displays) located within the Apple Menu bar at the top of your screen.
If the DisplayLink Manager Application is not running, please open a new Finder window and navigate to the ‘Applications’ folder and then double click on the ‘DisplayLink Manager’ application icon to start the application.

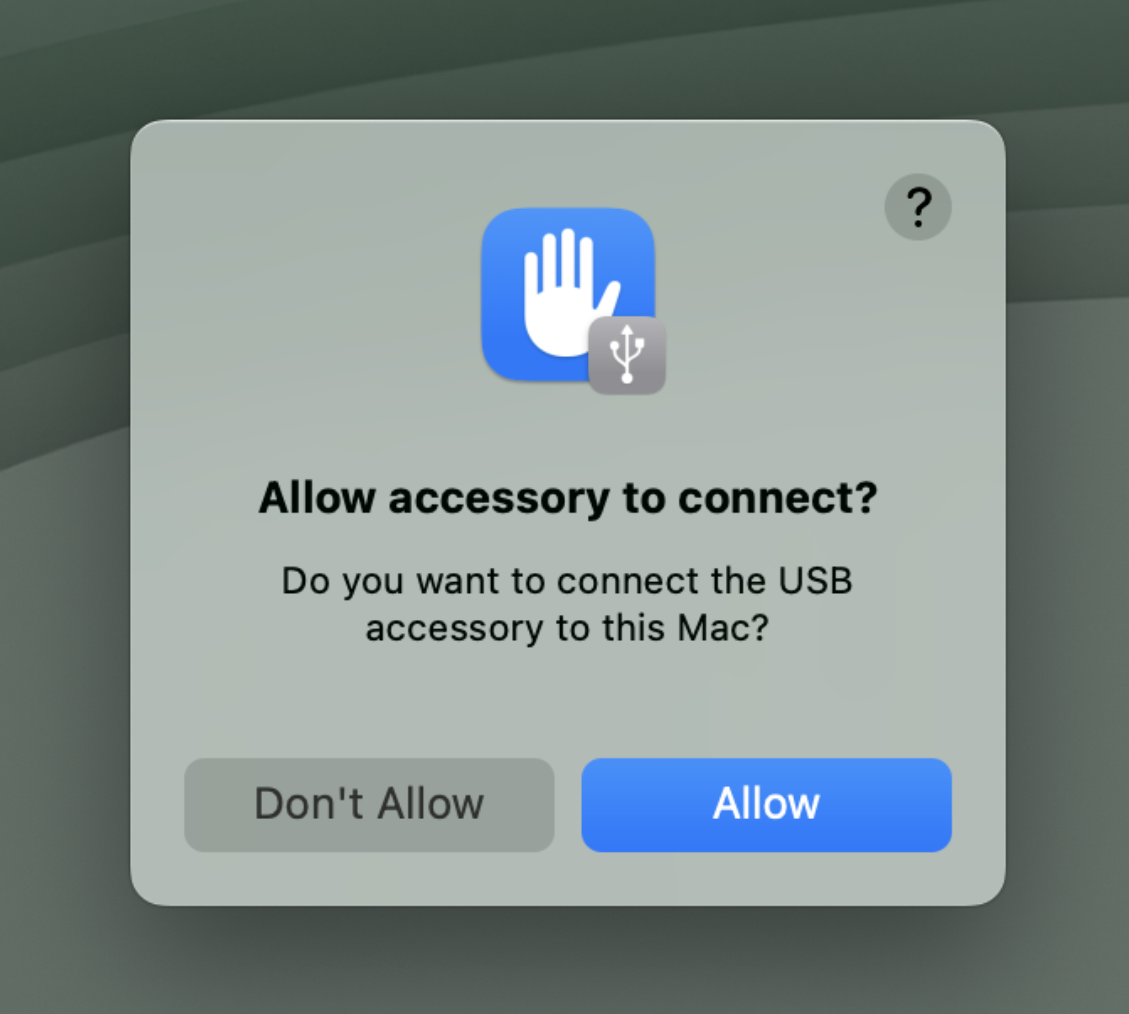
4. On Apple Silicon MacBooks with macOS Ventura version 13 or later, the Plugable product must be granted permission in order to connect the device to the Mac
For portable Macs with Apple silicon running macOS Ventura version 13 or later, any external USB accessory must first be ‘Allowed’ in order for the device to function. If the device is not ‘Allowed’, then the device will not work.
Apple provides more information on this process at the links below:
macOS Sonoma 14 - Allow accessories to connect to Mac
macOS Ventura 13 - Allow accessories to connect to Mac
If the actions above are not taken, then the Plugable DisplayLink device will not work as expected. If after having taken all of the actions above your Plugable DisplayLink-based product is not working, please reach out to us directly via support@plugable.com and we will be happy to assist you further.
My DisplayLink-based USB Docking Station or USB Video Adapter Is Not Working As Expected with a Windows computer
When a Plugable DisplayLink device is not working as expected with a Windows system, the best practice is to disconnect the device from the host system (and remove it's external power source, if it has one) and perform a 'clean' manual installation of the latest version we recommend of the required DisplayLink software driver to help ensure both are in a good state. To do so, please follow these steps:
- Disconnect the Plugable USB docking station or video adapter from the host system. If the product you are using has an external power adapter (for example a USB docking station), please also disconnect the power adapter from the product so that the unit resets. Please keep everything disconnected until prompted
- Uninstall any and all software with 'DisplayLink' in the title that is present from within the Control Panel Programs and Features (Apps and Features in Windows 10). Don't worry if these entries are not present or if the process does not work for any reason, just move onto the next step
-
Download and run the DisplayLink Installation Cleaner utility
- We have a short video that demonstrates this process
- Once the cleaning utility has completed running, restart the host system (even if not prompted to)
- Download and install the latest version (that we recommend) of the DisplayLink software driver
- If you disconnected the power adapter from your product in step one, please reconnect it so the device powers on, then reconnect the product to the host system. If the product is still not working as expected, please restart the host system one more time.
If, after having completed this process, your Plugable DisplayLink device is still not working as expected, please reach out to us directly via support@plugable.com with the output of our PlugDebug diagnostic utility and we will be happy to help
I Can't Use My Intel, NVIDIA, or AMD/ATI Graphics Utility to Manage the Monitors Connected to My DisplayLink-Based Docking Station/Graphics Adapter. Why?
The graphical software utilities provided by Intel, NVIDIA and AMD/ATI are designed to only recognize and work with graphics adapters made by their respective manufacturers. As a result, they will not recognize USB-attached displays connected to a DisplayLink-based docking station or graphics adapter.
It is recommended to use the facilities built-in to Windows to manage the connected displays. These would be the ‘Display Settings’ application on Windows 10 and ‘Screen Resolution’ application on Windows 8.1 and 7. Both of these applications are available by right-clicking on empty space within the Windows desktop and selecting the appropriate choice from the context menu that appears.
Note: Intel has released an updated 'Intel Graphics Command Center' application that can recognize DisplayLink-attached displays and configure them to a certain extent. However, some of the features within the Intel Graphics Command Center application that are specific to Intel graphics adapters may not work on a DisplayLink-attached display.
Why Doesn't the "Display Color Calibration" Tool in Windows Affect the Display(s) Attached to My DisplayLink-Based Docking Station/Video Adapter?
The DisplayLink driver does not support color calibration functionality of any kind. Most monitors have built-in controls that can be used to adjust the characteristics of the display, though we realize this approach may not be ideal in all cases. For environments that necessitate near-perfect color reproduction and display calibration capabilities via software, a dedicated graphics card is recommended.
Are Plugable USB Video Adapters or Docking Stations Based on DisplayLink Technology Compatible With Touchscreens?
Touchscreens that do not require drivers and use the host’s operating system’s built-in USB Human Interface drivers (HID) to record touch inputs can be made to work with our products, however Plugable does not provide support for doing so due the complexity of multi-monitor touch screen setups.
If I Add a DisplayLink-Based Docking Station or Graphics Adapter to My System, Will That Prevent My System’s Built-In Video Outputs From Working?
No, the DisplayLink device's presence on your system will not preclude the use of any of your system’s built-in video outputs.
Are Powerline Network Adapters Supported in Conjunction With the Ethernet Port Within My DisplayLink-Based Docking Station or Video Adapter?
The use of Powerline-based network adapters in conjunction with the Ethernet port within our DisplayLink-based docking stations or video adapters is not supported.
Can I Adjust the Brightness of a Display Connected to My DisplayLink-Based Docking Station or Video Adapter via the Windows ‘Display Settings’ Application?
Windows does not have the ability to adjust the brightness of a display connected using DisplayLink technology. We recommend making use of the display’s internal on-screen menu options in order to adjust the display's brightness.
Can I Use My DisplayLink-Based Docking Station in Conjunction With a KVM (Keyboard, Video and Mouse) Switch?
No, Plugable does not recommend or support using our DisplayLink-based docking stations with a traditional KVM switch. If you simply need to share the dock between two systems, the dock can be manually disconnected from the first system and then manually connected to the second system.
For those using our USB 3.0 DisplayLink docking station products that would like a more permanent solution that does not require disconnecting the unit from the host system, our Plugable USB 3.0 Sharing Switch can be used as an alternative to share the dock between two systems (please keep in mind that the dock can only be used by one system at a time).
Troubleshooting Wi-Fi, Wireless Keyboard, and Mouse Issues While Using USB Docking Stations Based on DisplayLink Technology
Wi-Fi Performance Issues
Any time a USB 3.0 device is connected to a laptop system, there is a potential that the USB 3.0 connection can generate interference that can affect the performance of the laptop's built-in Wi-Fi adapter.
This behavior is not specific to Plugable products, and Intel has published a white paper on the topic for those who are curious about the technical details.
So now that we know that this can happen with any type of USB 3.0 connection, how do we solve the problem should it occur? Every person’s setup can be a little different so there will never be one definitive solution, but a few simple approaches can solve the problem in most cases:
- Option One—Move the device as far as away from the system as the USB cable will allow. This will try and ‘move’ the signals from both the USB connection and the Wi-Fi physically further apart. As a corollary to this, if the dock is located very close to the Wi-Fi router itself, placing more distance between the two can help.
- Option Two—Switch to a different USB port on the system, preferably one on the opposite side of the laptop. This employs the same approach as option one, in that physically separating the two signals (in this case the physical proximity of the USB connection and the internal Wi-Fi antennas within your system) can help. If your system has both USB 3.0 and USB 2.0 ports, try using the USB 2.0 port first.
- Option Three—Use a USB 2.0 cable, like one used connect to a USB printer, instead of a USB 3.0 cable. All USB 3.0 devices should be backward compatible with a USB 2.0 cable, and when a device is connected at USB 2.0 speeds there is no possibility for the interference.
- Option Four—Switch to using a 5GHz Wi-Fi connection. As the name implies, there are two common sets of frequencies used by most Wi-Fi networks (2.4GHz and 5GHz). If both your wireless router and the wireless network adapter in your system support a 5GHz connection (they both need to, one is not enough), connecting to your Wi-Fi in that manner will prevent the interference from happening due to the two very different frequencies in use.
- Option Five—If using a 5GHz connection is not possible, changing the ‘channel’ of a 2.4 GHz connection can help. Within the 2.4GHz band used for Wi-Fi, there are eleven different channels each using a slightly different frequency. The three most commonly used ones in the United States are channel 1, 6 and 11. Using the manual for your wireless router as a guide, switching channels can potentially help. Ideally you would want to switch the channel to the opposite end of the spectrum for the best results, for example if you are on channel one already try switching to channel eleven or vice-versa
Wireless Mouse or Wireless Keyboard Performance Issues (Radio Frequency Interference)
While the items listed above can help with Wi-Fi interference, there is another type of interference that can sometimes cause problems with wireless keyboards and wireless mice which we refer to as Radio Frequency (RF) interference.
To expand further, the USB wireless receiver 'dongles' used by many wireless keyboards and wireless mice operate within the same 2.4GHz radio frequency range as many Wi-Fi adapters.
If a USB 3.0 connection is generating interference, this can affect the behavior of a wireless keyboard or wireless mouse. This behavior typically manifests as inconsistent mouse movement and/or inconsistent or sporadic keystroke registration.
In general there are two methods to mitigate this behavior should it occur:
- RF Option One—Reconnect the USB wireless receiver 'dongle' to one of the USB Docking Station's USB 2.0 ports (if the dock has USB 2.0 ports), furthest away from the USB 3.0 host connection cable. Moving the USB receiver to a USB 2.0 port typically mitigates this interference.
-
RF Option Two—In rarer cases when moving the receiver is not enough or if the product in question does not have a USB 2.0 port, adding a short USB 2.0 extension cable can also help mitigate the behavior. In many cases wireless mice or keyboards include such a cable for this very reason, but if one is not available our USB2-2PORT is a good alternative solution.
In some less common instances on Windows computers, erratic keyboard/mouse behavior can be related to an issue with Intel Management Engine. We've written about this issue and the workaround that may fix it in another article in our Knowledge Base: https://kb.plugable.com/docking-stations-and-video/laggy-mouse-or-keyboard
What are the differences between and limitations of the DisplayLink Manager Application and Legacy DisplayLink Driver for macOS?
Plugable’s DisplayLink-based products are supported with macOS with the installation of the DisplayLink software.
There are different versions of the macOS driver that have been released by DisplayLink (the separate company that makes the primary chip within our DisplayLink-based products, and who also develops the software driver), with each version aligning with different versions of macOS. When first introduced there were several differences between the two driver versions. Over time, these differences have become fewer with updates to both the DisplayLink Manager and macOS, however this article is being retained for historical reference.
A ‘legacy’ version which uses a kernel extension in order to provide its functionality, and a newer ‘DisplayLink Manager Graphics Connectivity’ App which utilizes a new architecture that does not rely on a kernel extension to provide its functionality.
The choice of which driver to use is ultimately determined by one’s OS version and individual specific requirements, since each version offers different capabilities and operating system compatibility. We have provided a comparison table below that highlights their differences in an effort to help our customers make an informed decision.
Links to the latest DisplayLink driver versions for each version of macOS as well as installation instructions can be found on the “Downloads” tab of applicable products, or at www.plugable.com/displaylink
|
New DisplayLink Manager Graphics Connectivity App |
‘Legacy’ DisplayLink driver |
|
|
Supported operating system versions |
macOS 10.15 Catalina, macOS 11 Big Sur, macOS 12 Monterey, macOS 13 Ventura, macOS 14 Sonoma |
macOS 10.14 Mojave and macOS 10.15 Catalina |
|
Ease of installation |
Straightforward |
Can sometimes be more difficult, as compared to the new App |
|
Supports closed-display mode (aka clamshell mode) |
- No with macOS 10.15 Catalina and macOS 11 Big Sur on Intel-based systems - Yes with macOS 12 Monterey on Intel-based systems (an external power source must be connected to the Mac) - Yes with macOS 11 Big Sur, macOS 12 Monterey, macOS 13 Ventura, and macOS 14 Sonoma on Apple CPU-based systems (an external power source must be connected to the Mac) |
Yes |
|
Supports display ‘rotation’ |
- No with macOS 10.15 Catalina - Yes with macOS 11 Big Sur and macOS 12 Monterey on Intel CPU systems - No with macOS 11 Big Sur on Apple CPU-based systems - Yes with macOS 12 Monterey, macOS 13 Ventura, and macOS 14 Sonoma on Apple CPU-based systems using DisplayLink Manager version 1.6 and later *** |
Yes |
|
Supports macOS ‘Login screen’ |
Yes, with additional ‘Login screen’ application installation |
Yes |
| Supports display color adjustment | Beta support available via 3rd-party application f.lux starting with DisplayLink Manager version 1.7.1**** | No |
|
Manageability |
Via DisplayLink icon within the Apple Menu bar |
No management application |
|
Development status |
Actively being developed |
Being phased out due to changes within macOS |
*** Display rotation on Macs with an Apple CPU is accomplished within the DisplayLink Manager Application. It is NOT accomplished via the 'Displays' System Preferences application. More information on this feature is available here: Link
**** There is a 3rd-party application called 'f.lux' that allows the adjustment of a display's color according to the time of day. This functionality is in 'beta' status, and must be enabled within the DisplayLink Manager Application in order to function. This functionality is supported with devices based on the DisplayLink DL-3xxx chipset, DL-5xxx chipset, and DL-6xxx chipset. However, it is important to note that on DL-6xxx chipsets this functionality is limited to DisplayPort video outputs only. It is NOT supported on HDMI video outputs via DL-6xxx chipsets.
DisplayLink Manager App Installation Instructions for macOS 10.15
Unsure which version of macOS you have installed? Click on the ‘Apple’ icon in the menu bar on your desktop and select ‘About this Mac’. A new window will open and display the system’s macOS version.
How to install the DisplayLink Manager application
1. Download the DisplayLink Manager from our drivers page here: https://plugable.com/pages/displaylink#macos
2. Open the DisplayLink Manager Graphics Connectivity 1.x.pkg
3. Click ‘Continue’ on ‘Introduction’ page
4. Click ‘Continue’ on ‘Licence’ page
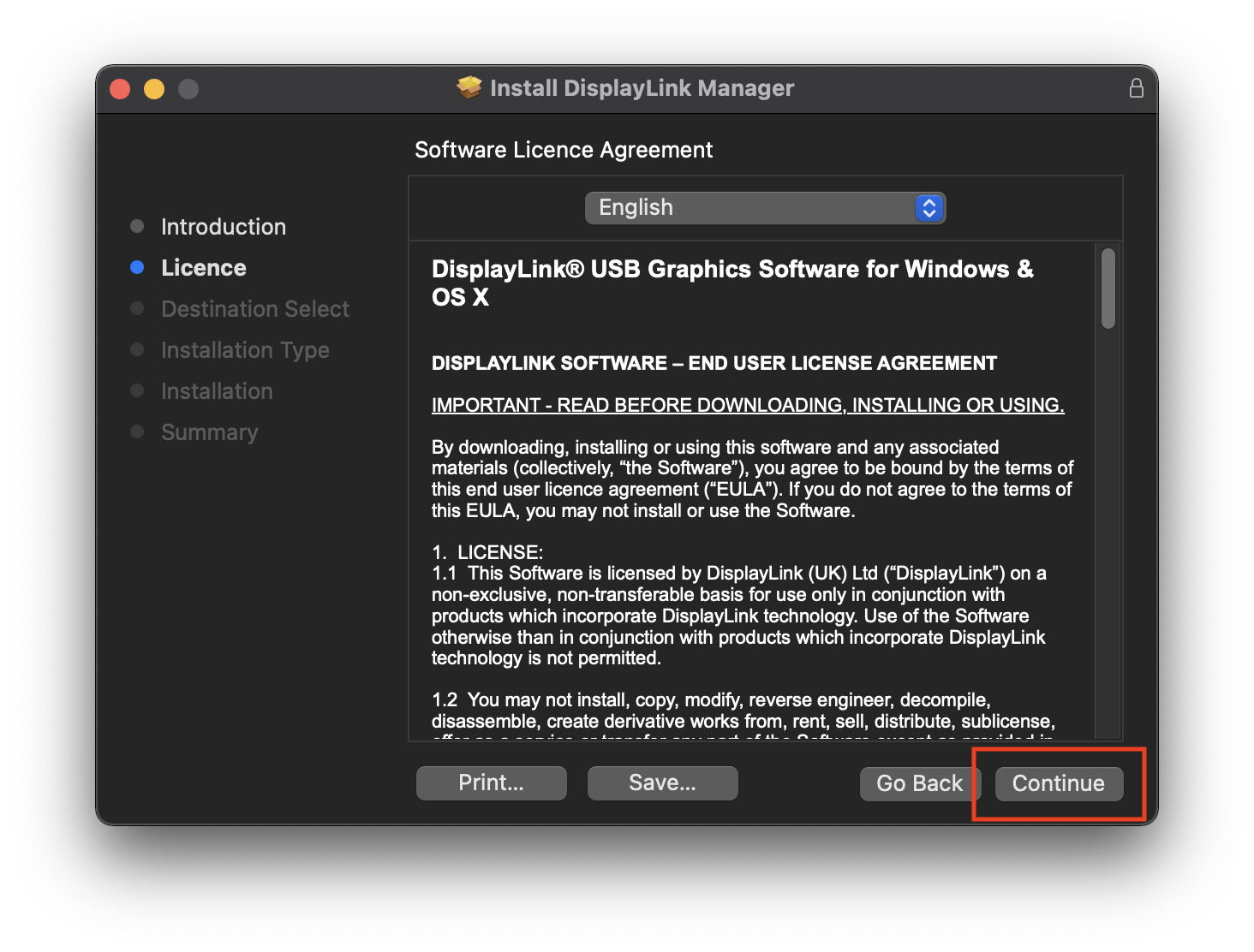
5. Click ‘Agree’ when prompted
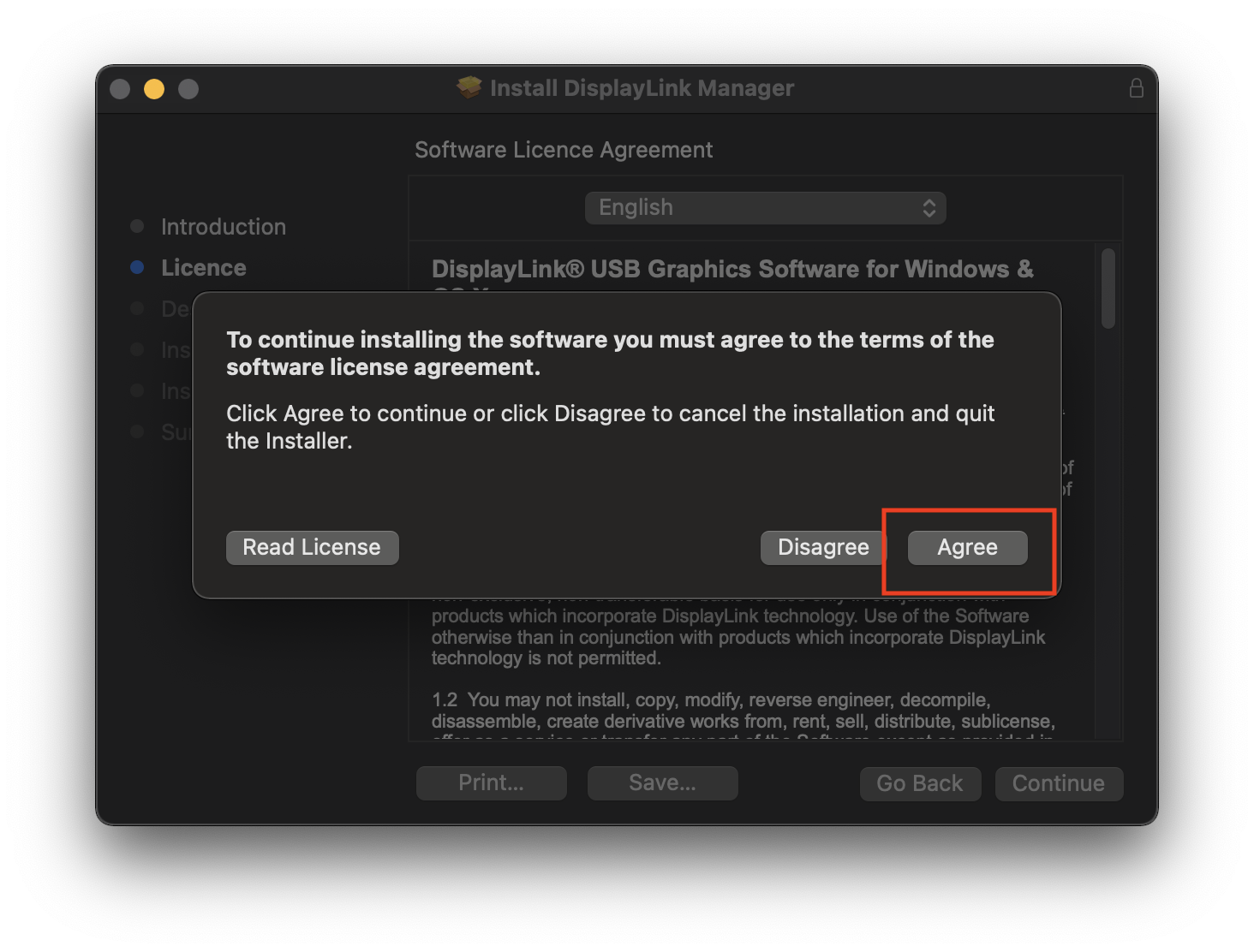
6. Click ‘Install’ on ‘Installation Type’ page
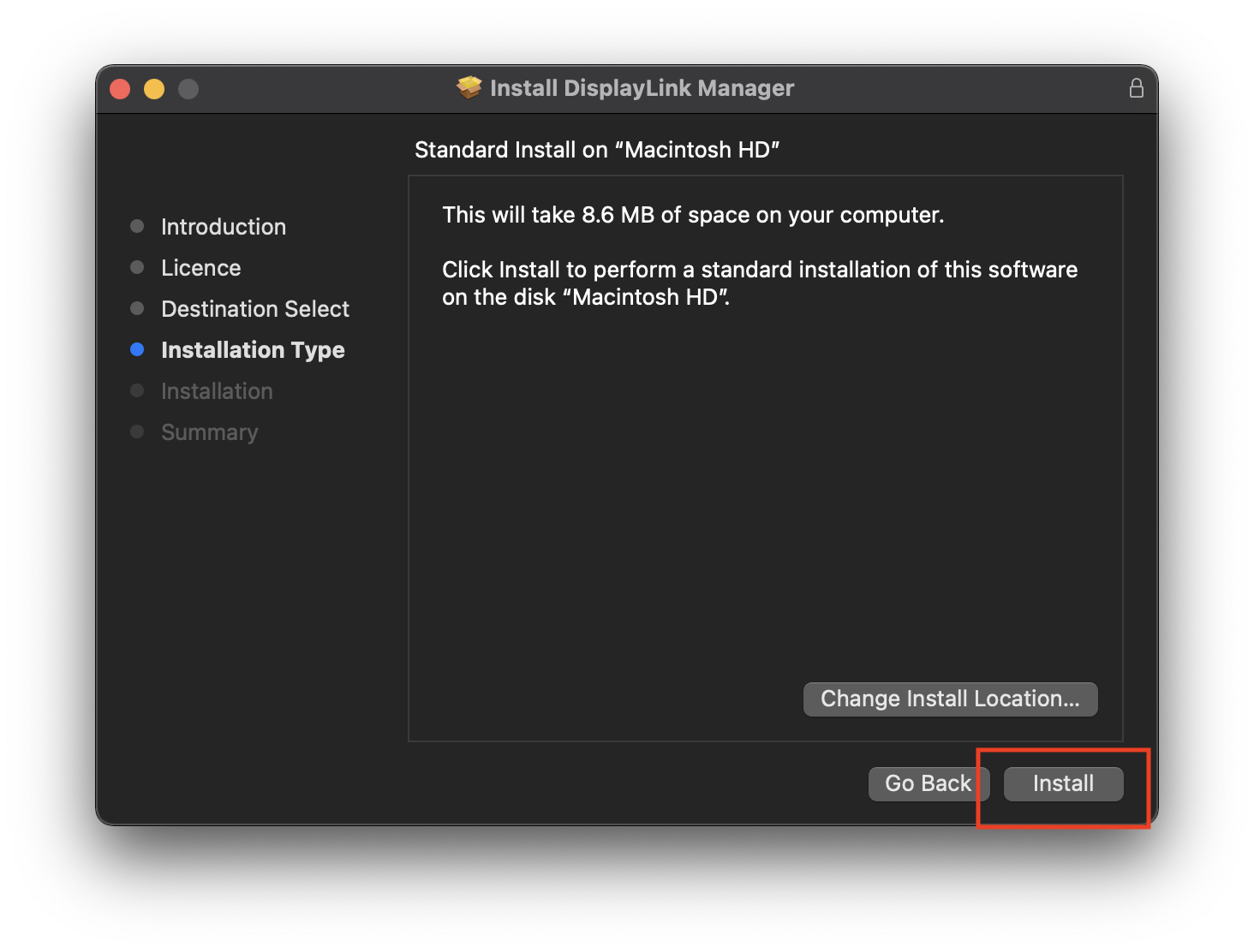
7. Input your password when prompted
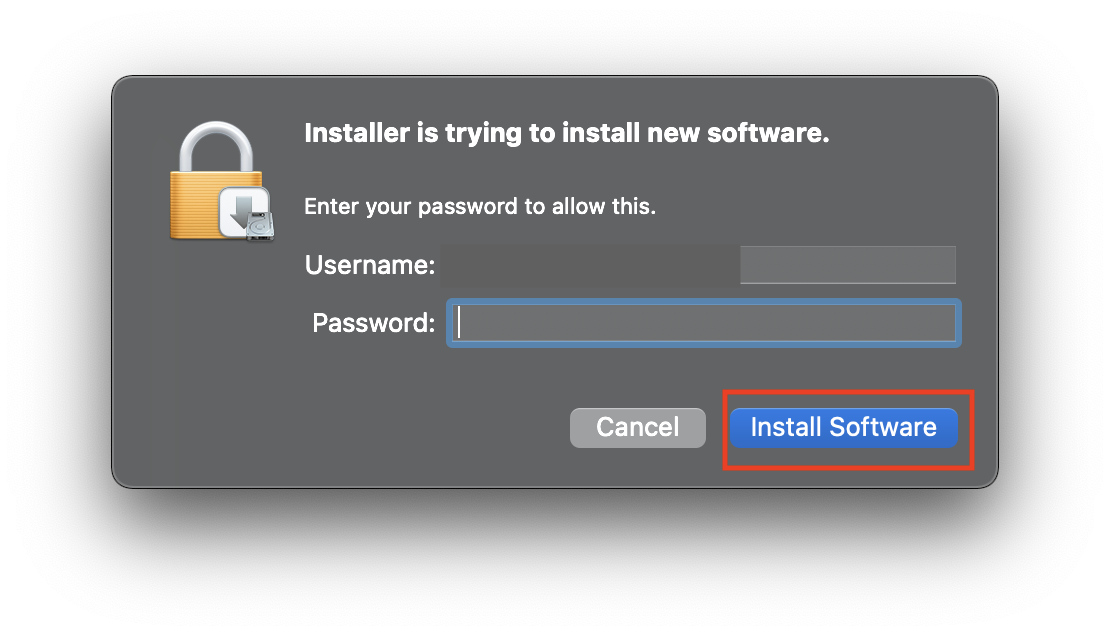
8. When installation finishes click ‘Close’ on ‘Summary’ page
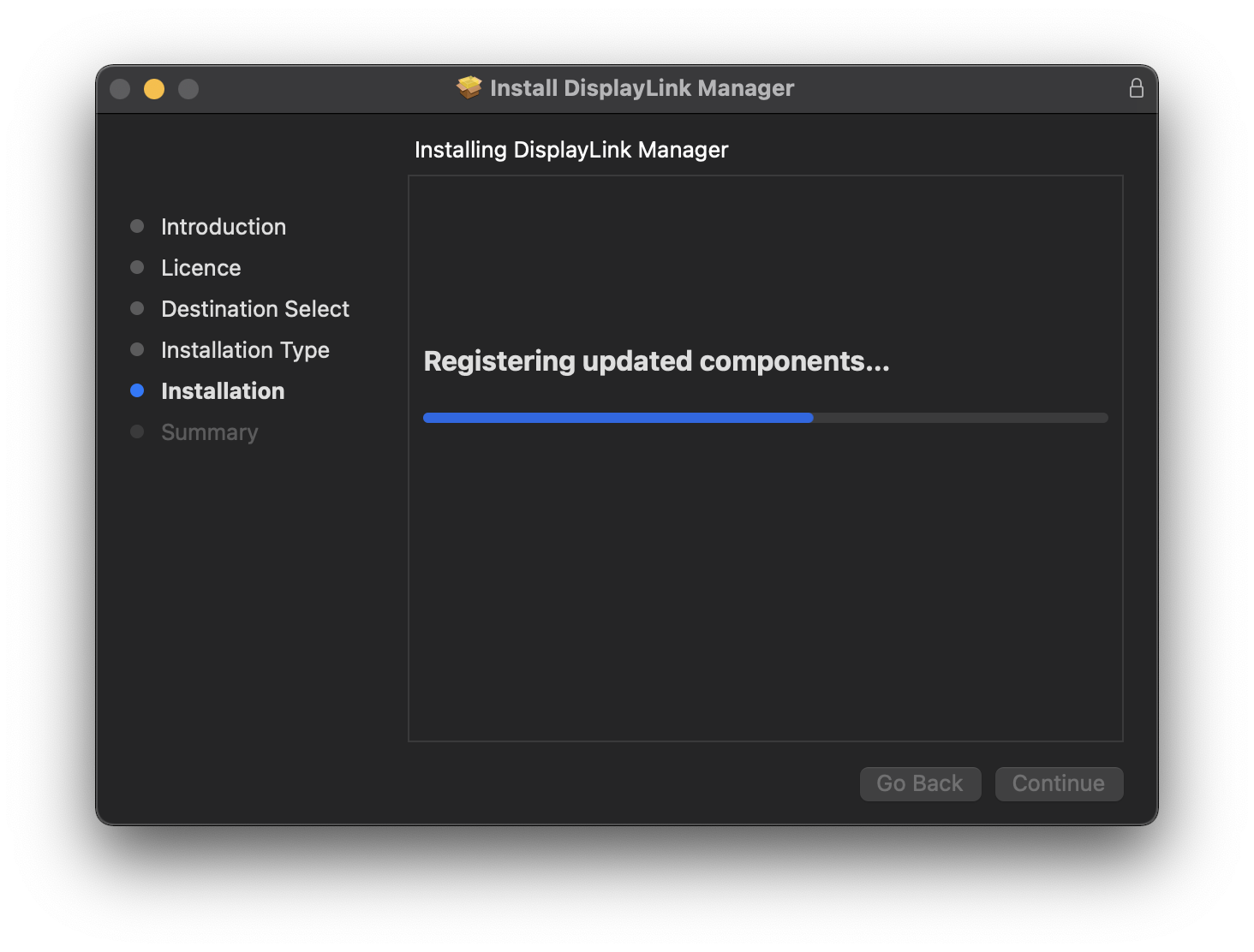
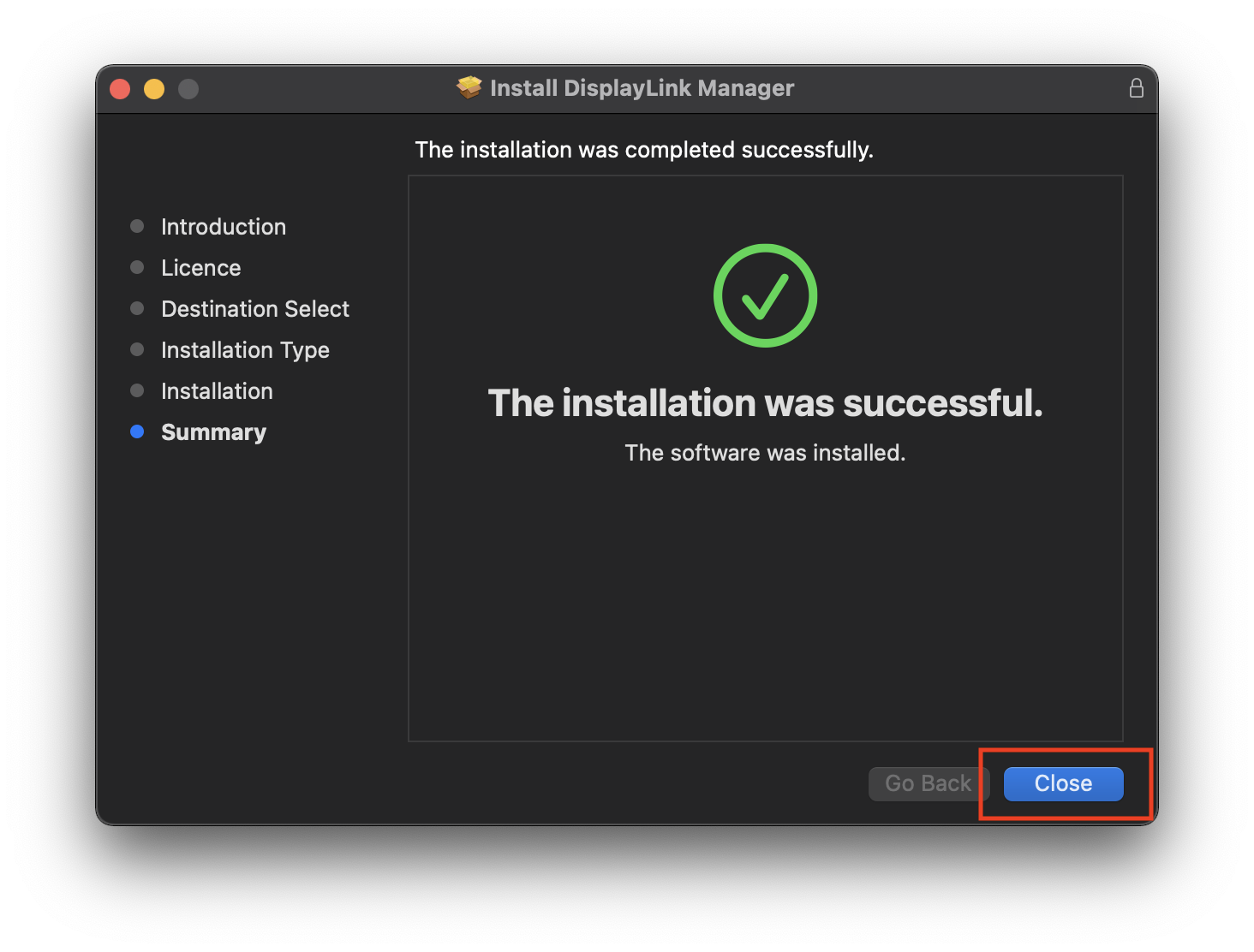
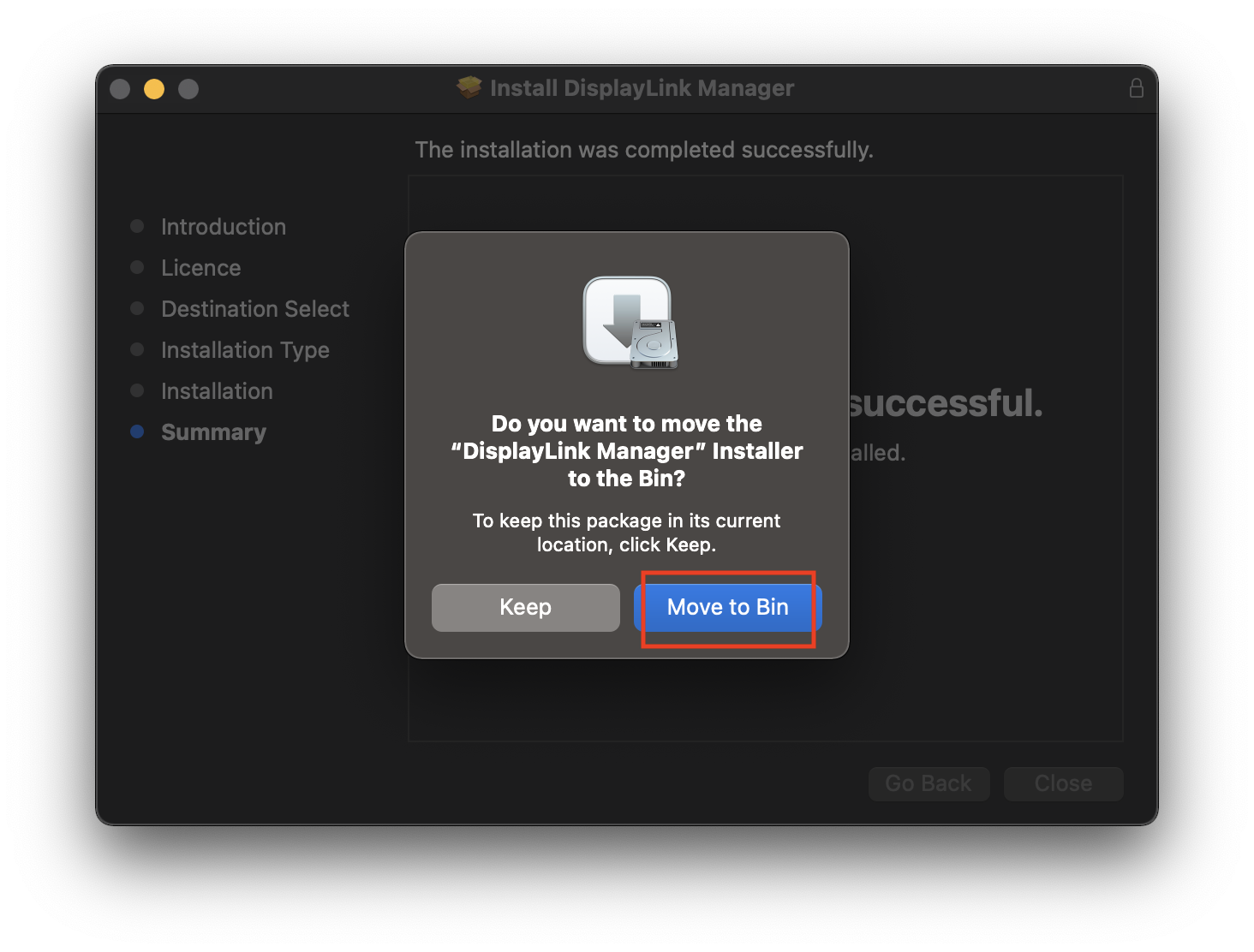
9. Click’ Move to bin’ when prompted
How to use DisplayLink Manager?
The following steps are to be followed once after installing the app.
1. After installation, the DisplayLink Manager app will start automatically and the DisplayLink Manager logo will show in the Menu Bar. It will be grey when the dock is disconnected (Connection status will show: No monitor detected) and white when connected (Connection status will show: Monitor detected).
NOTE: The DisplayLink Manager app will only start on its own once after the initial installation. Step 5 shows how to setup the app to always start after logging-in (recommended). Otherwise the app has to be started manually each time (see step 2).
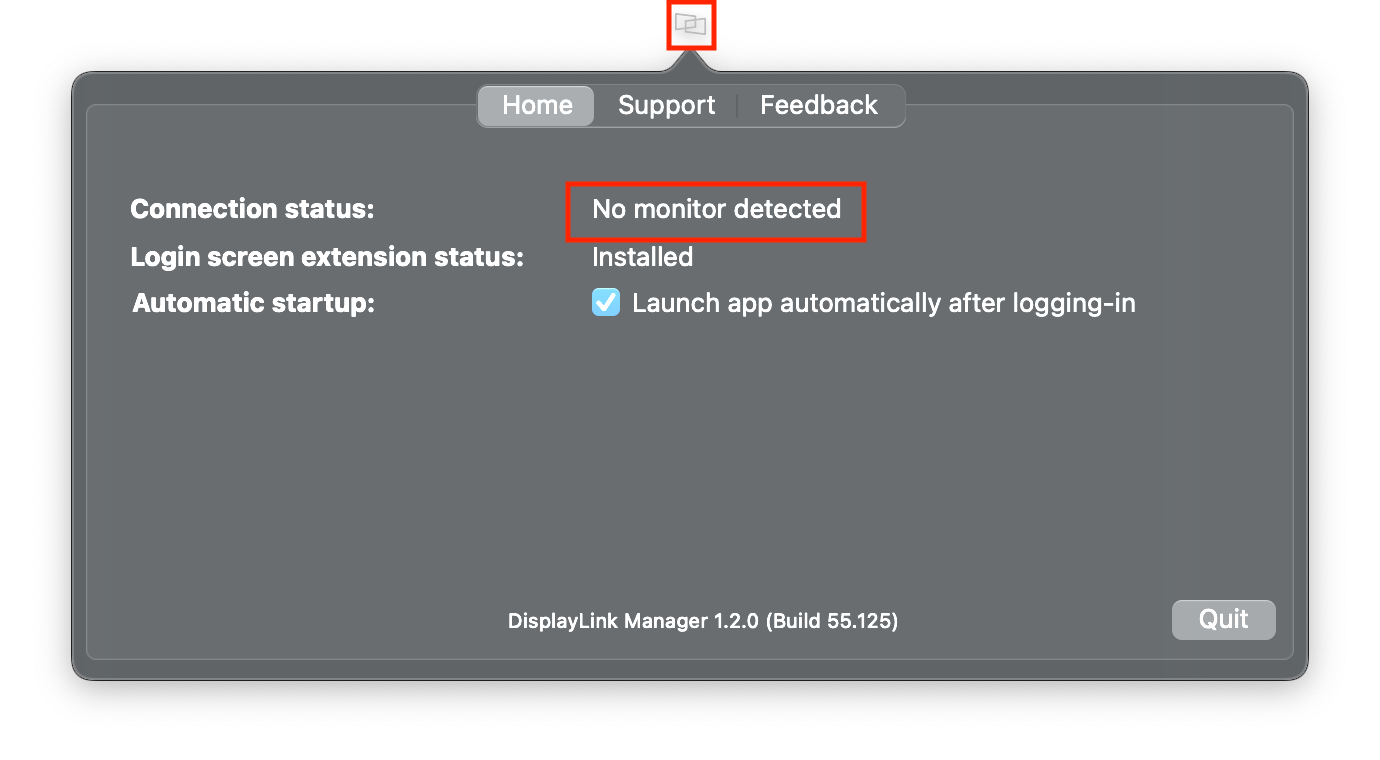
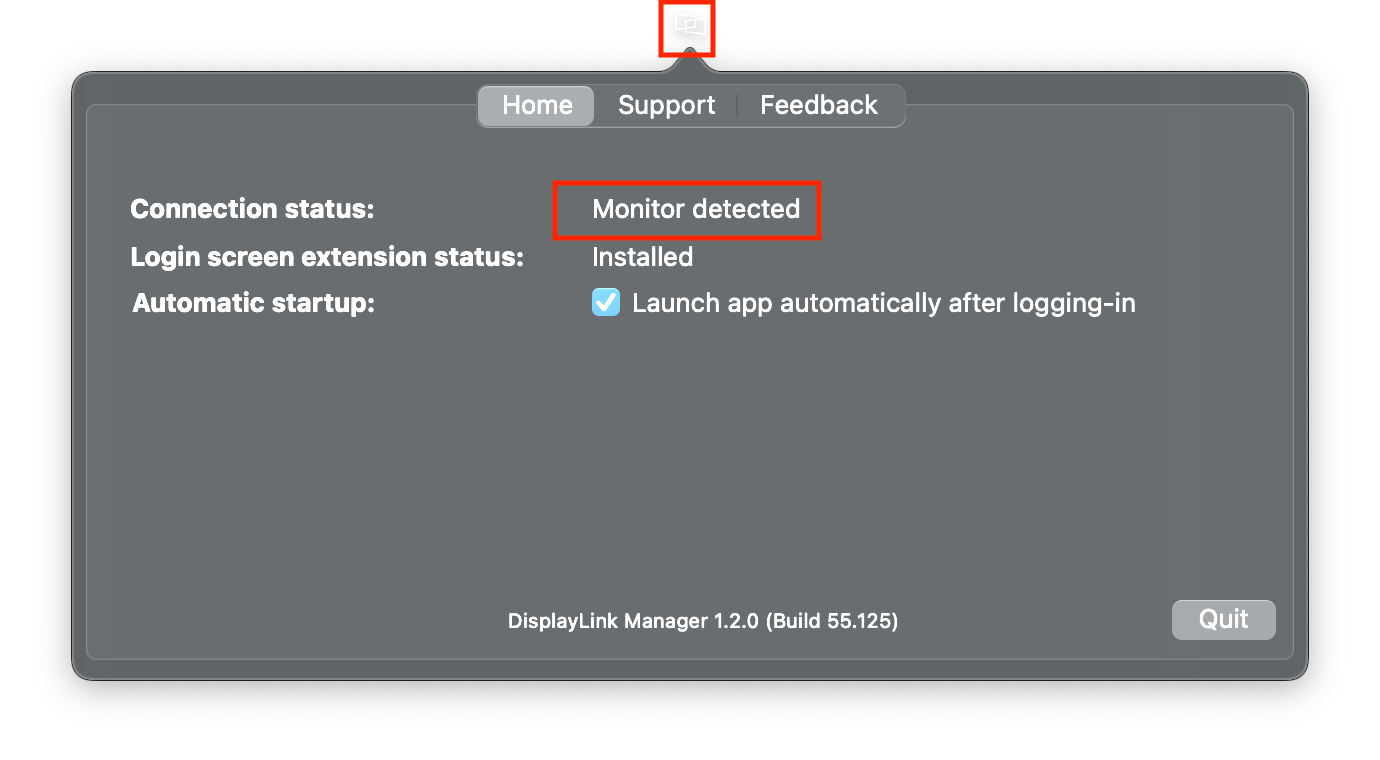
2. In case the app does not show in your Menu Bar, to start it manually, please press ‘command’ + ’space’ and type in DisplayLink Manager, click on the application to open it
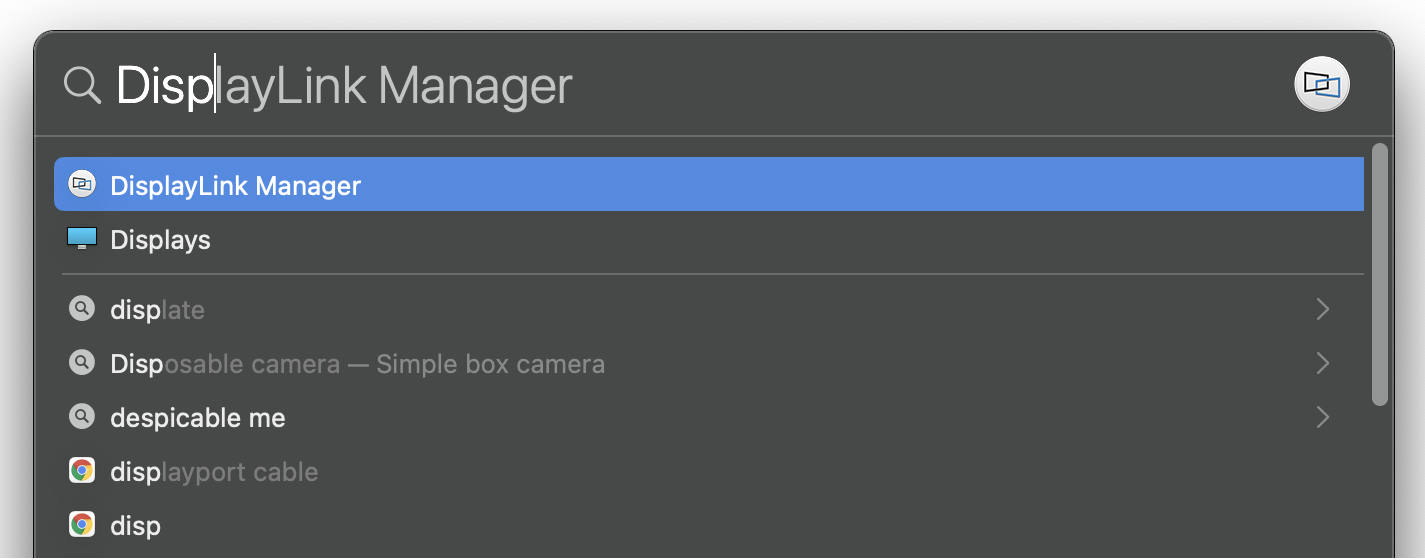
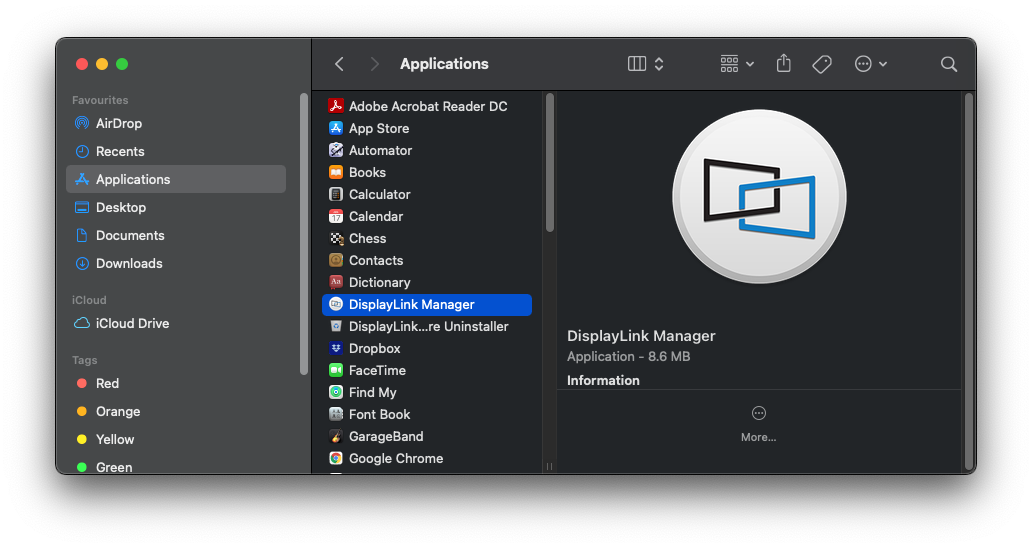
a. Alternatively you can go to the Applications folder in Finder and click on the DisplayLink Manager there
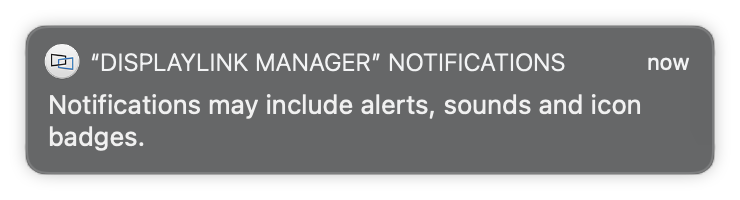
3. When first opened, DisplayLink Manager will ask you to turn on notifications for the app. Click on the notification below when it shows up. It will open a Notifications window.
4. Turn on ‘Allow Notifications’ for DisplayLink Manager
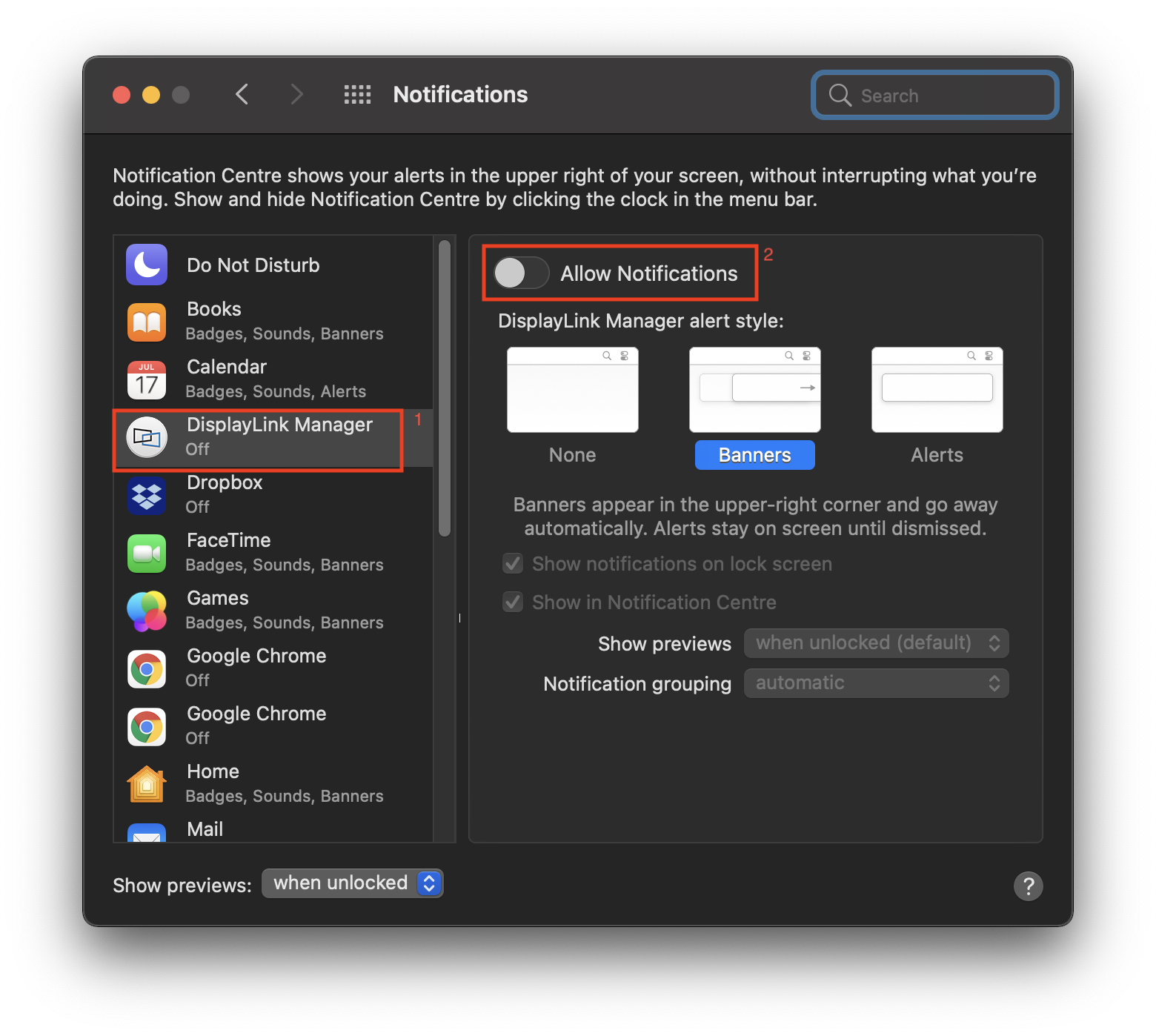
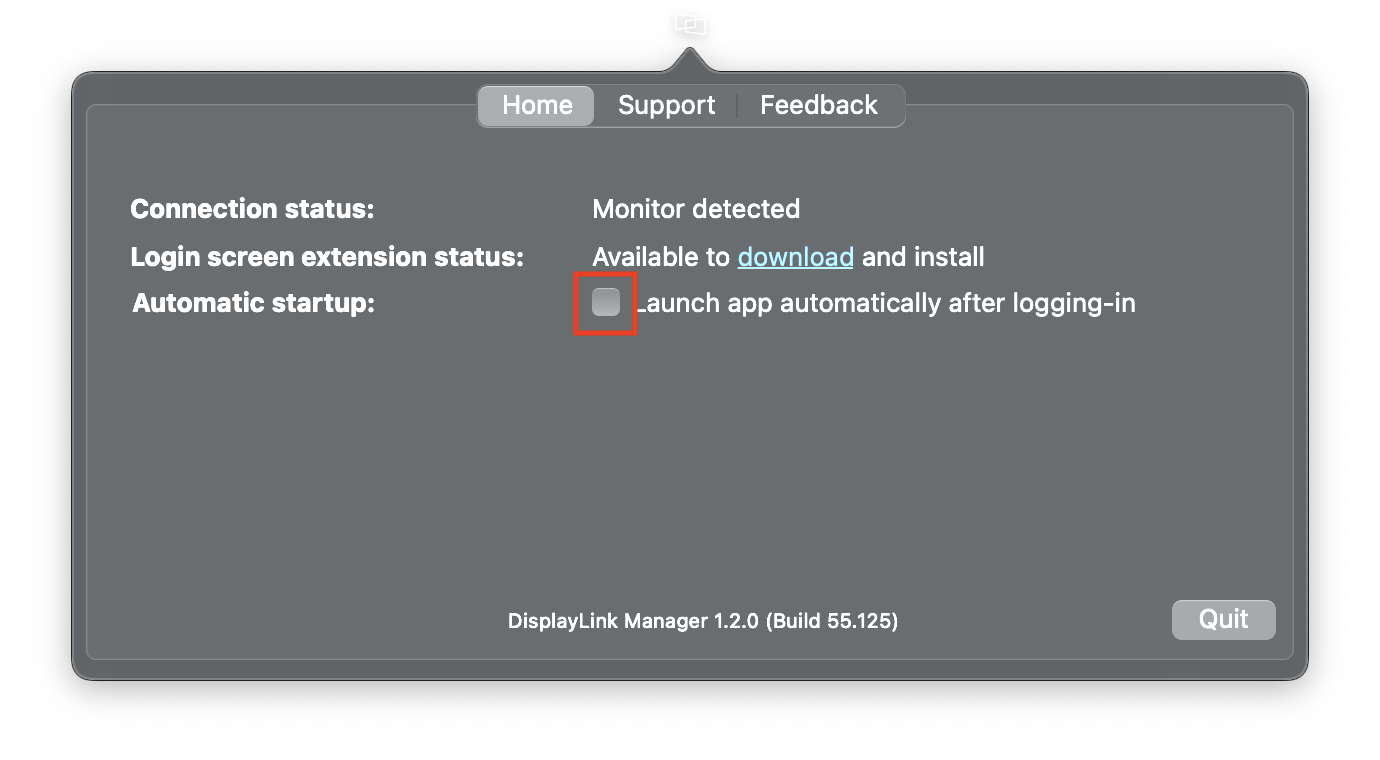
5. Select “Launch automatically after logging-in” for the software to start automatically every time you log-in.
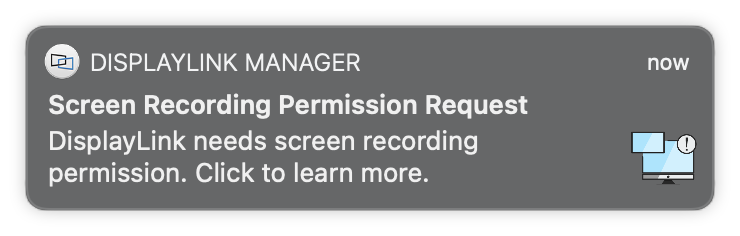
6. Screen Recording
NOTE: From macOS Catalina 10.15, the operating system requires the user to permit "Screen Recording" in order for DisplayLink based devices (like Plugable UD-3900) to work properly. The message is generated by the OS and the screen is not actually being recorded by DisplayLink. Approving it enables the DisplayLink driver to access the pixels it needs to render a mirrored or extended screen and send the pixels over USB from your computer to the DisplayLink display. DisplayLink Manager does not store or record any screen content.
a. If you enabled notifications in step 3 you will see the below message if Screen Recording is switched off
b. This message will also show in the DisplayLink Manager app window and there will be an exclamation mark ‘!’ next to the DisplayLink Manager icon.
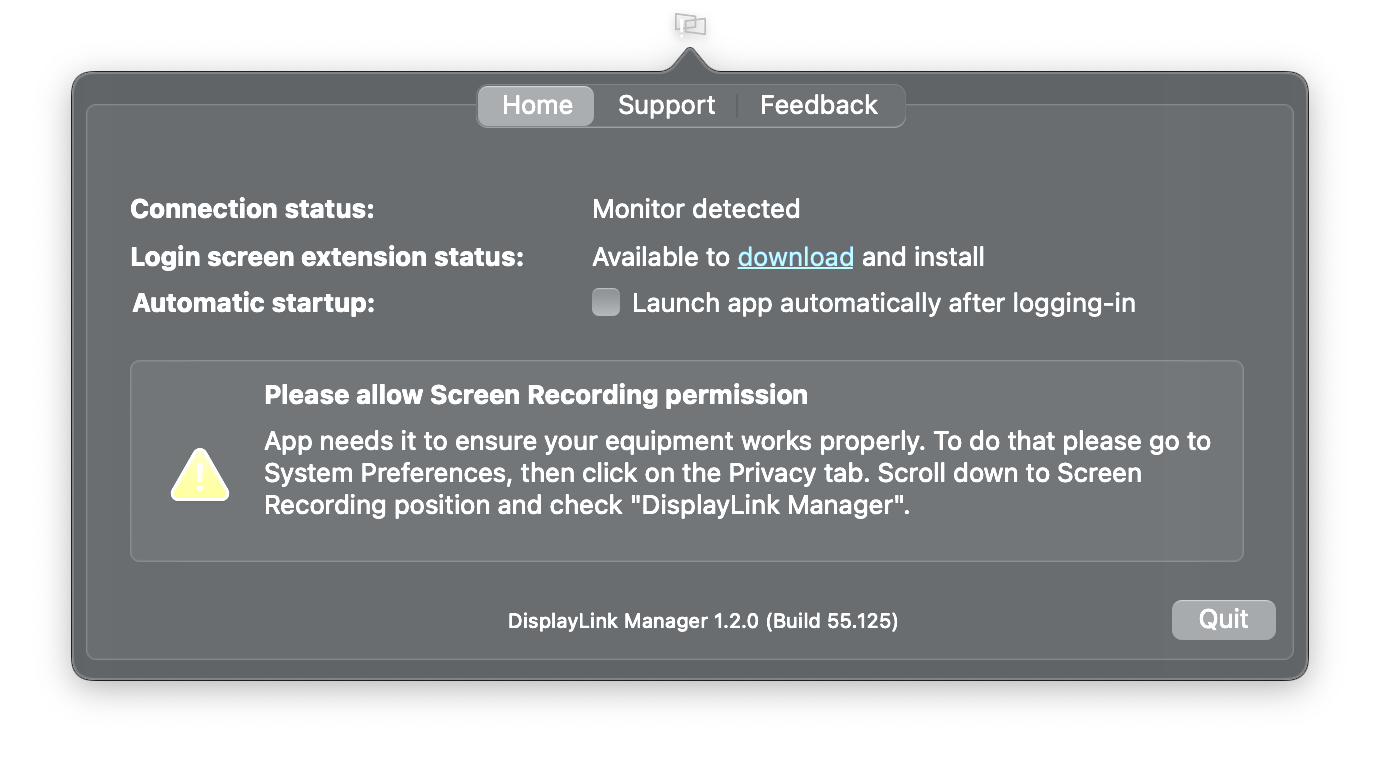
7. To enable “Screen Recording”
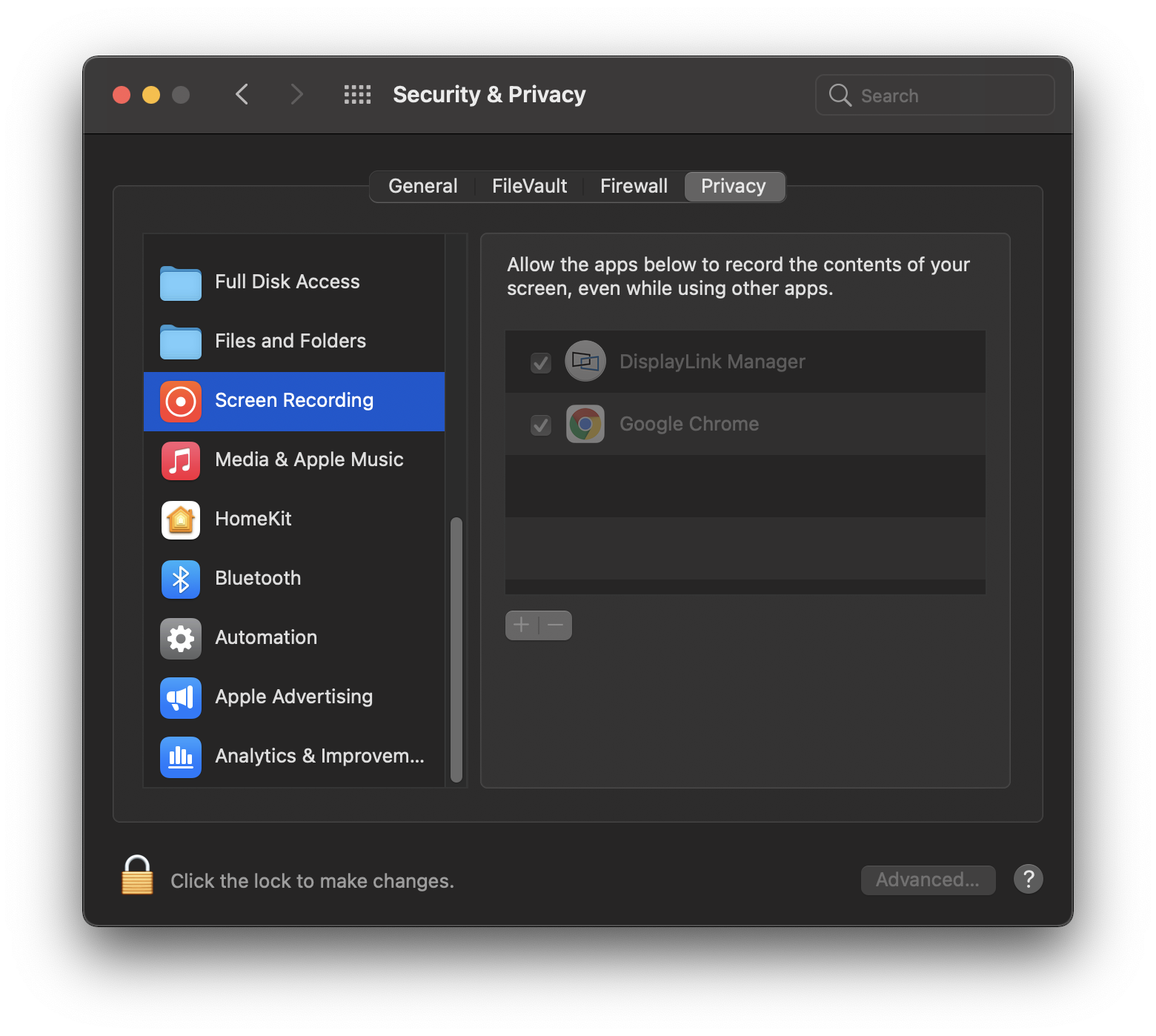
a. Go to System Preferences and click on Security & Privacy
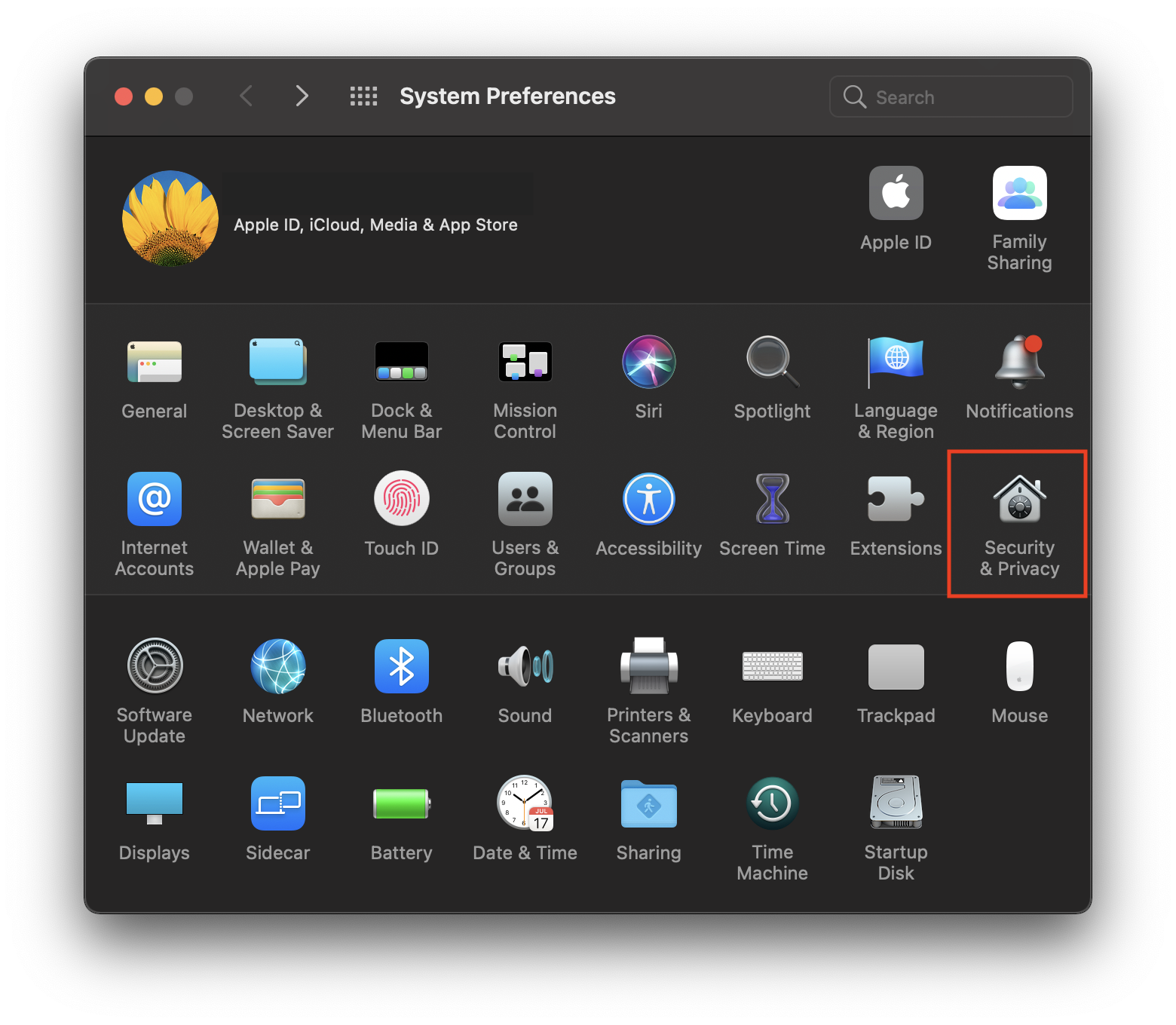
b. In the ‘Privacy’ tab scroll down to ‘Screen Recording’ and click on the padlock to make changes
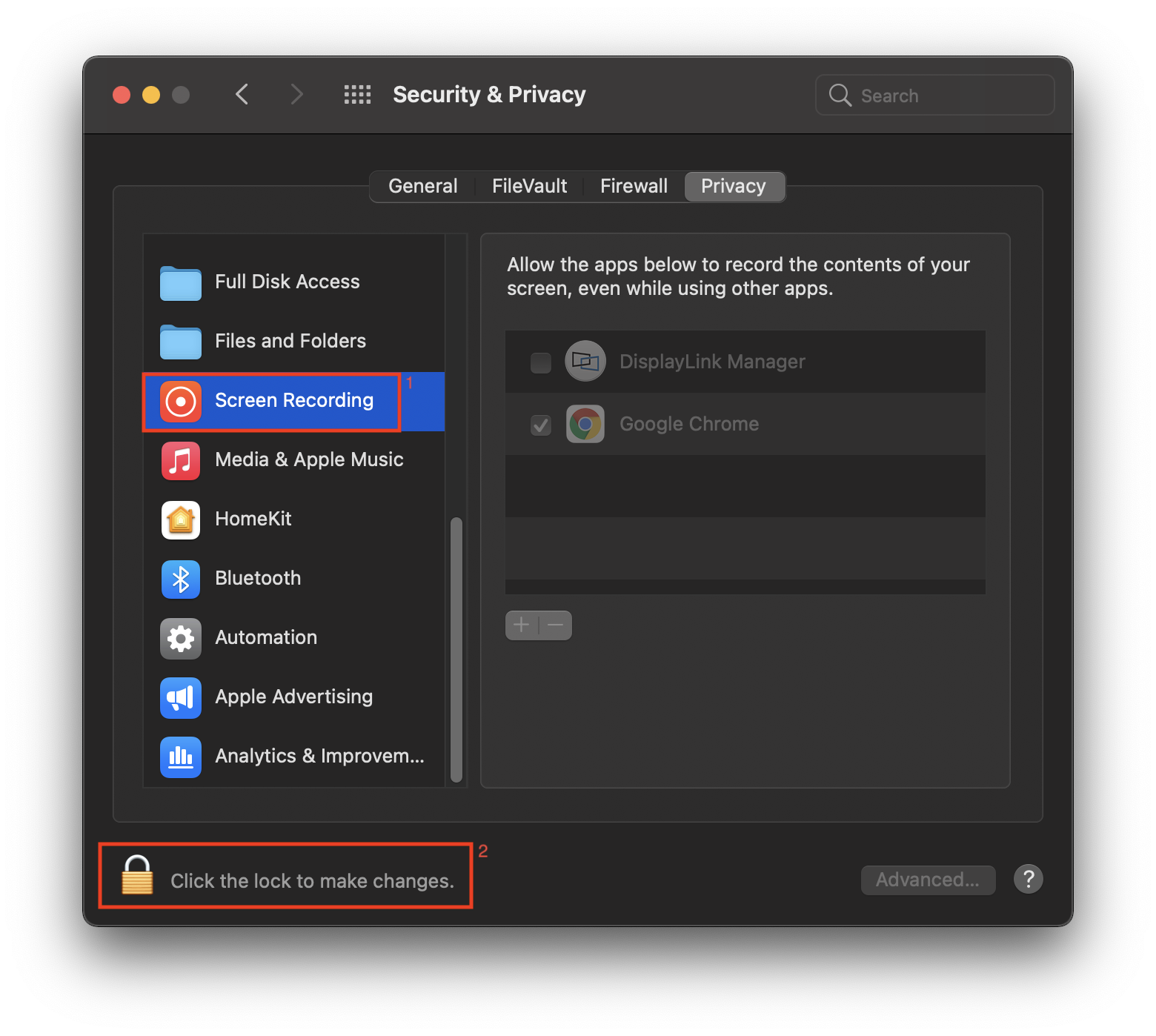
c. Enter password to allow the system to make changes
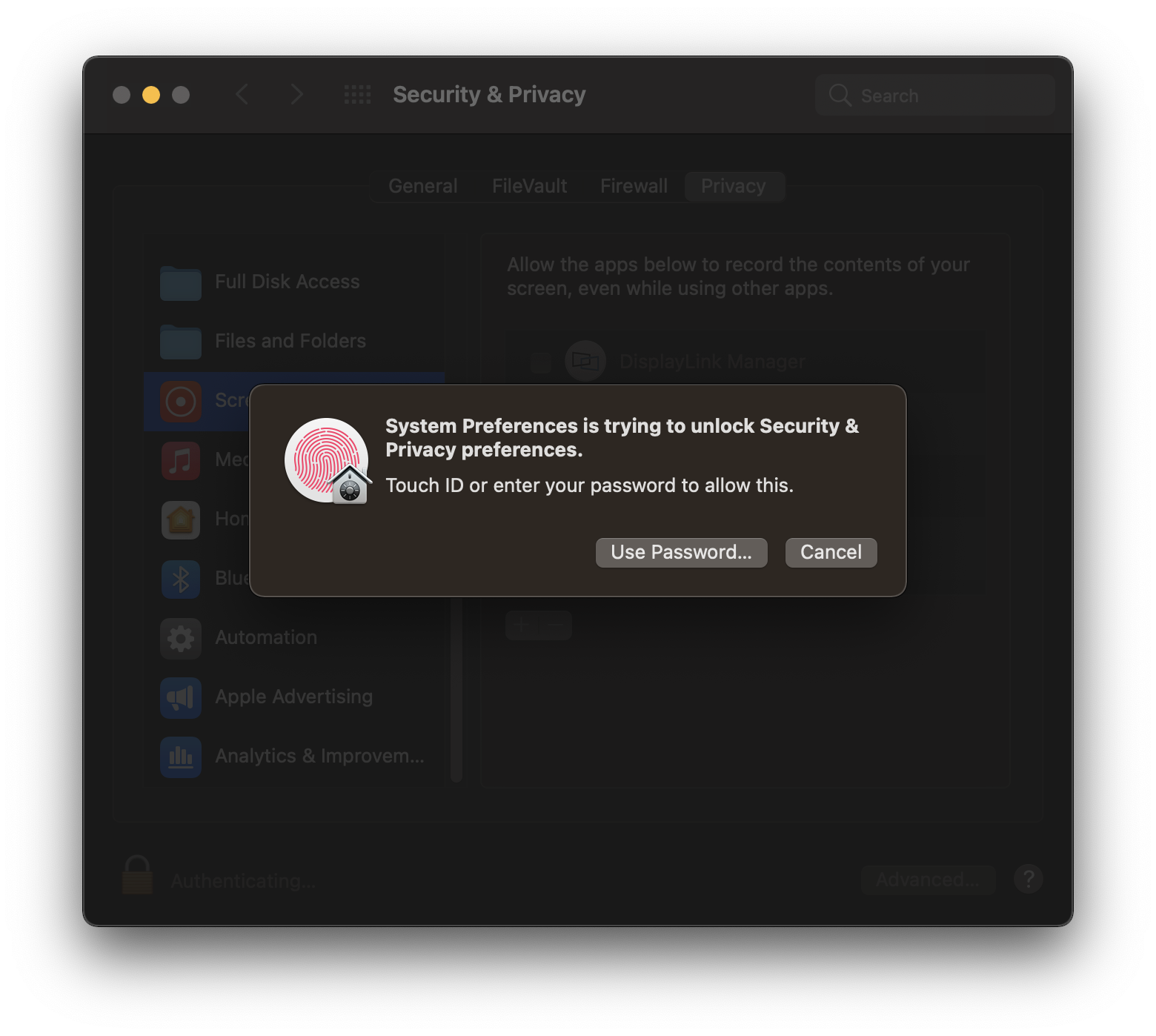
d. Tick the box next to ‘DisplayLink Manager’ and click ‘Quit and reopen’ when prompted.
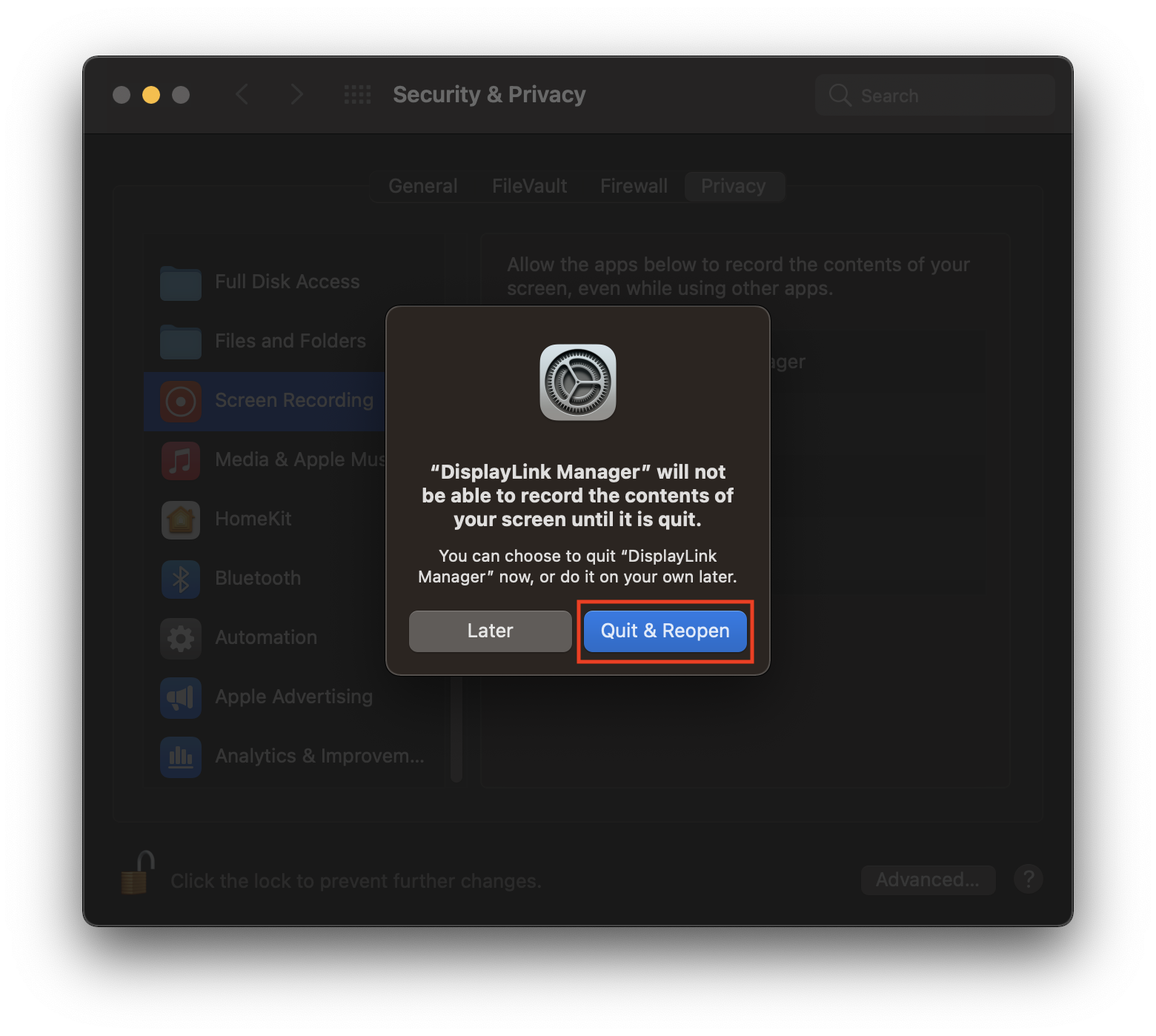
e. Click on a padlock to save the changes.
Other functions of the DisplayLink Manager
Login screen extension (Optional)
This enables the external screens to be available on the login screen prior to the app loading after logging into your account.
1. Download the Login Screen Extension from the link available on the front page of the DisplayLink Manager.
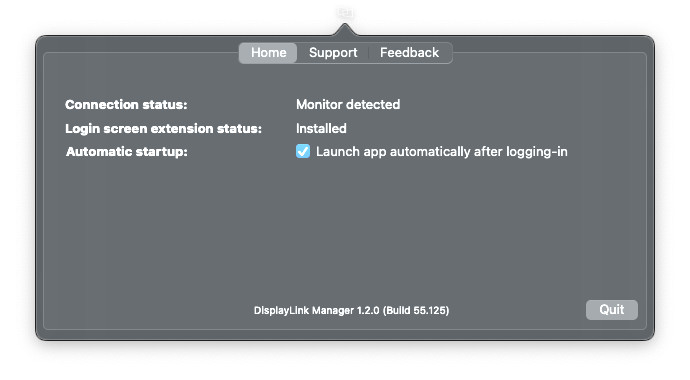
2. Install the extension.

3. Once the installation is complete the extension will show as ‘Installed’
Support
NOTE: Opening a ticket through the Support tab will contact the DisplayLink engineering team in Europe. We recommend contacting support@plugable.com if you have any questions or issues.
DisplayLink Manager App Installation Instructions for macOS 11 or macOS 12
Before you begin
Unsure which version of macOS you have installed on your Mac? Click on the ‘Apple’ icon within the menu bar located at the top of your desktop and select ‘About this Mac’. A new window will open and display the system’s macOS version.
Guided Video Demonstration
For those who prefer, we have a video demonstration of the installation procedure available (an embedded link is below).
For those who prefer, a detailed text-based description of the installation process (including screenshots) is available within the next section.
How to install the DisplayLink Manager application
1. Download the correct version of the DisplayLink Manager Application for your version of macOS from here → Link
2. Double-click on the file you downloaded to start the application installer:

3. From within the ‘Introduction’ section of the application installer, click on the ‘Continue’ button to start the installation process:
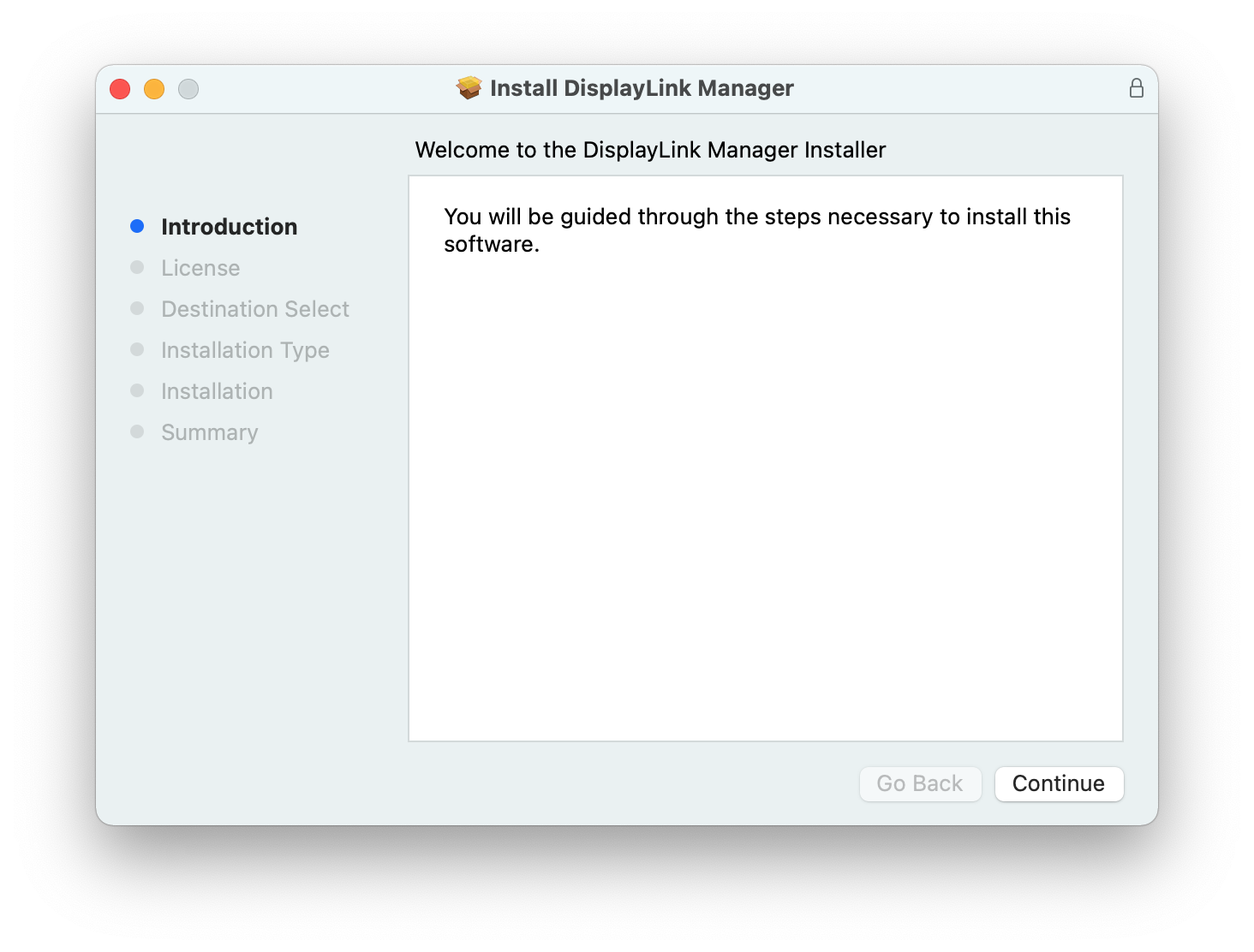
4. After having read the license information from within the ‘License’ section of the application installer, click on the ‘Continue’ button
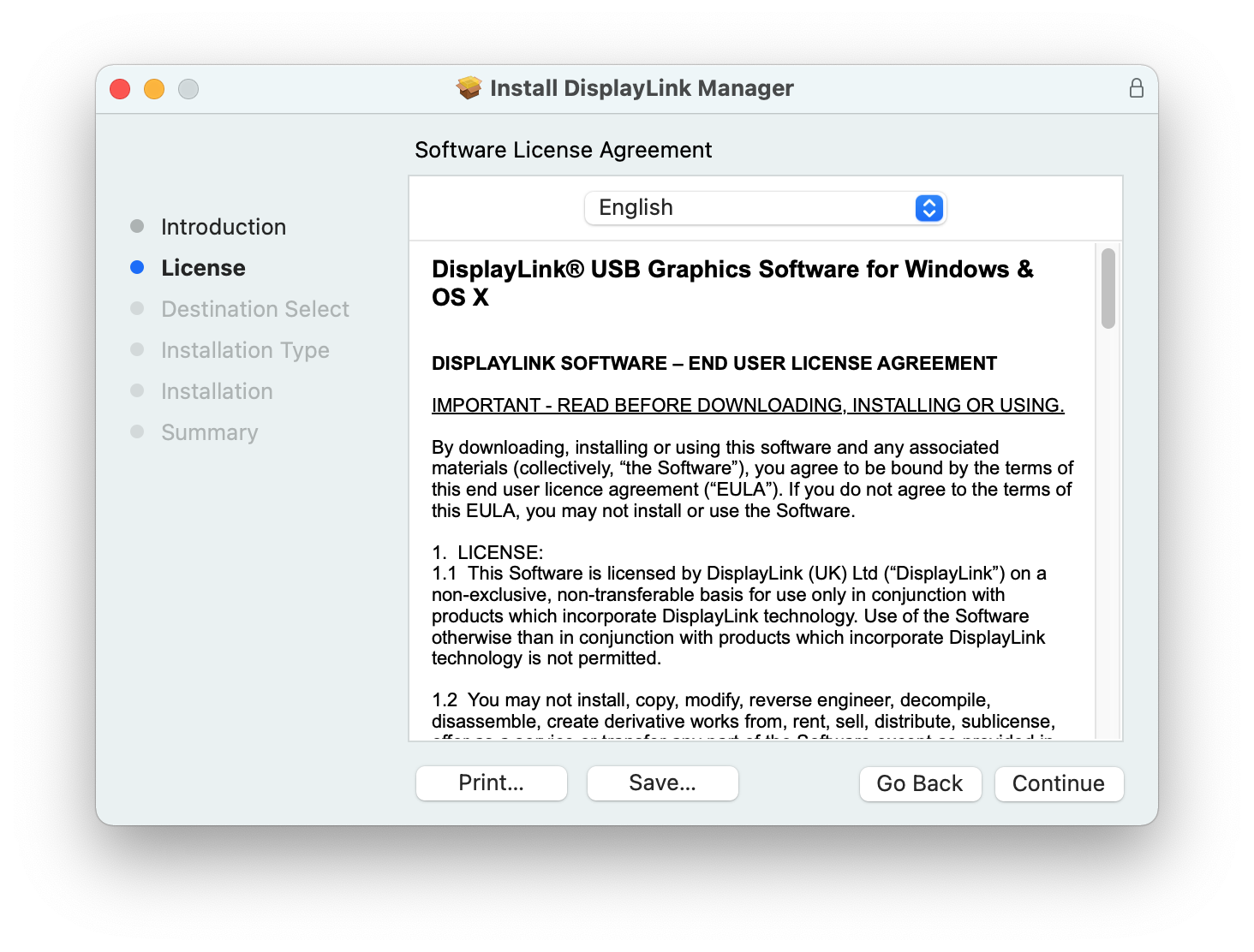
5. Click on the ‘Agree’ button in order to agree to the software license agreement.
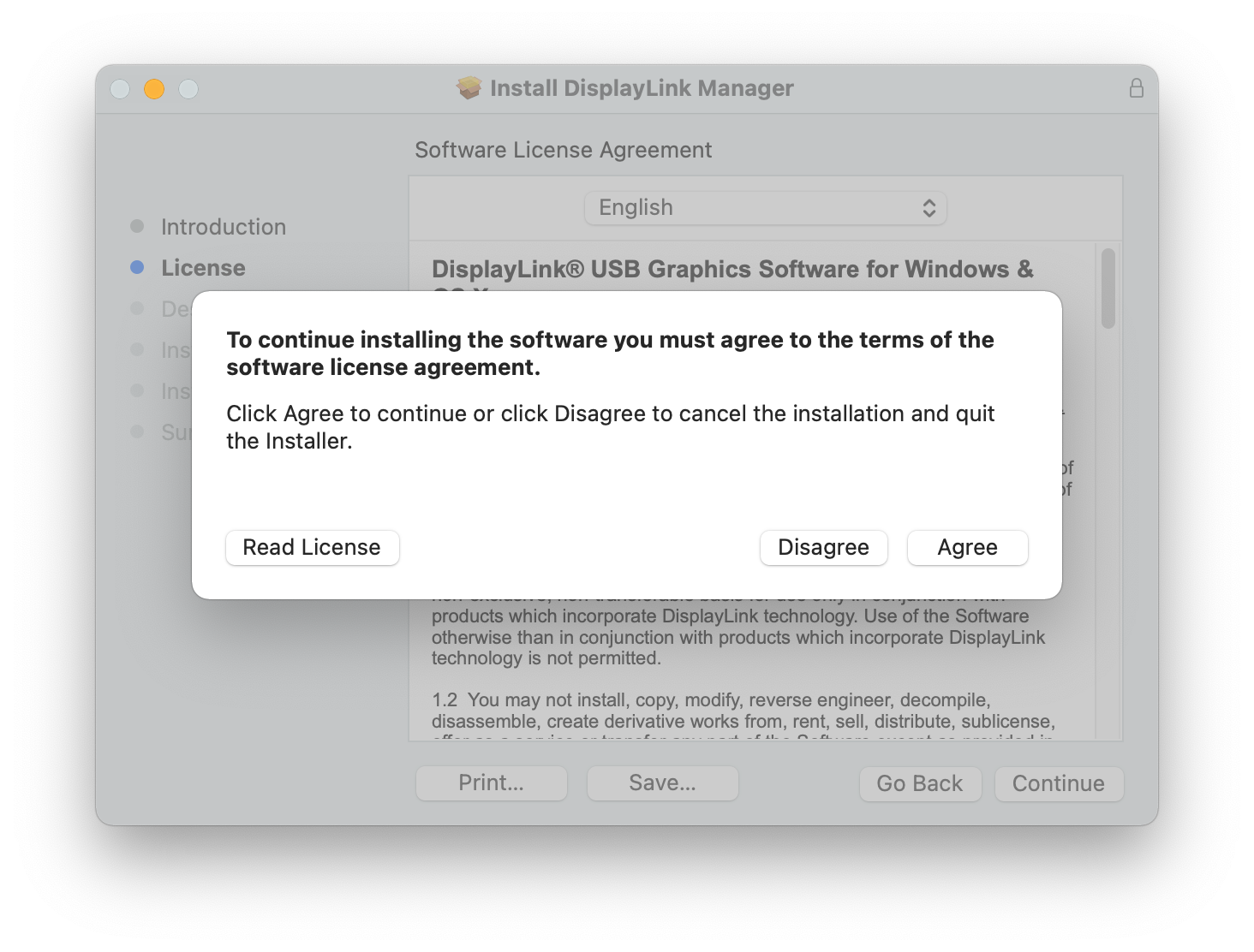
6. From within the ‘Installation Type’ section of the application installer, click on the ‘Install’ button:
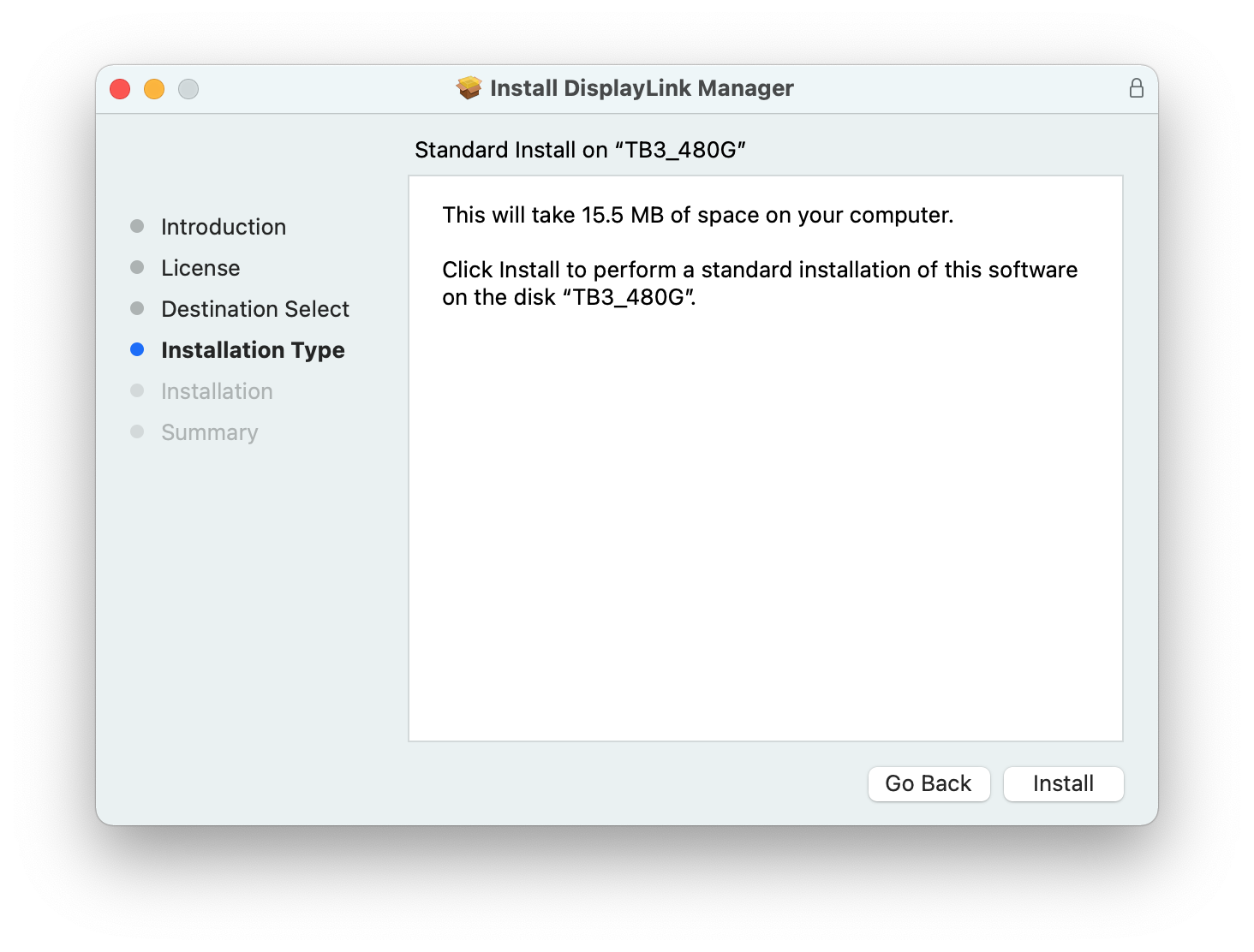
7. When prompted, please enter your system password and click on the ‘Install Software’ button to start the installation. The installation process will begin:
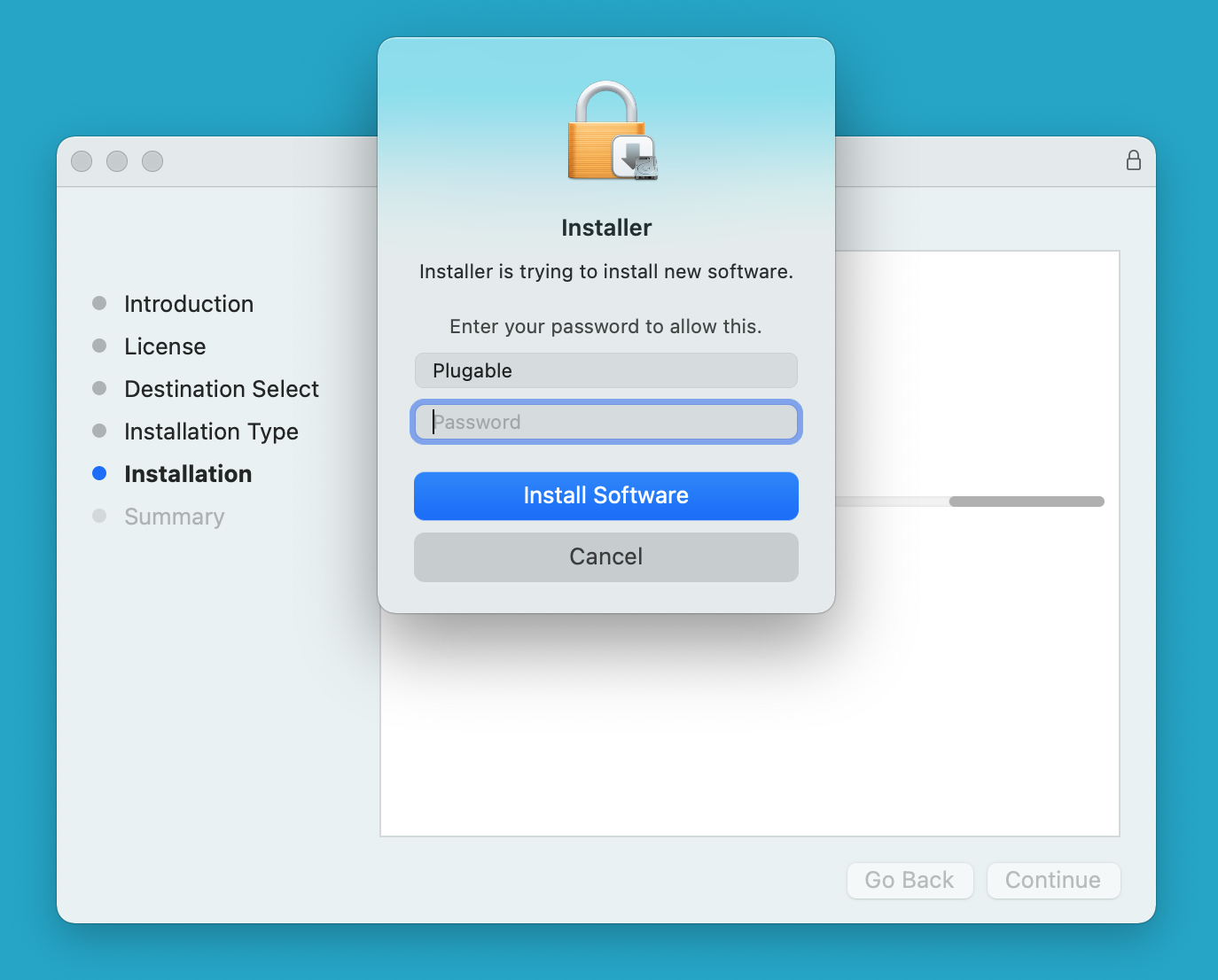
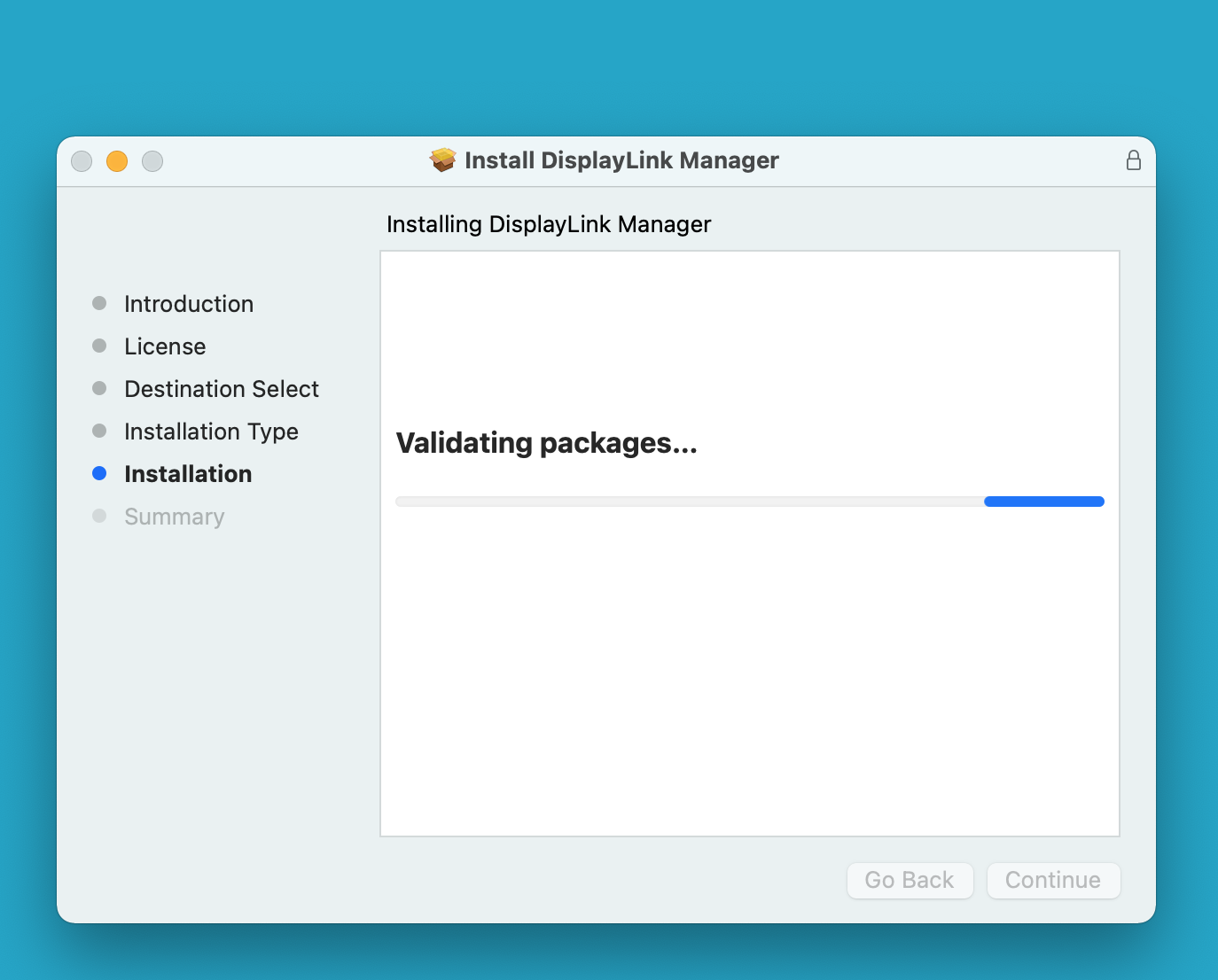
8. The application installer will notify you when the installation process has been completed. Please click on the ‘Close’ button in order to close the application installer.
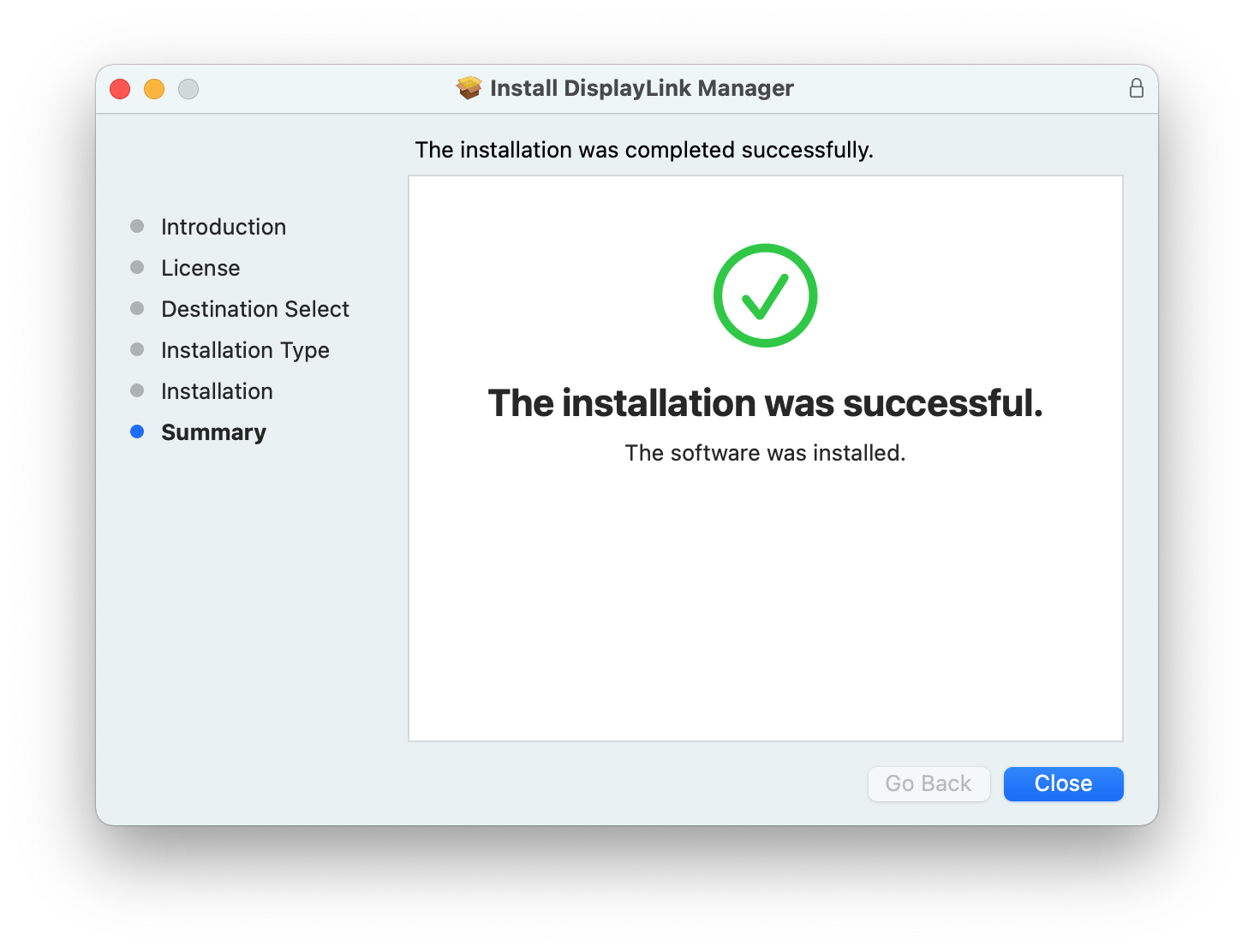
*** NOTE - If the installation process does not complete successfully, please see this knowledge base article --> LINK for a list of potential causes and possible solutions. ***
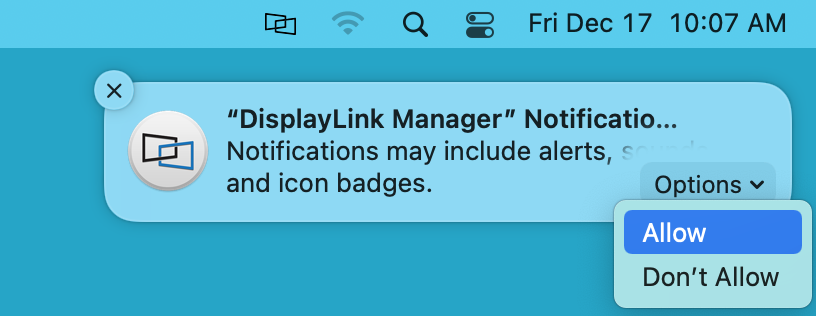
9. You should see a request from the DisplayLink Manager Application to allow the application to display notifications, when necessary. Click on the ‘Options’ button within the request and click the ‘Allow’ option:
10. Once the application installation is complete, please connect your DisplayLink device to your Mac
11. Once the device is connected, macOS will notify you that the ‘DisplayLink Manager’ application would like to record the computer’s screen. Click the ‘Open System Preferences’ button in order to grant this access.
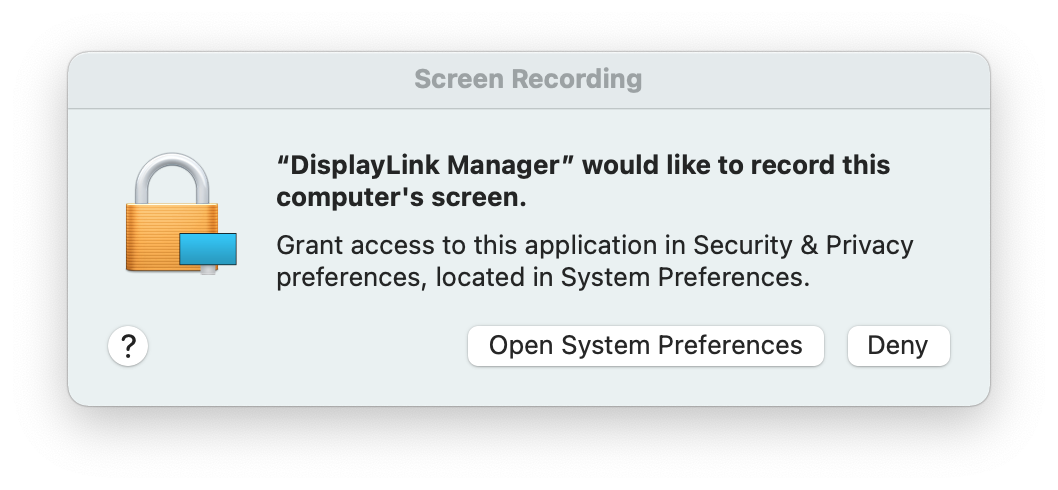
12. The ‘Security & Privacy’ application will open, with the default view showing the ‘Privacy’ tab with the ‘Screen Recording’ option selected by default:
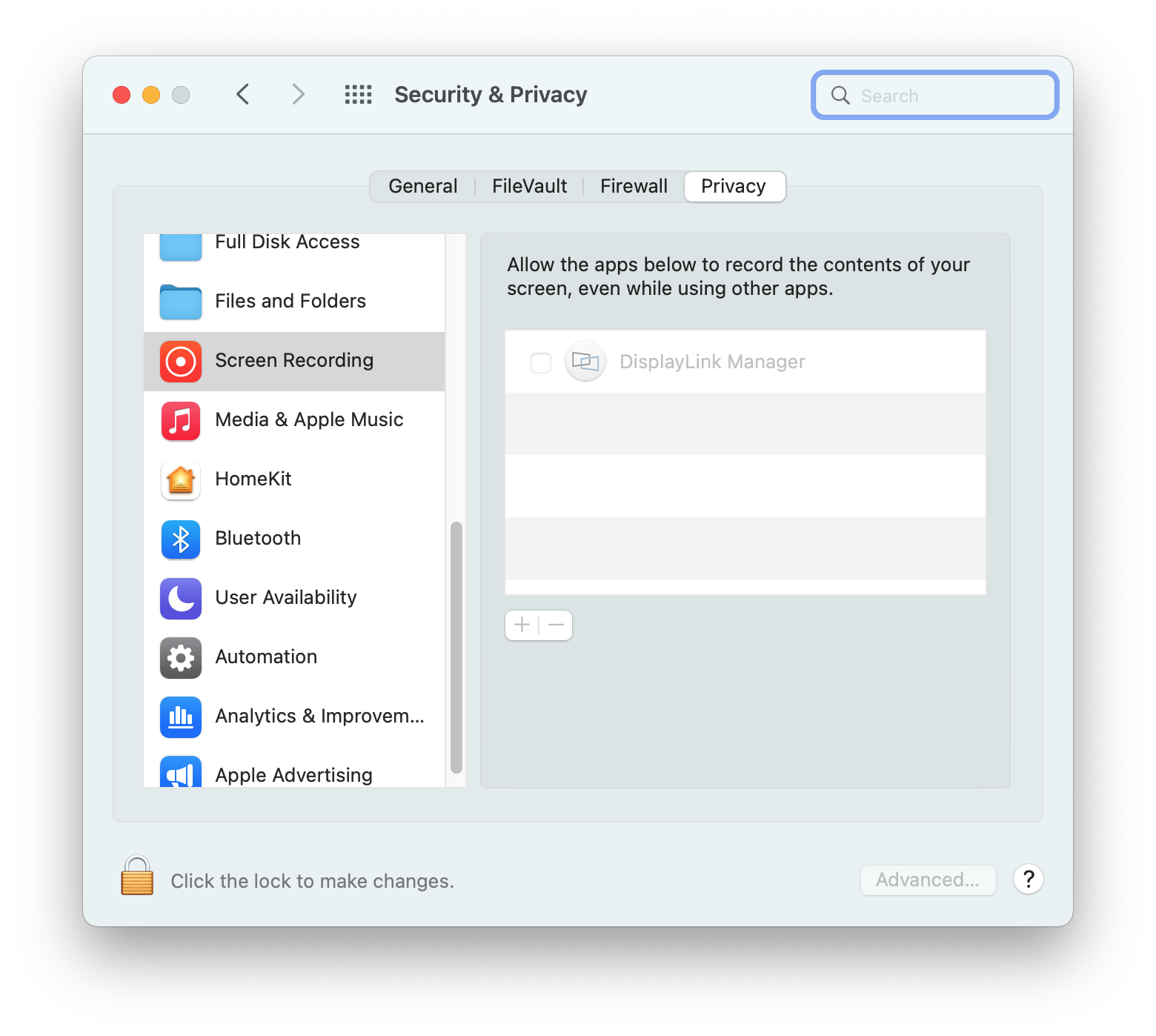
13. Click on the gold padlock at the bottom of the application window to enable changes.
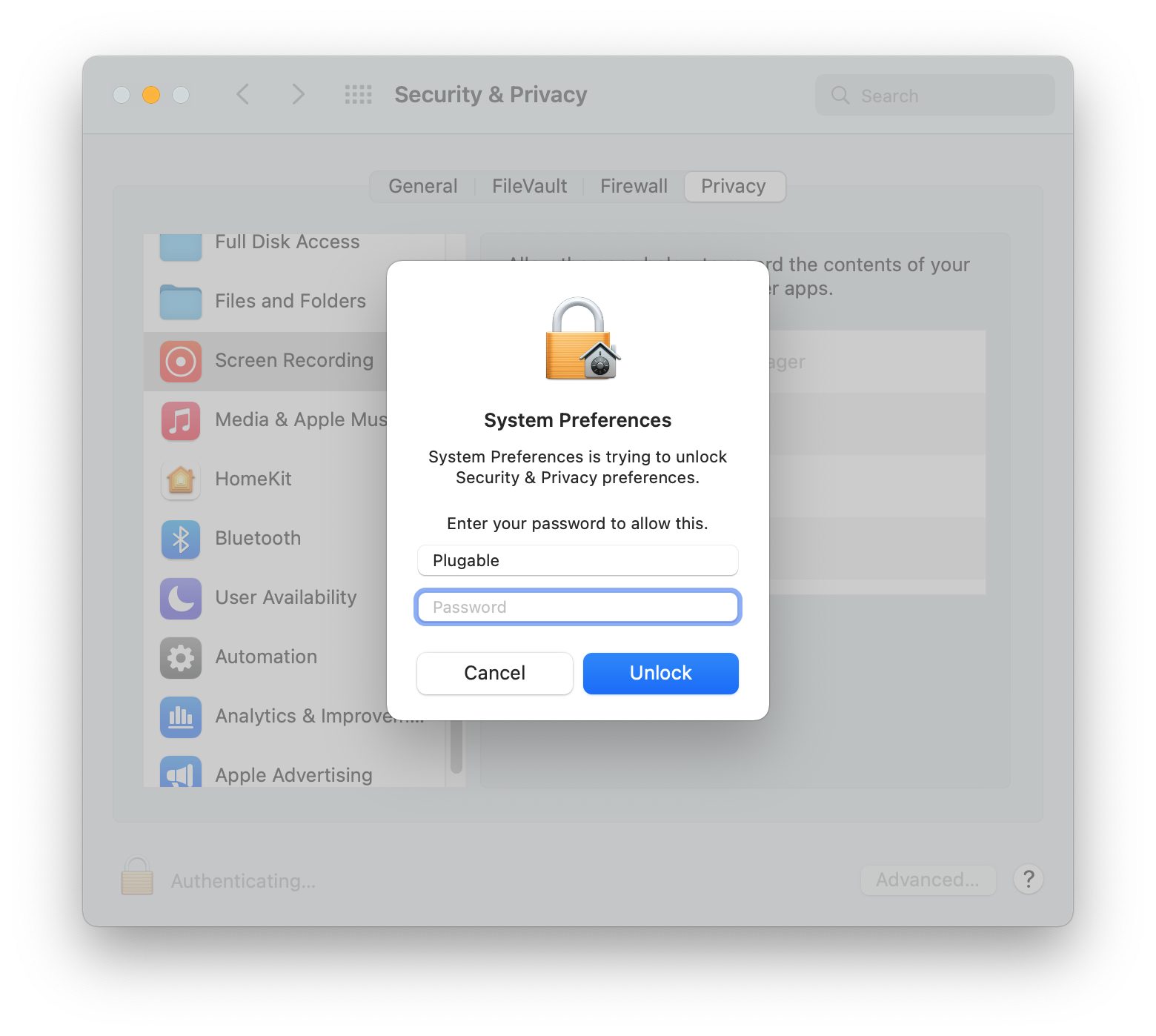
14. If prompted, enter your password and click the ‘Unlock’ button:
15. Click to place a checkmark next to the DisplayLink Manager entry:
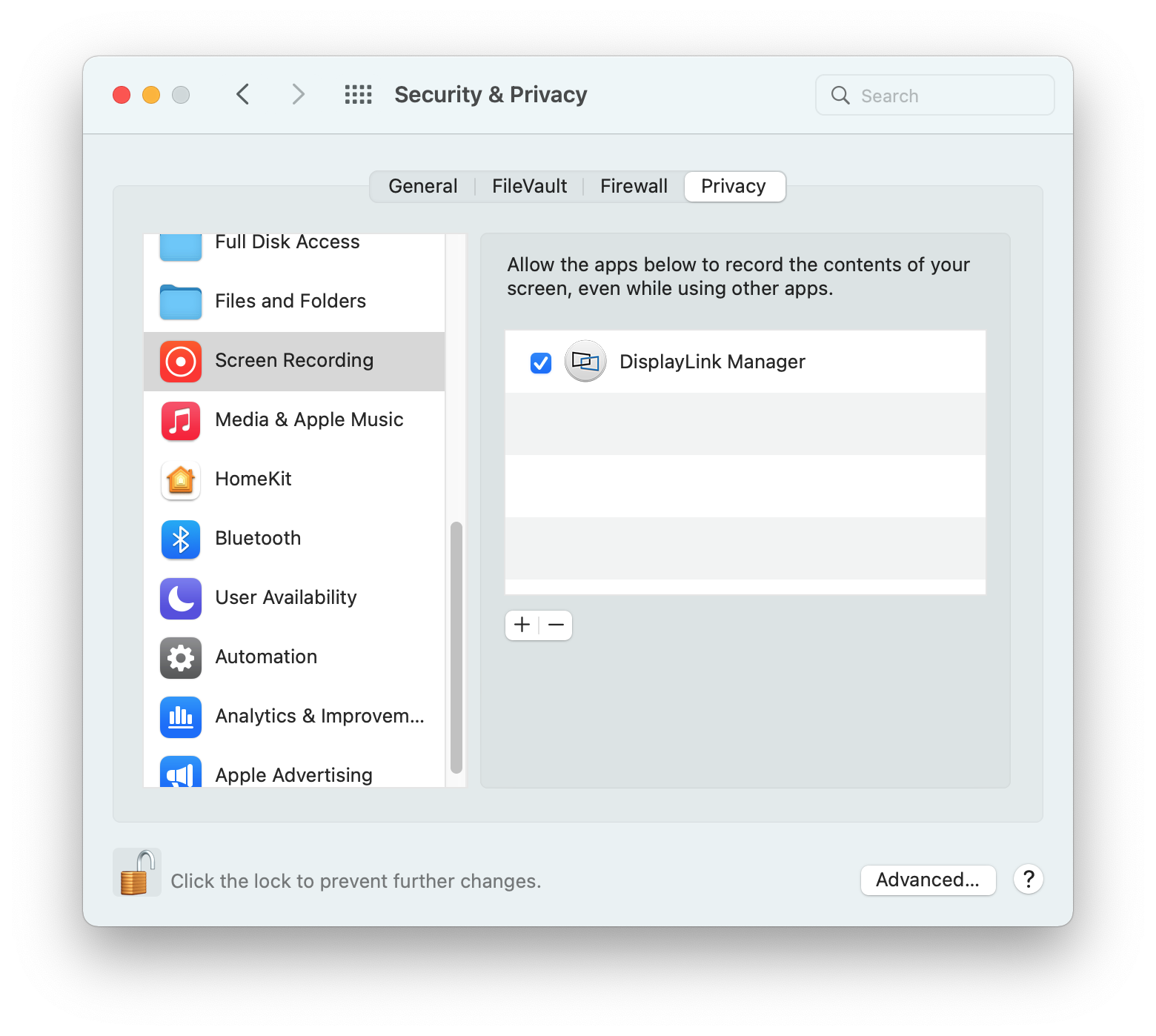
16. You will be prompted to Quit and Reopen the DisplayLink Manager application in order for the change to take effect. Please do so:
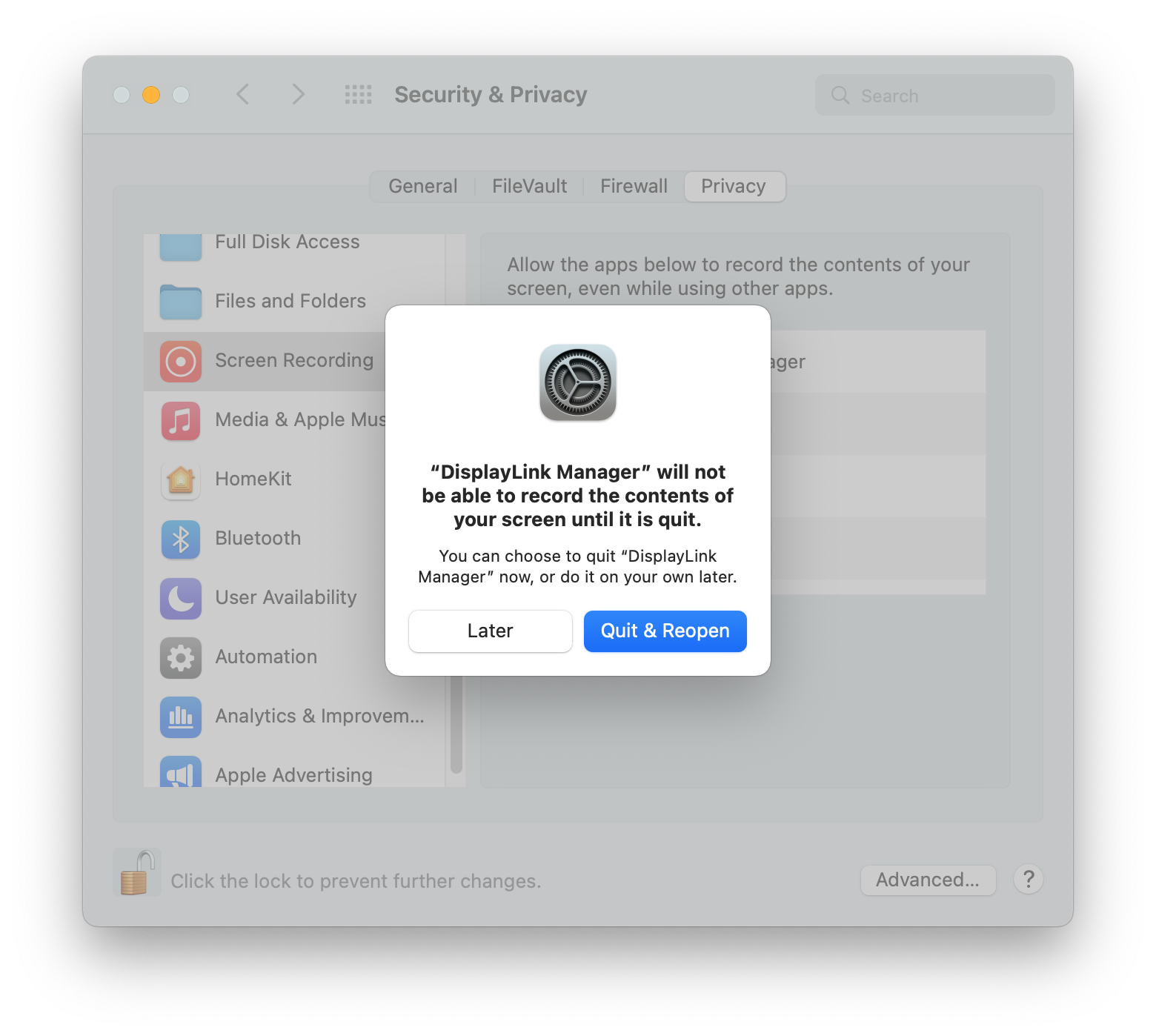
18. Once this change is complete, the displays connected to your DisplayLink-based product will start working automatically.
** Please note - The DisplayLink Manager Application does NOT in fact record or store any information. This permission must be granted in order for the DisplayLink Application to access the information it needs in order to generate the image shown on the DisplayLink-connected displays. **
19. Click on the DisplayLink Manager Application icon that is now present within the Apple Menu bar at the top of your screen. This will reveal the DisplayLink Manager Application status window:
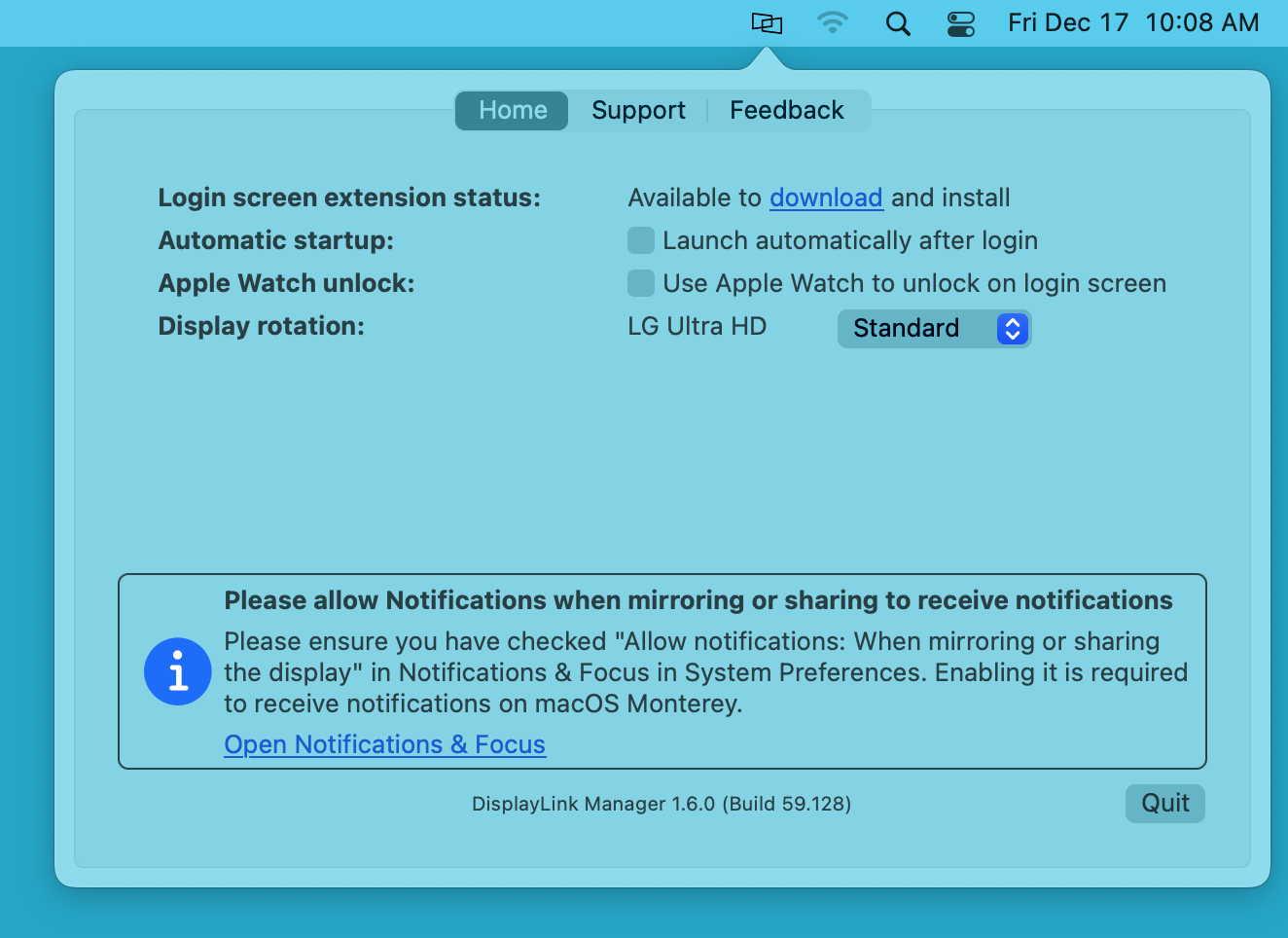
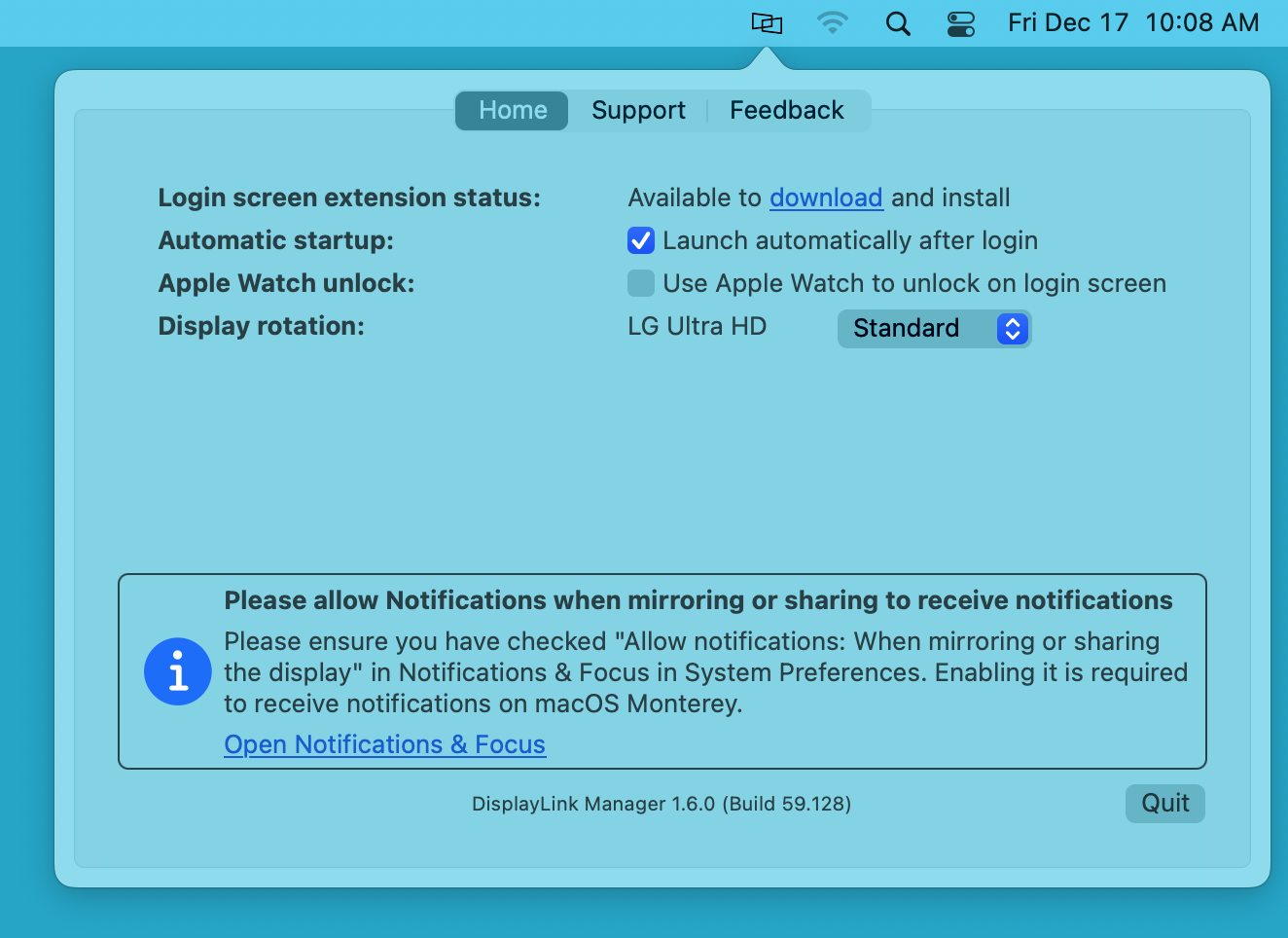
20. Within the DisplayLink Manager Application status window, next to the ‘Automatic startup’ section, click to place a checkmark next to the ‘Launch automatically after login’ option. This ensures that the application will be started each time you start your Mac.
21. In order to receive notifications from macOS while a DisplayLink device is connected to your Mac, you must make a change within the ‘Notifications & Focus’ System Preferences application.
Click on the ‘System Preferences’ icon (which looks like a gear) within the macOS Dock at the bottom of your screen.
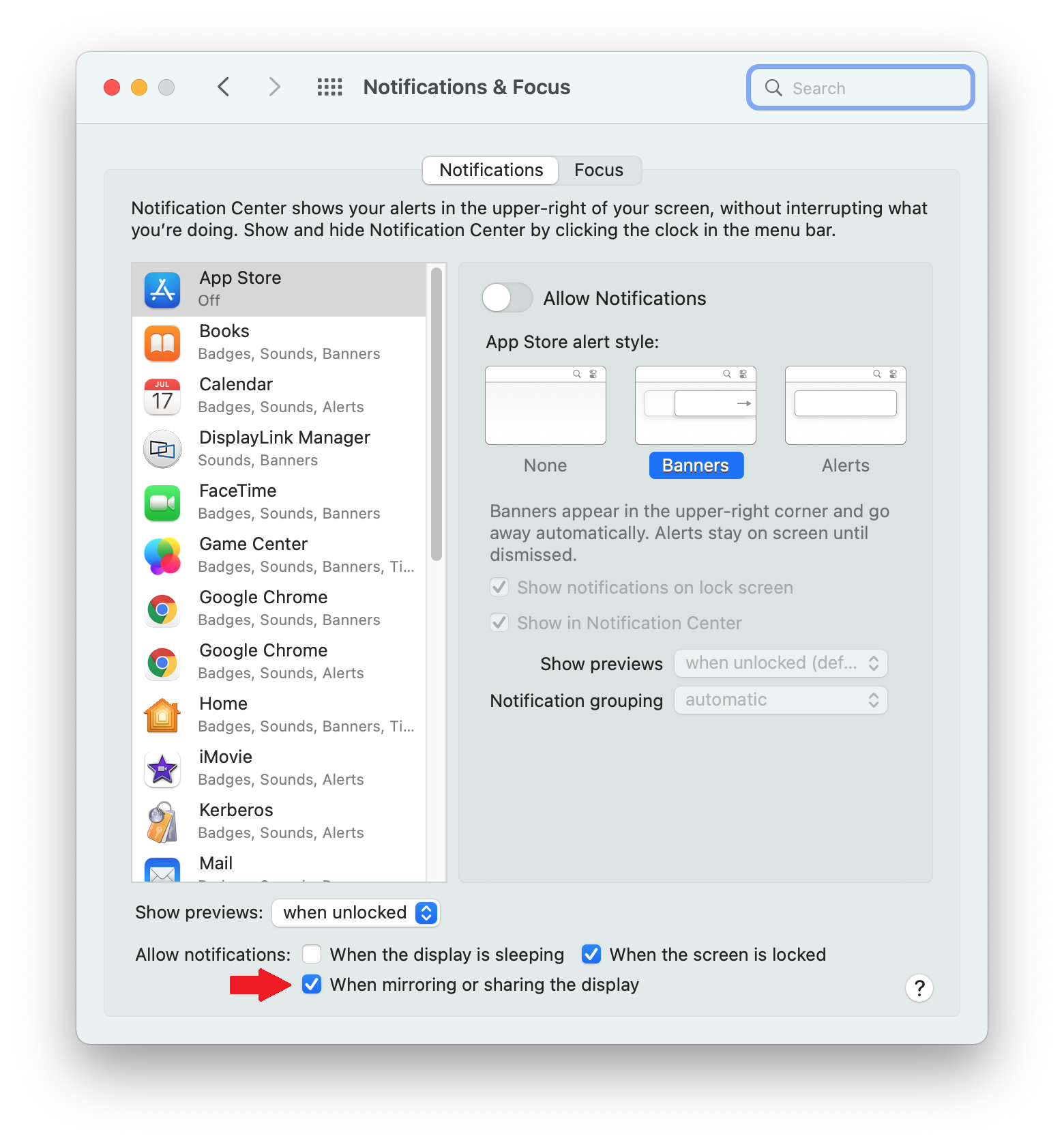
Click on the ‘Notifications & Focus’ application icon:
22. Within the ‘Notifications’ tab of the ‘Notifications & Focus’ application, next to the ‘Allow notifications’ label, click to place a checkmark next to the ‘When mirroring or sharing the display’ option. This will allow you to receive notifications from macOS while the DisplayLink device is connected.
23. Once all of the previous steps are done, the installation process is now complete.
How to use DisplayLink Manager for macOS
Once the DisplayLink Manager Application is installed, the application can be accessed via the DisplayLink Manager application status icon located within the Apple Menu Bar at the top of your screen:
** If the DisplayLink Manager Application status icon is not visible within the Menu Bar, then the application has not been started. Please open a new ‘Finder’ window and navigate to the ‘Applications’ folder. Within the ‘Applications’ folder, double-click on the DisplayLink Application icon in order to start the application. **
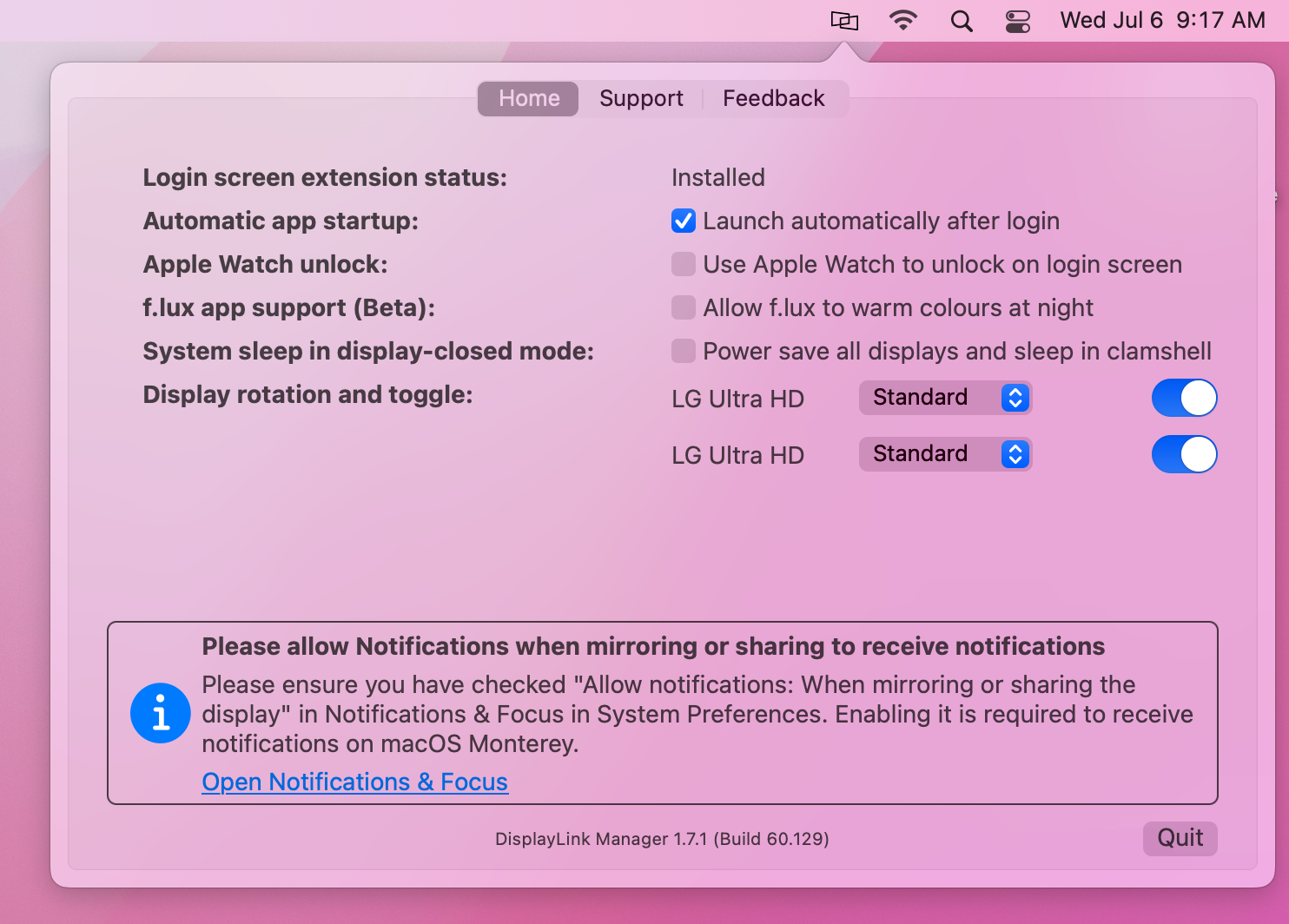
Within the ‘Home’ tab of the DisplayLink Manager Application, there are a few different items listed. The items listed will vary depending upon which version of the DisplayLink Manager Application that is installed, and the following list describes the features present in DisplayLink Manager version 1.7.1.
Login Screen Extension
By default, the ‘Login screen extension status:’ section will display, “Available to download and Install”
When an Apple Mac system is first powered on and reaches the login prompt, 3rd-party applications (such as the DisplayLink Manager application) are not yet running. As a result, DisplayLink-connected displays will not function.
Downloading and installing the Login screen extension (available by clicking on the ‘download’ link within DisplayLink Manager) will allow the DisplayLink-connected displays to function prior to logging in.
This is of course an optional feature, and is not required to use DisplayLink devices. However, this option is useful in certain situations, such as when only DisplayLink-connected displays are connected to the host Mac.
Automatic startup
As the name suggests, placing a checkmark next to the ‘Launch automatically after login’ option allows the DisplayLink Application to start automatically each time the system is powered on. We recommend checking this option in the interest of efficiency.
Apple Watch unlock
As the name suggests, placing a checkmark next to the ‘Use Apple Watch to unlock on the login screen’ will allow you to unlock your Mac using an Apple Watch while connected to a DisplayLink device.
Apple has more information on this process here → https://support.apple.com/en-us/HT206995
** Please note that this feature is not compatible with screensavers. To use Apple Watch unlock with your DisplayLink device, you must disable your screensaver. **
f.lux app support (Beta)
There is a 3rd-party application called 'f.lux' --> https://justgetflux.com/ that allows the adjustment of a display's color according to the time of day. If the f.lux application has been installed, placing a checkmark next to the 'f.lux app support (Beta)' option will enable f.lux to change the color of a DisplayLink connected display.
A few important notes about this feature:
A. This functionality is in 'beta' status, as the label suggests. As a result, there may be cases where things may not work as expected when this option is enabled.
B. This functionality is supported with devices based on the DisplayLink DL-3xxx chipset, DL-5xxx chipset, and DL-6xxx chipset. However, it is important to note that on DL-6xxx chipsets this functionality is limited to DisplayPort video outputs only. It is NOT supported on HDMI video outputs via DL-6xxx chipsets.
System sleep in display-closed mode
Mac laptops running macOS 12 Monterey or newer can be used in one of two ways when used in conjunction with a DisplayLink-based product.
The first way is with the laptop lid open, with the laptop's built-in internal display enabled.
The second way is with the laptop lid closed, with the laptop's built-in internal display disabled. This is known as closed display mode or 'clamshell' mode.
In order to enter closed display mode while connected to a DisplayLink-based product, the host Mac must have an external power source connected and an external keyboard and mouse connected.
Placing a checkmark next to 'Power save all displays and sleep in clamshell' changes this behavior, in that closing the laptop lid will cause the host Mac to go to sleep.
This feature is of course optional, and its use is a matter of personal preference.
Display rotation and toggle
The functionality presented within this section of the DisplayLink Manager Application will vary depending upon which type of processor is within the host Mac.
Macs with an Intel processor
When DisplayLink devices are used in conjunction with Apple Mac systems that have an Intel processor, a list of all the DisplayLink-connected displays will appear within this section.
The individual displays can be turned on or off as desired by clicking on the toggle switch next to each display's name. You can differentiate between each display by hovering the mouse pointer over each display name. When doing so, a red identification box will appear within the selected display.
You can rotate the orientation of the DisplayLink-connected displays within the ‘Displays’ macOS System Preferences application.
Macs with an Apple M1 or M2 processor
When DisplayLink devices are used in conjunction with Apple Mac systems that have an Apple M1 or M2 processor, display rotation must be done from within the DisplayLink Manager Application and the host Mac must be running macOS 12 Monterey or later (display rotation is not available on M1 Macs running macOS 11 Big Sur).
Each DisplayLink-connected display attached to the M1 or M2 system will be listed next to the ‘Display rotation’ area. Click on the drop-down selection box and select the appropriate degree of rotation.
If multiple displays are present, you can differentiate between each display by hovering the mouse pointer over each display name. When doing so, a red identification box will appear within the selected display.
Synaptics (the creators of DisplayLink technology) have more information on this feature here --> Link
In addition to the rotation aspect described above, the individual displays can be turned on or off as desired by clicking on the toggle switch next to each display's name. As mentioned above, you can differentiate between each display by hovering the mouse pointer over each display name. When doing so, a red identification box will appear within the selected display.
DisplayLink Manager App Installation Instructions for macOS 13 Ventura and macOS 14 Sonoma
Before you begin
Unsure which version of macOS you have installed on your Mac? Click on the ‘Apple’ icon within the menu bar located at the top of your desktop and select ‘About this Mac’. A new window will open and display the host system’s macOS version.
Guided Video Demonstration
For those who prefer, we have a video demonstration of the installation procedure available (an embedded link is below).
For those who prefer, a detailed text-based description of the installation process (including screenshots) is available within the next section.
How to install the DisplayLink Manager application
*** Note - the screenshots in this article (and the demonstration video) were produced using macOS 13 Ventura, however the process and appearance is virtually identical in macOS 14 Sonoma. ***
1. Download the correct version of the DisplayLink Manager Application for your version of macOS from here → LINK
2. Double-click on the file you downloaded to start the application installer:

3. From within the ‘Introduction’ section of the application installer, click on the ‘Continue’ button to start the installation process:
4. After having read the license information from within the ‘License’ section of the application installer, click on the ‘Continue’ button
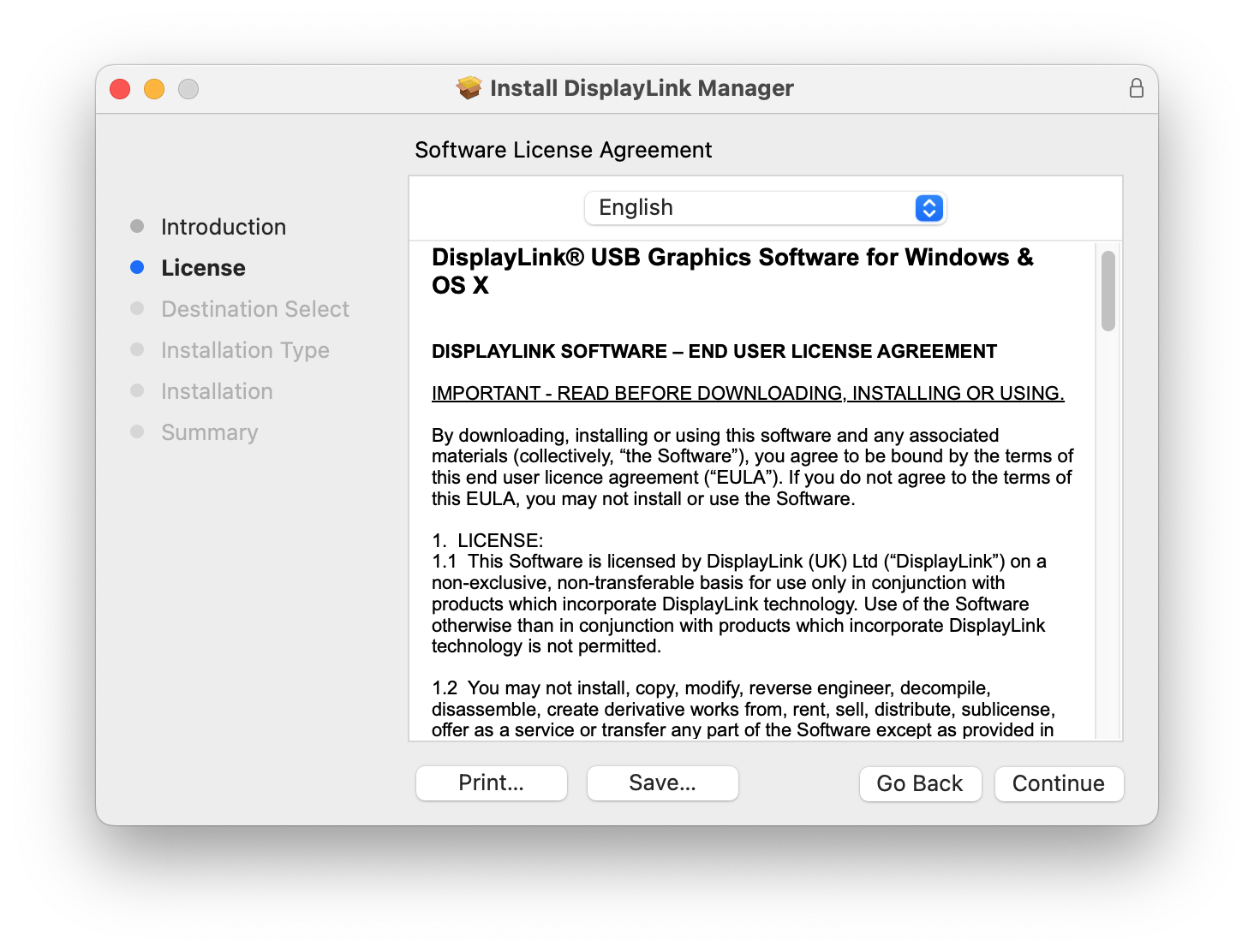
5. Click on the ‘Agree’ button in order to agree to the software license agreement.
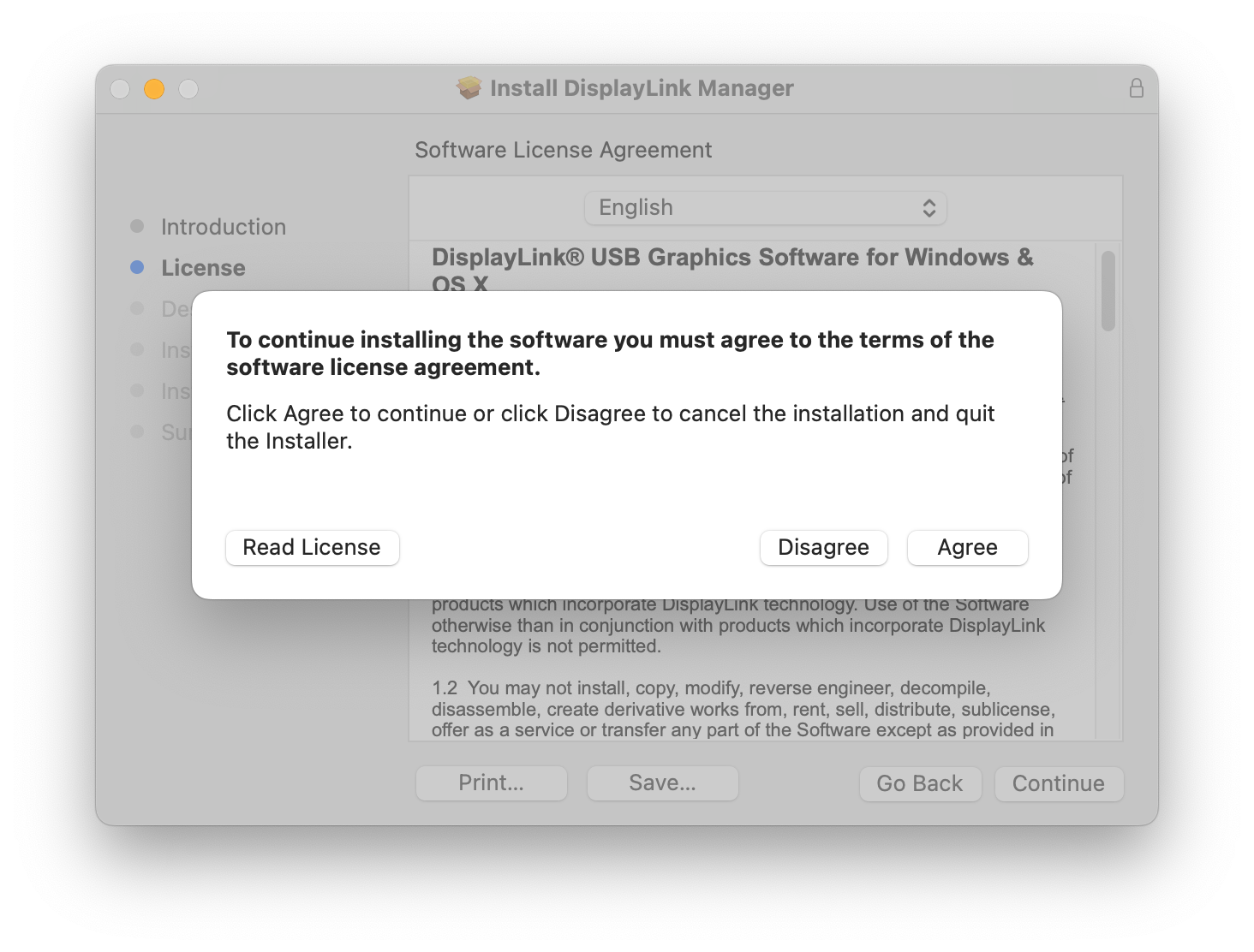
6. From within the ‘Installation Type’ section of the application installer, click on the ‘Install’ button:
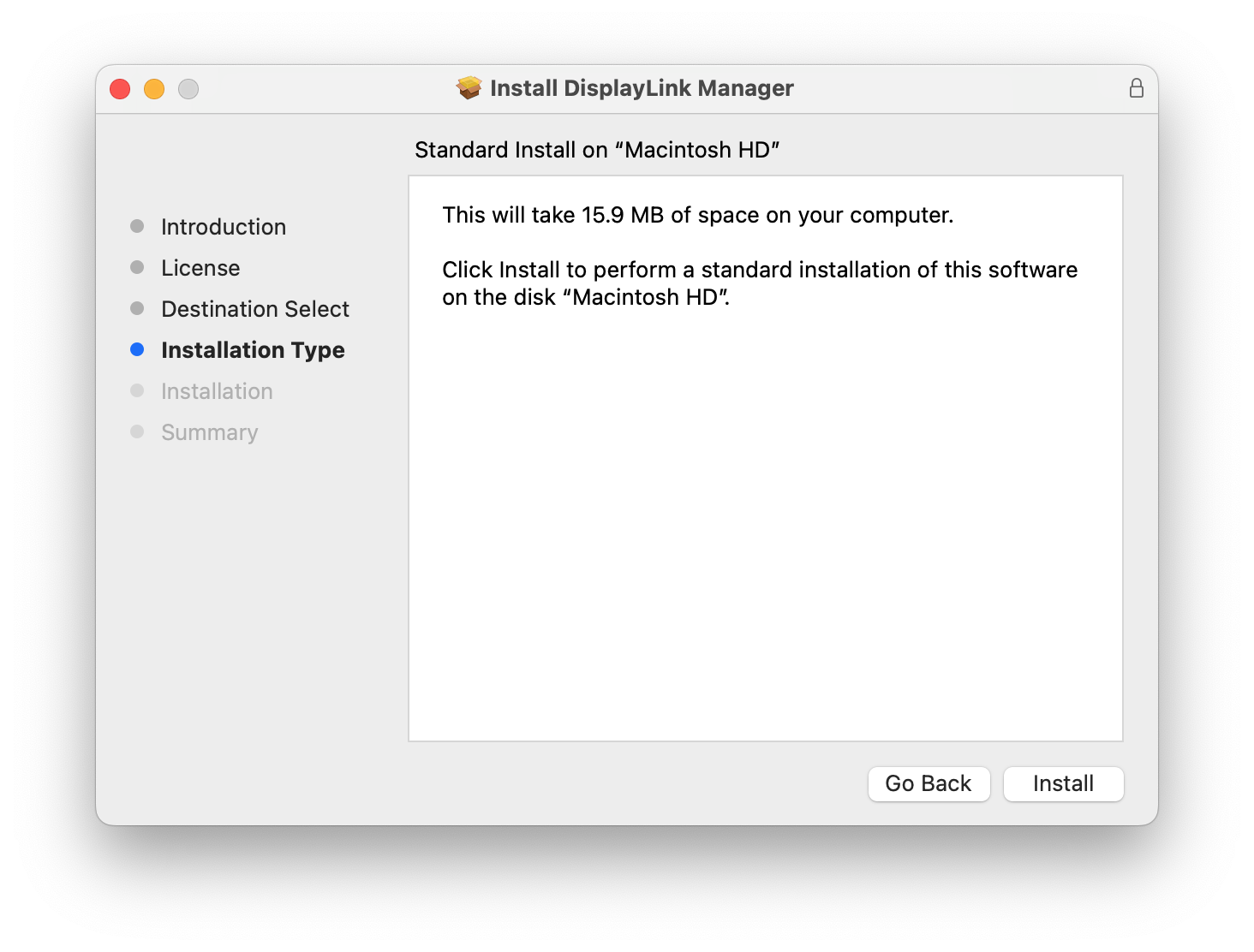
7. When prompted, please enter your system password and click on the ‘Install Software’ button to start the installation. The installation process will begin:
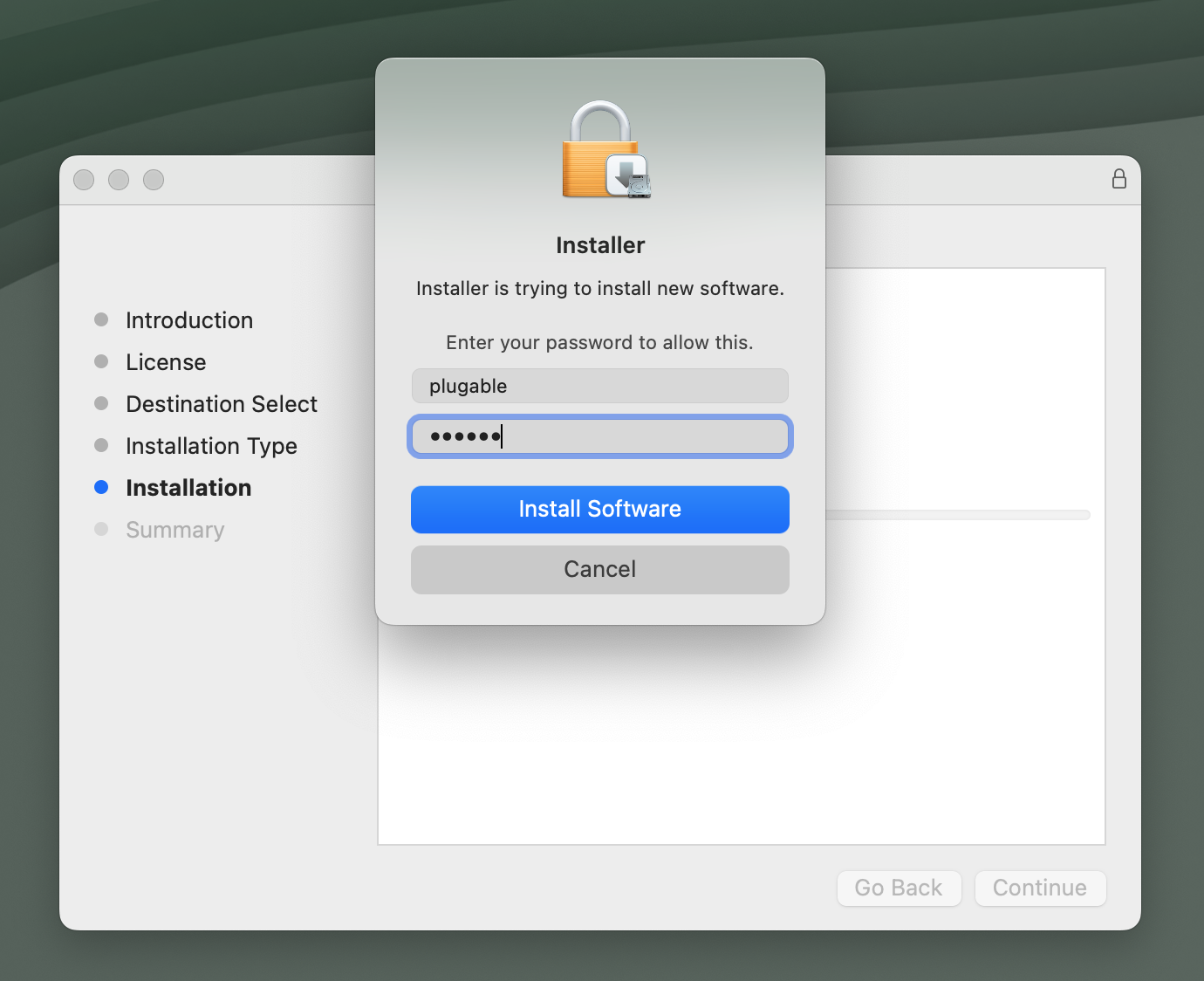
8. If prompted to access files, click OK:
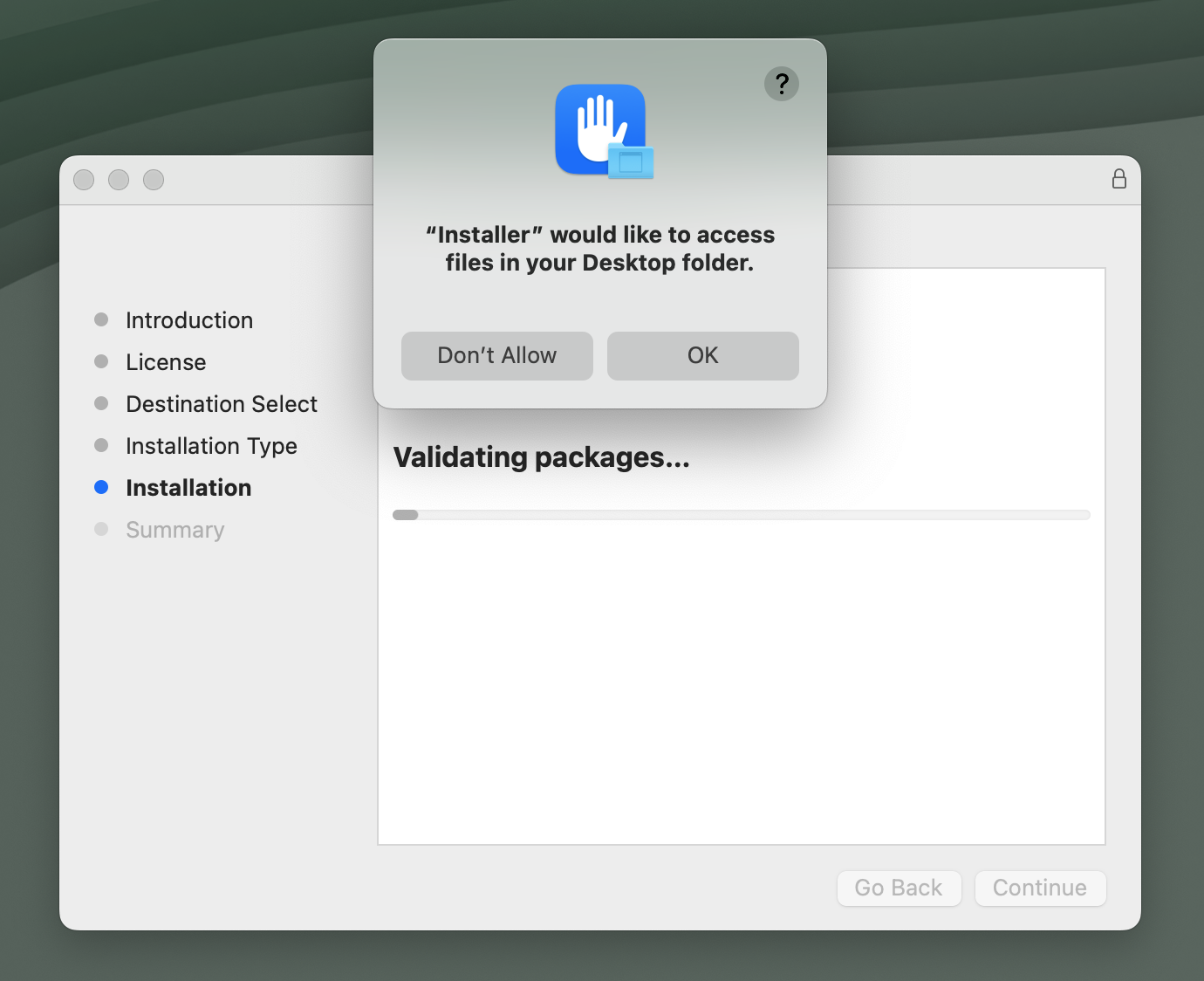
9. The application installer will notify you when the installation process has been completed. Please click on the ‘Close’ button in order to close the application installer.
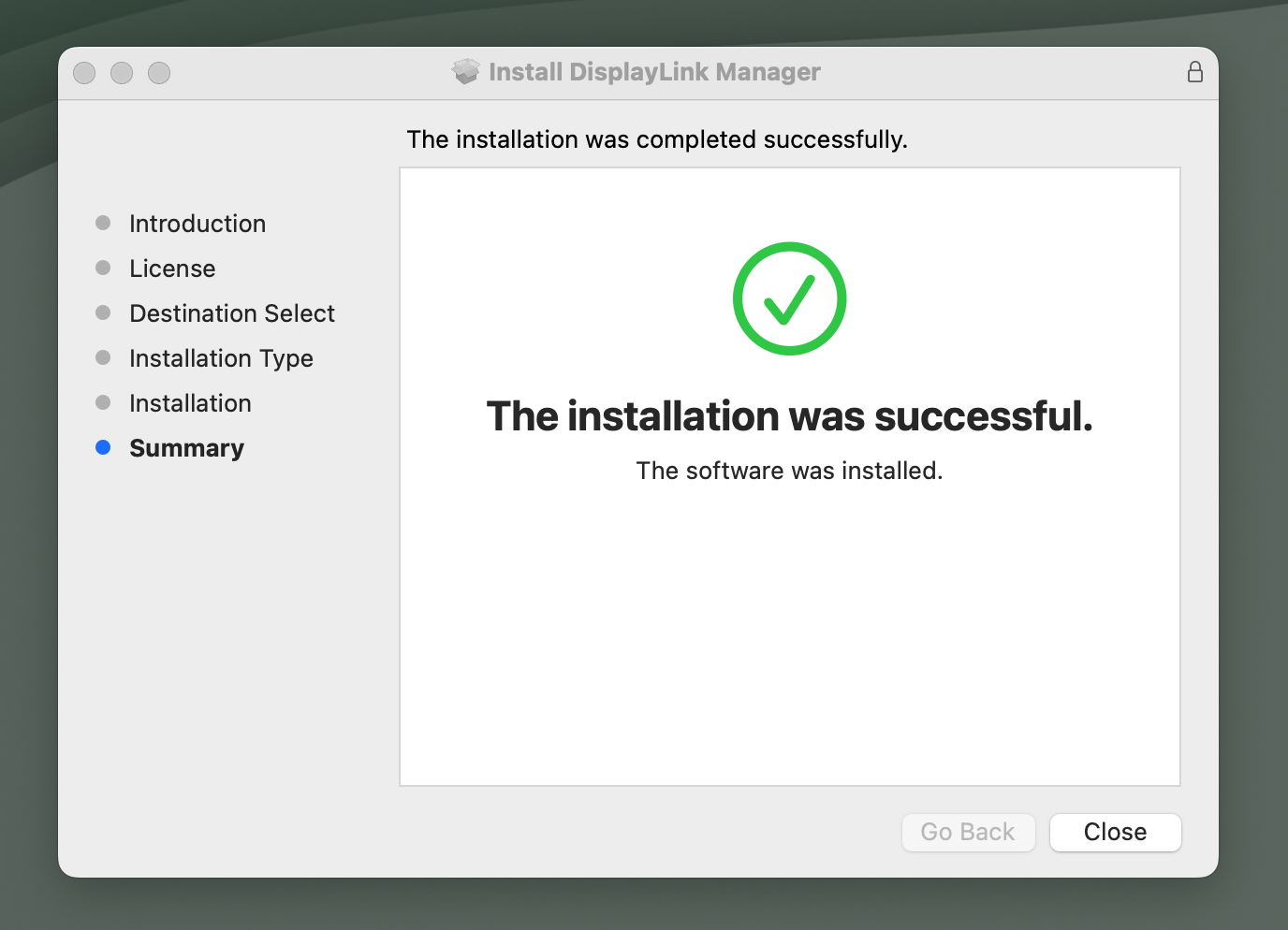
*** NOTE - If the installation process does not complete successfully, please see this knowledge base article --> LINK for a list of potential causes and possible solutions. ***
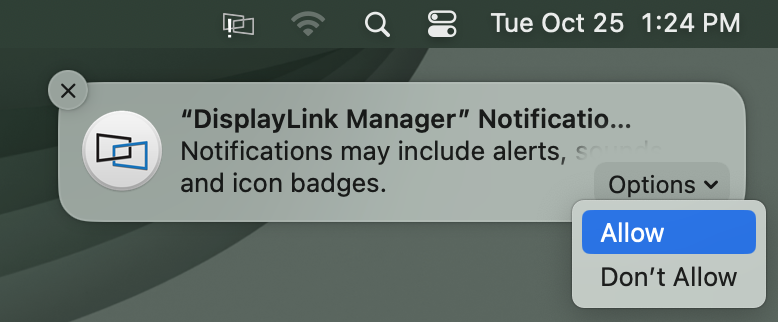
10. You should see a request from the DisplayLink Manager Application to allow the application to display notifications, when necessary. Click on the ‘Options’ button within the request and click the ‘Allow’ option:
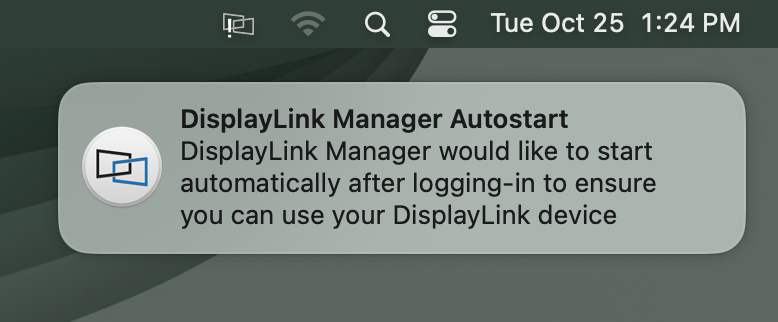
11. You should also see a request from the DisplayLink Manager Application to start the application automatically each time you log in to your Mac. Please click the notification and select the ‘Allow’ option
12. macOS will notify you that the ‘DisplayLink Manager’ application would like to record the computer’s screen and audio. Click the ‘Open System Settings’ button in order to grant this permission.
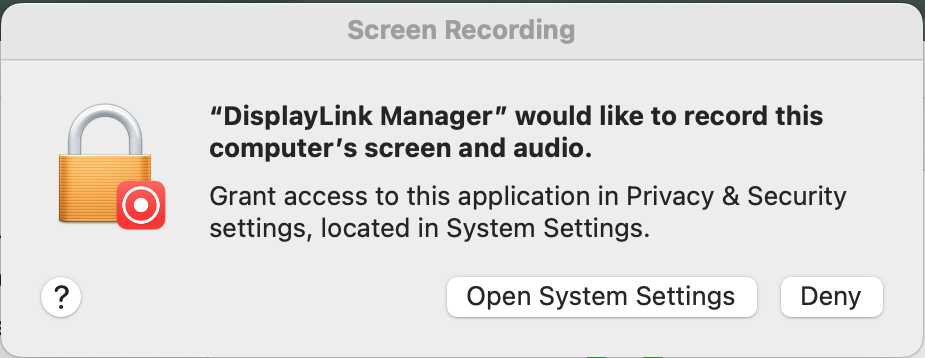
13. The ‘System Settings’ application will open, with the ‘Privacy & Security’ section highlighted by default. The ‘Screen Recording’ section will be visible on the right side of the application window:
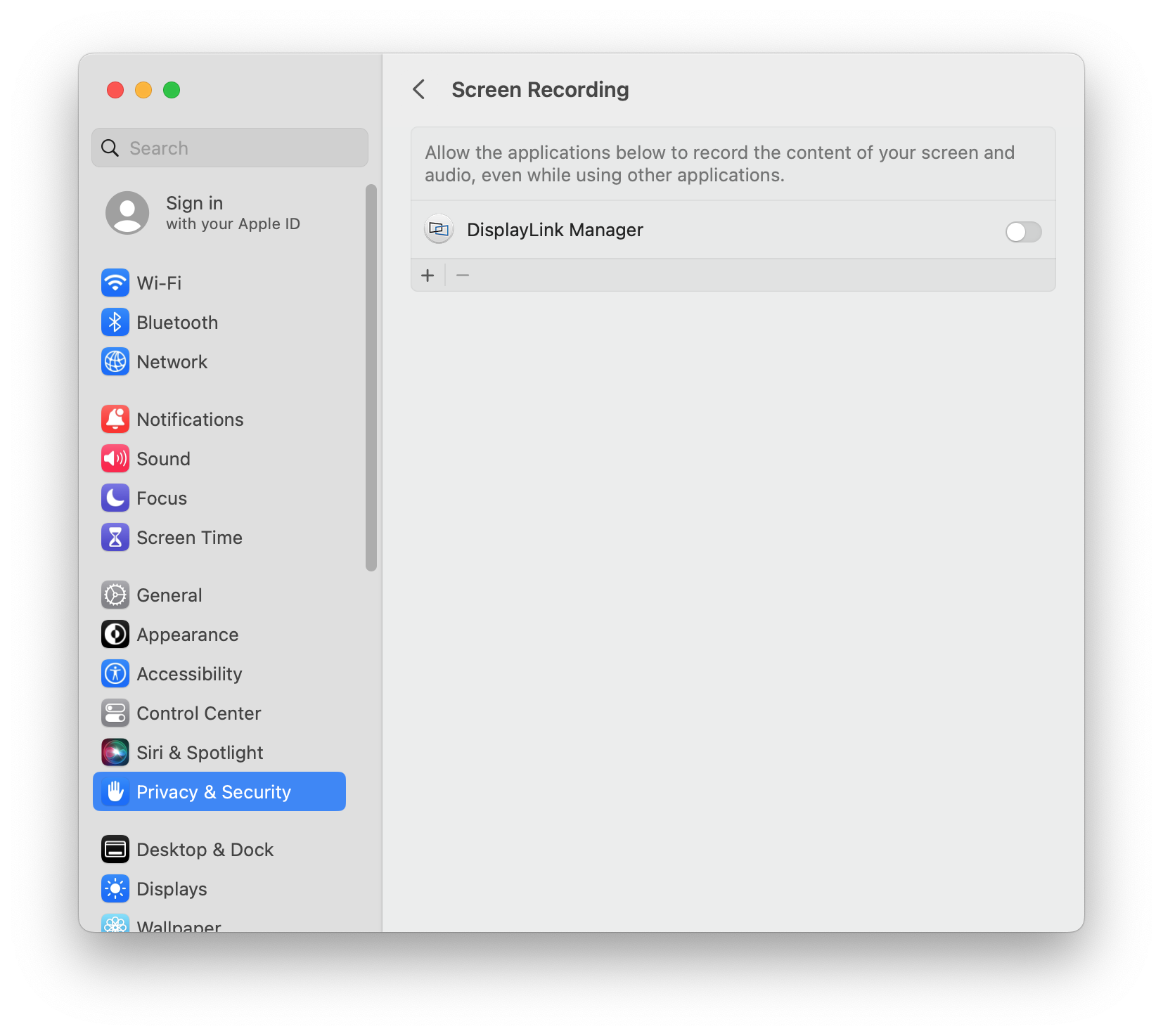
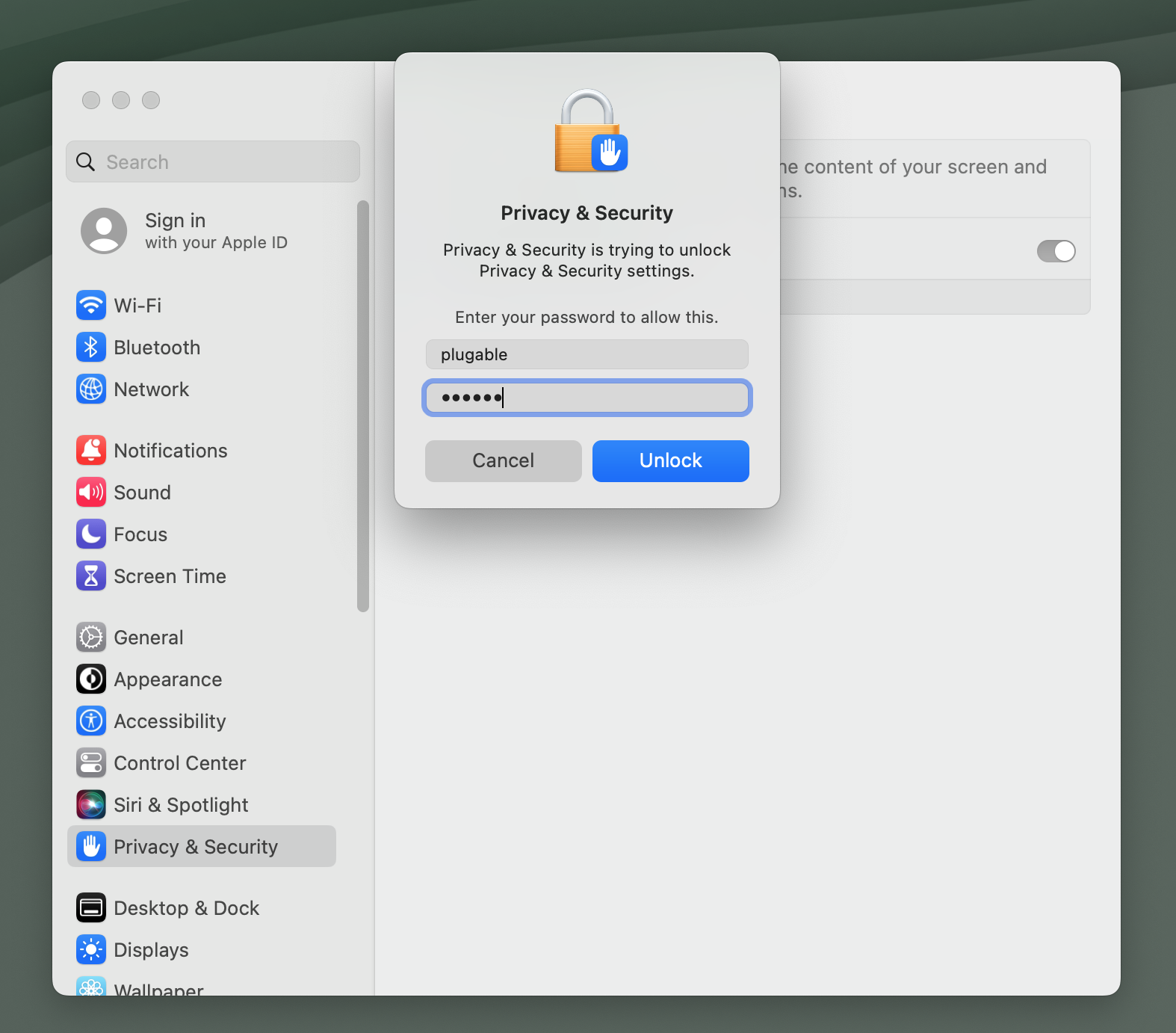
14. Click the toggle switch next to the ‘DisplayLink Manager’ entry in order to grant the required permission. When doing so, you will be prompted to enter your password. Enter your password and click the ‘Unlock’ button to continue:
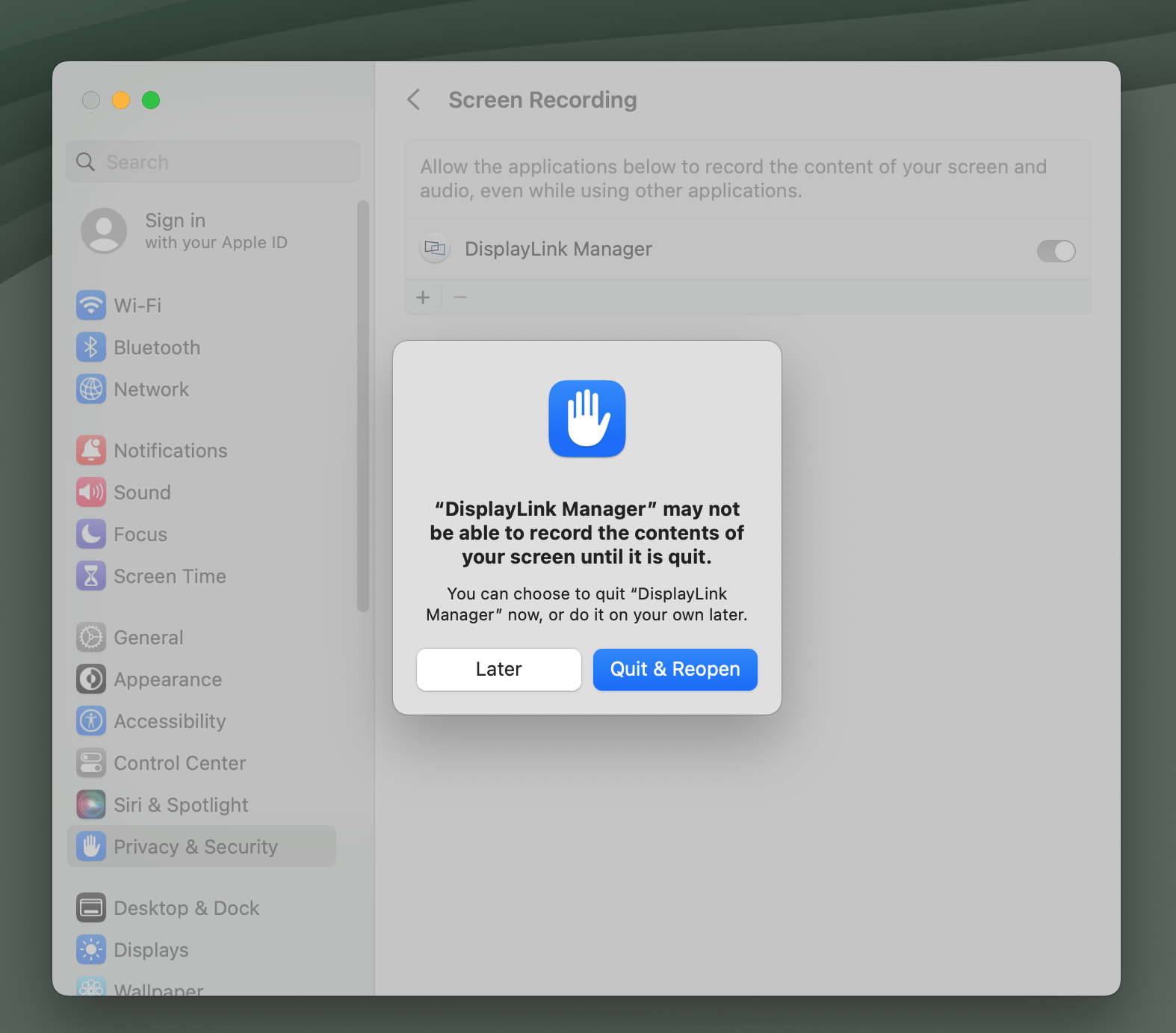
15. You will be prompted to Quit and Reopen the DisplayLink Manager application in order for the change to take effect. Please do so:
*** Please note - The DisplayLink Manager Application does NOT in fact record or store any information. This permission must be granted in order for the DisplayLink Application to access the information it needs in order to generate the image shown on the DisplayLink-connected displays. ***
16. Once complete, the ‘DisplayLink Manager’ application toggle switch will indicate that the permission has been granted. The ‘System Settings’ application window can now be closed.
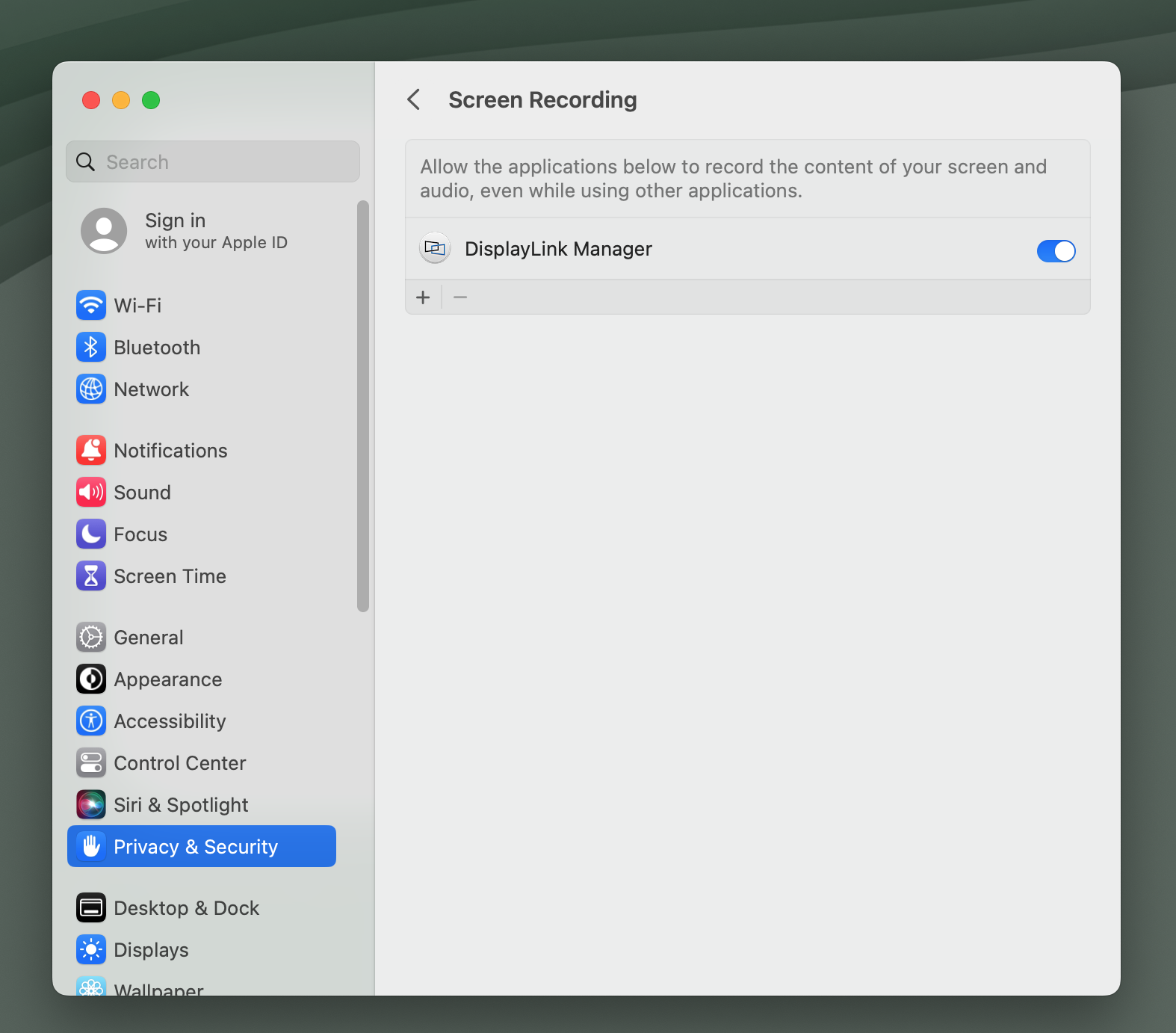
NOTE - In macOS 14 Sonoma, whenever the DisplayLink Manager Application is running you will see a notification within the Apple Menu bar that the DisplayLink Manager Application is capturing your screen. This is both normal and expected behavior.
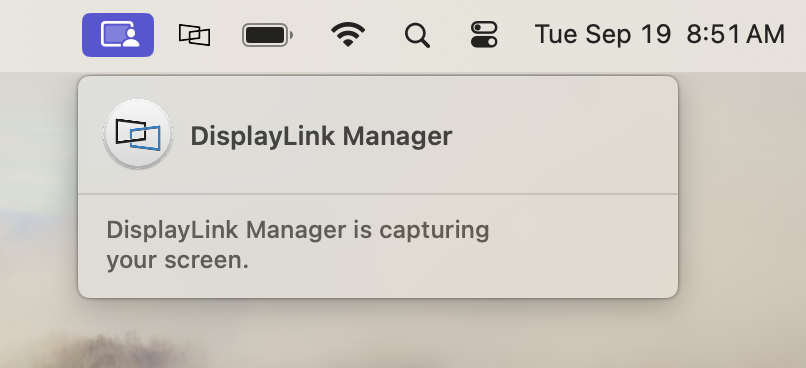
17. Click on the DisplayLink Manager Application icon that is now present within the Apple Menu bar at the top of your screen. This will reveal the DisplayLink Manager Application status window:
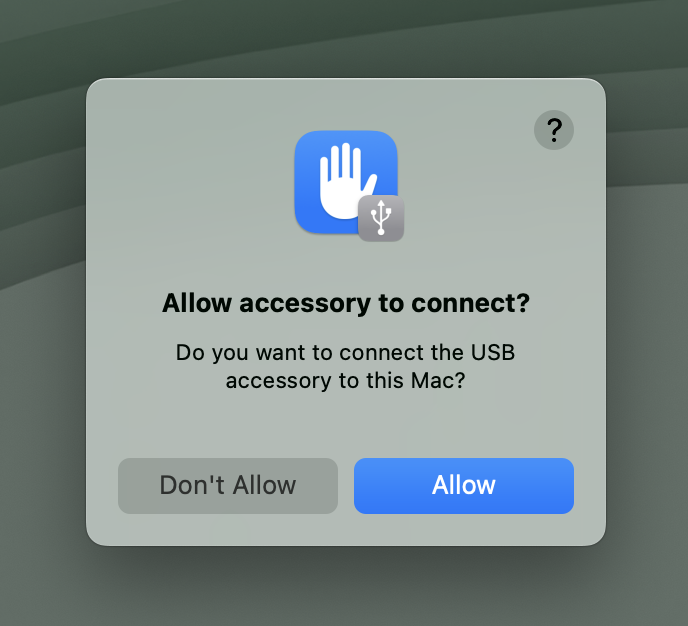
18. Connect your DisplayLink-based product to your Mac. On portable Macs based on an Apple processor, you may be prompted to allow the accessory to connect. If you are prompted, please click the ‘Allow’ button in order to allow the accessory to connect:
More information about this process is available here → LINK
*** This process will only occur on portable Macs (such as Mac laptops) that have an Apple processor. This will NOT occur on desktop Macs or Macs that have an Intel processor. ***
Once the product is connected, the DisplayLink Manager Application status window will update with information about the display connected:
19. The notification you received in step #11 to allow the DisplayLink Manager Application to start automatically each time you log in to your Mac should have automatically placed a checkmark next to the ‘Launch automatically after login’ option.
If the checkmark is not present, please click to place a checkmark next to the ‘Launch automatically after login’ option. This will help ensure that the DisplayLink Manager Application is running each time you login to your Mac.
*** If the DisplayLink Manager Application is not running, the displays connected to your DisplayLink-based product will not work ***
How to use DisplayLink Manager for macOS
Once the DisplayLink Manager Application is installed, the application can be accessed via the DisplayLink Manager application status icon located within the Apple Menu Bar at the top of your screen:

*** If the DisplayLink Manager Application status icon is not visible within the Menu Bar, then the application has not been started. Please open a new ‘Finder’ window and navigate to the ‘Applications’ folder. Within the ‘Applications’ folder, double-click on the DisplayLink Application icon in order to start the application. ***
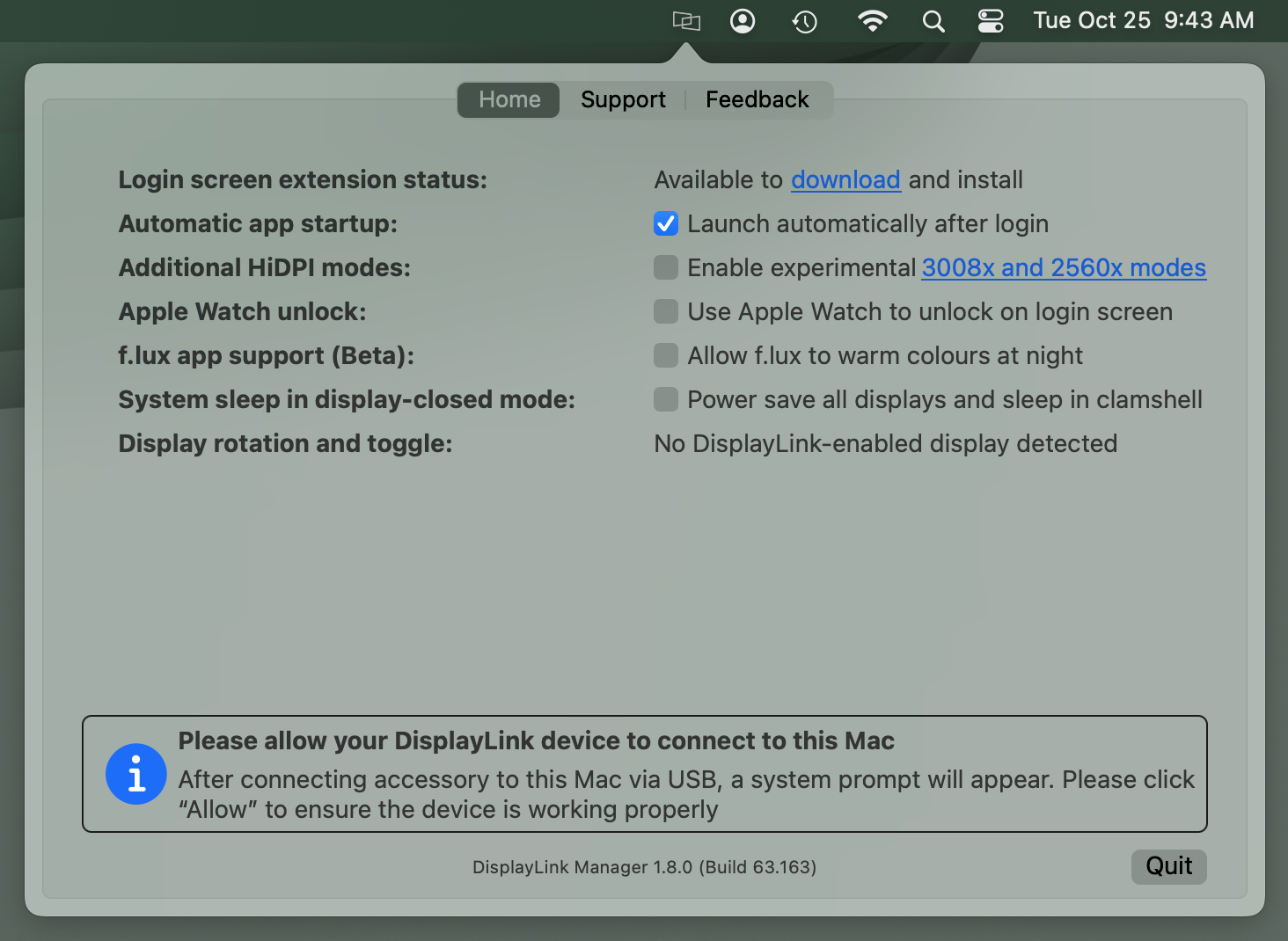
Within the ‘Home’ tab of the DisplayLink Manager Application, there are several items listed. The items listed will vary depending upon which version of the DisplayLink Manager Application that is installed and the type of processor within the host Mac (Intel processor or Apple processor).
The following list describes the features present in DisplayLink Manager version 1.8.0:
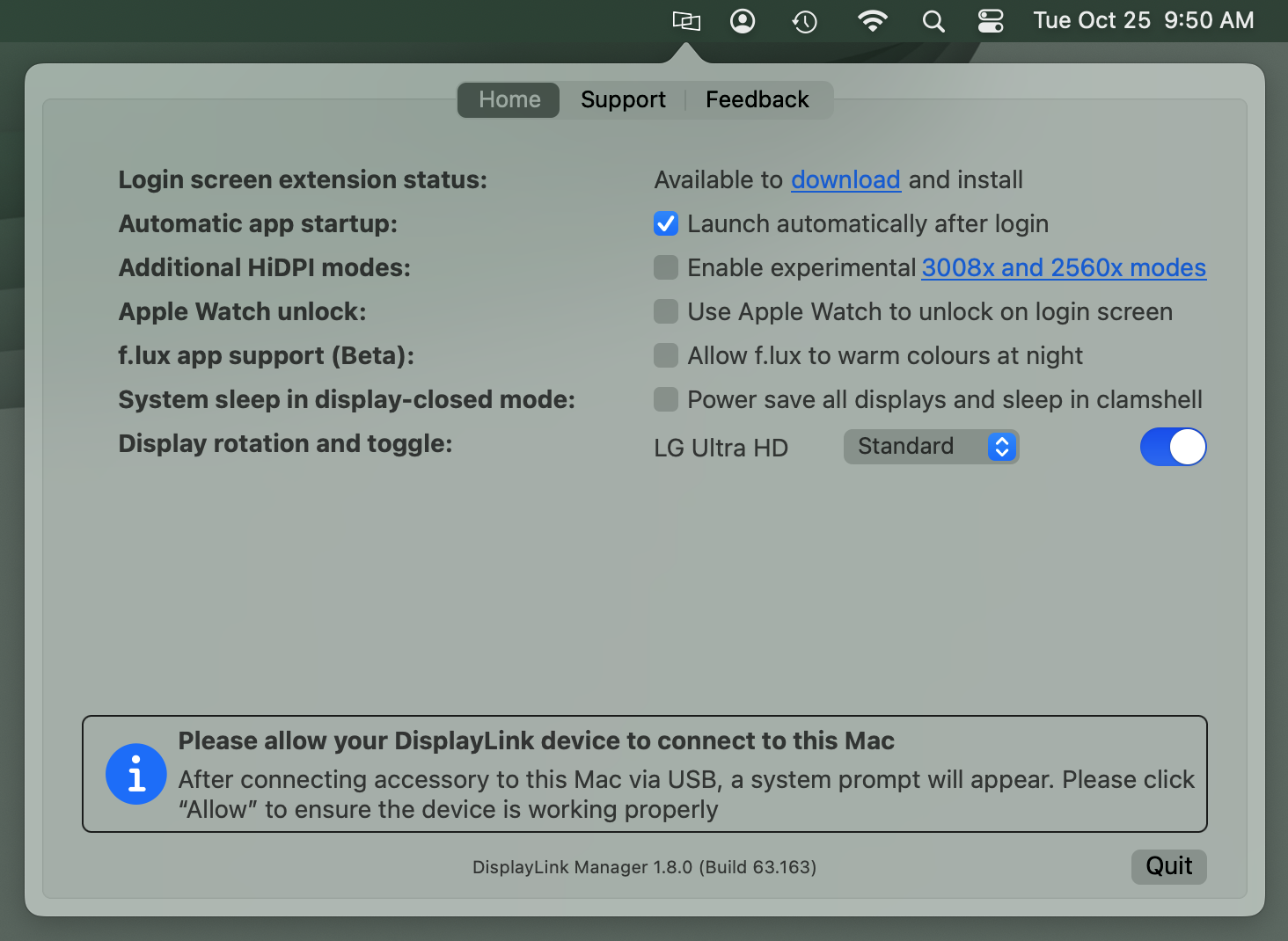
Login screen extension status
By default, the ‘Login screen extension status:’ section will display, “Available to download and Install”
When an Apple Mac system is first powered on and reaches the login prompt, 3rd-party applications (such as the DisplayLink Manager application) are not yet running. As a result, DisplayLink-connected displays will not function.
Downloading and installing the Login screen extension (available by clicking on the ‘download’ link within DisplayLink Manager) will allow the DisplayLink-connected displays to function prior to logging in.
This is of course an optional feature, and is not required to use DisplayLink devices. However, this option is useful in certain situations, such as when only DisplayLink-connected displays are connected to the host Mac.
Automatic app startup
As the name suggests, placing a checkmark next to the ‘Launch automatically after login’ option allows the DisplayLink Application to start automatically each time the system is powered on. We recommend checking this option in the interest of efficiency.
Additional HiDPI modes
In brief, HiDPI mode is a feature of macOS that can make images within a display appear sharper.
In some cases, the host Mac will not enable HiDPI mode for the displays connected to a DisplayLink-based product.
Placing a checkmark next to the ‘Enable experimental 3008x and 2560x modes’ option will create new resolution choices for the DisplayLink-connected displays within the ‘Displays’ section of the ‘System Settings’ application that may help improve the sharpness of the image.
*** Please note - This feature is experimental, and may not always work as expected. If things do not work as expected after enabling this option, please disable the option. ***
Synaptics (the creators of DisplayLink technology) have more information on this feature here --> LINK
Apple Watch unlock
As the name suggests, placing a checkmark next to the ‘Use Apple Watch to unlock on the login screen’ option will allow you to unlock your Mac using an Apple Watch while connected to a DisplayLink device.
Apple has more information on this process here → LINK
*** Please note that this feature is not compatible with screensavers. To use Apple Watch unlock with your DisplayLink device, you must disable your screensaver. ***
f.lux app support (Beta)
There is a 3rd-party application called 'f.lux' --> LINK that allows for the adjustment of a display's color according to the time of day. If the f.lux application has been installed, placing a checkmark next to the 'f.lux app support (Beta)' option will enable f.lux to change the color of a DisplayLink connected display.
A few important notes about this feature:
A. This functionality is in 'beta' status, as the label suggests. As a result, there may be cases where things may not work as expected when this option is enabled.
B. This functionality is supported with devices based on the DisplayLink DL-3xxx chipset, DL-5xxx chipset, and DL-6xxx chipset. However, it is important to note that on DL-6xxx chipsets this functionality is limited to DisplayPort video outputs only. It is NOT supported on HDMI video outputs via DL-6xxx chipsets.
System sleep in display-closed mode
Mac laptops running macOS 13 Ventura can be used in one of two ways when used in conjunction with a DisplayLink-based product.
The first way is with the laptop lid open, with the laptop's built-in internal display enabled.
The second way is with the laptop lid closed, with the laptop's built-in internal display disabled. This is known as closed display mode or 'clamshell' mode.
In order to enter closed display mode while connected to a DisplayLink-based product, the host Mac must have an external power source connected and an external keyboard and mouse connected.
Placing a checkmark next to 'Power save all displays and sleep in clamshell' changes this behavior, in that closing the laptop lid will cause the host Mac to go to sleep.
This feature is of course optional, and its use is a matter of personal preference.
Display rotation and toggle
The functionality presented within this section of the DisplayLink Manager Application will vary depending upon which type of processor is within the host Mac.
A. Macs with an Intel processor
When DisplayLink devices are used in conjunction with Apple Mac systems that have an Intel processor, a list of all the DisplayLink-connected displays will appear within this section.
The individual displays can be turned on or off as desired by clicking on the toggle switch next to each display's name. You can differentiate between each display by hovering the mouse pointer over each display name. When doing so, a red identification box will appear within the selected display.
You can rotate the orientation of the DisplayLink-connected displays within the ‘Displays’ section of the macOS ‘System Settings’ application.
B. Macs with an Apple M1 or M2 processor
When DisplayLink devices are used in conjunction with Apple Mac systems that have an Apple M1 or M2 processor, display rotation must be done from within the DisplayLink Manager Application and the host Mac must be running macOS 12 Monterey or later (display rotation is not available on M1 Macs running macOS 11 Big Sur).
Each DisplayLink-connected display attached to the M1 or M2 system will be listed next to the ‘Display rotation’ area. Click on the drop-down selection box and select the appropriate degree of rotation.
If multiple displays are present, you can differentiate between each display by hovering the mouse pointer over each display name. When doing so, a red identification box will appear within the selected display.
Synaptics (the creators of DisplayLink technology) have more information on this feature here --> LINK
In addition to the rotation aspect described above, the individual displays can be turned on or off as desired by clicking on the toggle switch next to each display's name. As mentioned above, you can differentiate between each display by hovering the mouse pointer over each display name. When doing so, a red identification box will appear within the selected display.
After updating to macOS 13 my external displays are no longer working
After updating to macOS 13, DisplayLink controlled external displays may no longer be working, this can occur with older versions of the DisplayLink Manager App installed on the computer, or if the macOS "Screen Sharing" settings have been reset. The most reliable way to resolve this is to fully remove and reinstall the DisplayLink Manager App using the latest released version compatible with macOS 13 Ventura.
Remove and reinstall DisplayLink Manager App
- Disconnect the dock from the system and please remove the power cable from the dock so it turns off completely (this is important so the unit resets). Please keep it disconnected until the last step.
- Restart the computer ( Apple Menu > Restart )
- Log into the computer and open the Finder > Go > Applications window
- Double-click on the "DisplayLink Software Uninstaller" and follow the onscreen steps to remove the DisplayLink software
- If you encounter an error where the DisplayLink Manager App is running and you cannot close it please continue with 4B-4E below:
- Open the Finder > Go > Utilities > Activity Monitor
- Scroll down and select the "DisplayLinkUserAgent" from the list
- Click on the button at the top of the screen to "Stop" the application ( an octagon with an 'x' in the center )
- Retry step #3, if it still will not uninstall: open the Applications window, then click and drag the DisplayLink Manager App to the trash
- When the software removal has completed please restart the computer ( Apple Menu > Restart )
- Log back into the computer and install the latest DisplayLink software following these detailed instructions ( https://kb.plugable.com/1595423 )
- Restart the computer when completed ( Apple Menu > Restart )
- Reattach the power cable to the dock first. Once the dock is powered on, reconnect it to your system and check for the displays and USB devices to be detected
Applies to:
- Plugable USB 3.0 Dual Display Docking Stations with DisplayLink USB Graphics Technology
- Plugable USB-C Triple Display Docking Stations with DisplayLink USB Graphics Technology
- Plugable USB 3.0 Graphics Adapters with DisplayLink USB Graphics Technology
Why doesn't streaming video play correctly when using a docking station with my Mac?
Many steaming video services require HDCP (High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection) enabled devices from the video source all the way to the display. We speak more to HDCP here (https://kb.plugable.com/en_US/docking-stations-and-video/381072-video-hdcp). The DisplayLink hardware and software used to enable multiple external displays with our docking stations requires enabling the "Screen Recording" permissions in macOS, this disables HDCP video playback system-wide.
The DisplayLink software isn't exactly recording the screen, as the setting's name suggests, instead it is rendering the external display and transmitting it as USB data to the docking station, however Apple does not have a security category for USB external displays and "Screen Recording" is the best fit.
This disables HDCP system-wide because there is no differentiation within macOS for the DisplayLink controlled external displays from the displays controlled by the internal graphics controller: the built-in LCD, or directly connected display(s).
Working around HDCP limitations:
Apple's Intel based Macs with Thunderbolt 3 can support up to two displays connected through a Thunderbolt 3 docking station, these displays do not require installing the DisplayLink Manager App and can be used for video playback.
- 13-inch MacBook Air and MacBook Pro systems with Intel processors can support up to two external displays in this configuration.
- 15-inch/16-inch MacBook Pro systems with Intel processors and AMD graphics can support up to four external displays ( two on the docking station, and two more either connected directly to the computer or with a second Thunderbolt 3 docking station ).
- iMac and Mac Mini systems with Thunderbolt 3 and Intel processors can support up to three total displays ( one built-in/HDMI, and two with the docking station ).
Apple Silicon (M1 and M2) based Macs support varying numbers of displays:
- M1 and M2 13-inch MacBook Pro and MacBook Air systems, and the M1 iMac can only support a single external display with a Thunderbolt 3 or USB-C single display docking station with HDCP video compatibility. For supporting more than one external display, DisplayLink or similar technology is required and will prevent HDCP video playback.
- M1 Mac Mini can support up to two displays, one connected to the HDMI output, the second connected to a Thunderbolt 3 or USB-C single display docking station with HDCP protected video playback enabled. For supporting more than two external displays, DisplayLink or similar technology is required and will prevent HDCP video playback.
- M1 MacBook Pro 14-inch, or 16-inch with M1 Pro or M1 Max processors can support up to two external displays with a Thunderbolt 3 docking station, or multiple displays using direct USB-C connections, with these displays supporting HDCP video playback.
Please feel free to contact our support team at 'support@plugable.com' if you have any additional questions regarding HDCP compatibility, video playback, or multiple display support with your computer.
Applies to:
Apple Mac computers with external displays connected through:
- Plugable USB-C Triple Display Docking Stations with DisplayLink USB Graphics Technology
- Plugable USB 3.0 Dual Display Docking Stations with DisplayLink USB Graphics Technology
- Plugable USB 3.0 Graphics Adapters with DisplayLink USB Graphics Technology
My external displays blink, flicker, or reset from time to time
External displays connected to our DisplayLink based docking stations or graphics adapters may intermittently "blink" off and on again, flicker, or reset - moving active windows to another display.
Common Causes
For Windows 10 and Windows 11 host computers, the most common cause is out of date graphics hardware drivers, or DisplayLink graphics software. Most Windows computers receive updated graphics drivers through Windows Update, however this often provides significantly out of date drivers, some dating back over two years, that may not be fully compatible with the installed version of Windows.
Graphics controller manufacturers provide the latest graphics drivers from their websites, these generally provide better performance, security, and compatibility than the out of date drivers from Windows Update or the system manufacturer's website.
The exception to the above is for systems with two or more active graphics controllers, for example a laptop computer may have an Intel Graphics Controller built into the processor, as well as an NVIDIA Graphics Controller with the operating system automatically switching between the two graphics controllers based on the applications running on the computer. These systems require a delicate balance between the graphics drivers for the primary and secondary graphics controllers, Windows version, and the DisplayLink software.
Determining your computer's graphics controller
Most hardware manufacturer's provide a single unified driver package for a wide range of graphics controllers, however it is best practice to ensure the drivers are compatible with the hardware. We can look up the graphics controller through Windows "msinfo32.exe" System Information application:
- Open the Start Menu
- Search for "msinfo32" then select the b est match "System Information App"
- Note the "Processor" model details in the "System Summary" section, as some graphics drivers are referenced by the processor model
- In the left pane, expand the section "System Summary > Components" and then select "Display"
- In the right pane note the value for the item "Name", this will be the graphics controller for discrete graphics controller
Updating the Graphics Drivers to the latest version
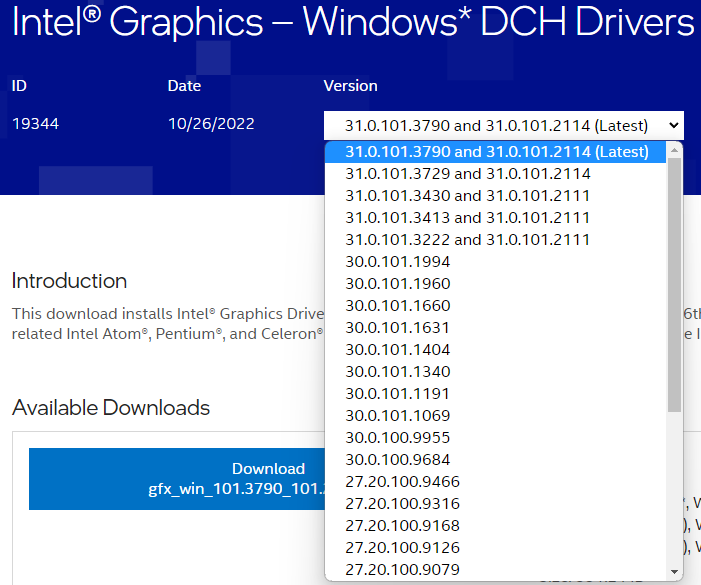
For systems with Intel Graphics Controllers
Intel uses a unified driver installer for all of their processor graphics from the 6th Generation CPU onward (Intel i-series 6000 and newer).
-
Download the latest Intel Graphics Drivers from Intel's website by selecting the blue "Download" button for the graphics driver ".exe" file (normally the top option). Save this file to the Downloads directory or Desktop
- Save and close any open applications, unplug the docking station or graphics adapter from the computer, and connect the original power supply (for laptop/notebook computers)
- Right-click on the Intel Graphics Driver package and select "Run as Administrator" from the drop down menu
- Allow the installer in the Windows User Account Control pop-up
- Follow the on screen instructions to install the latest graphics drivers
-If there is an error message while updating the graphics drivers with regard to an "OEM" or "System Manufacturer's" driver or that these drivers are incompatible with the computer, Intel provides additional details and steps to remove OEM or legacy drivers from the system - When complete, restart the computer before reconnecting the docking station or graphics adapter
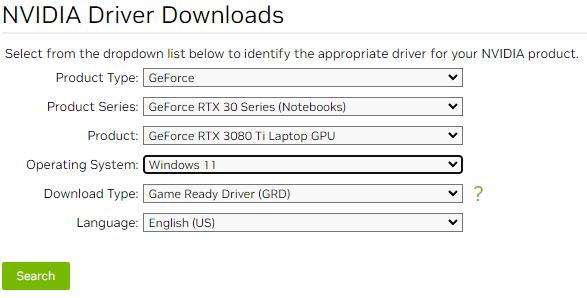
For systems with NVIDIA Graphics Controllers
NVIDIA also uses a unified driver installer for most of their discrete desktop and notebook graphics controllers.
- Locate and download the latest NVIDIA graphics driver using the graphics controller model details from msinfo32, save the file to the Downloads directory or Desktop
- Save and close any open applications, unplug the docking station or graphics adapter from the computer, and connect the original power supply (for laptop/notebook computers)
- Right-click on the NVIDIA Graphics Driver package and select "Run as Administrator" from the drop down menu
- Allow the installer in the Windows User Account Control pop-up
- Follow the on screen instructions to install the latest graphics driver, select the "Custom" or "Advanced" installation option if available, at the custom installation screen select the option to "Perform a clean installation"
- When complete, restart the computer before reconnecting the docking station or graphics adapter
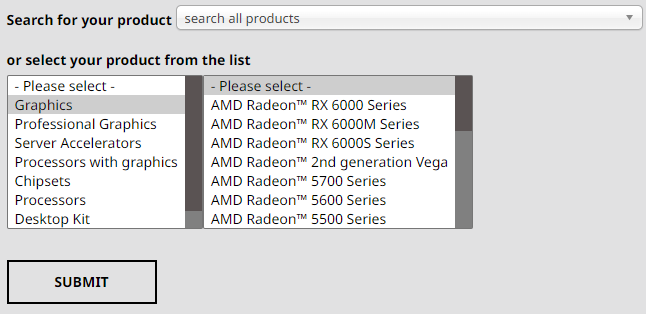
For systems with AMD Graphics Controllers
AMD also uses a unified driver installer for most of their discrete desktop and notebook graphics controllers.
- Locate and download the latest AMD graphics driver either by selecting the graphics controller or AMD processor with integrated graphics from the lists, or by searching for the specific controller or CPU from msinfo32 in the "Search All Products" drop down menu
- Save and close any open applications, unplug the docking station or graphics adapter from the computer, and connect the original power supply (for laptop/notebook computers)
- Right-click on the AMD Graphics Driver package and select "Run as Administrator" from the drop down menu
- Allow the installer in the Windows User Account Control pop-up
- Follow the on screen instructions to install the latest graphics driver
- When complete, restart the computer before reconnecting the docking station or graphics adapter
macOS login failure, or WindowServer error when using DisplayLink controlled external displays
With macOS 13.3.1 update we have started to see reports of the macOS window server crashing on Apple Silicon based computers (M1/M2 processors). Either at login if a DisplayLink based docking station or USB graphics adapter is connected to the computer, when connecting the DisplayLink controlled display to the computer after login, or when launching the DisplayLink Manager App with the external display connected to the computer.
We have seen this behavior when the macOS's display persistence files have become corrupt, or include incompatible display configurations or settings. The fix was to manually remove two display persistence ".plist" files, however now the DisplayLink Support Tool for macOS has an option to reset the display persistence to quickly resolve this behavior, the process is detailed below:
- Unplug the DisplayLink controlled external display from the computer and log into the desktop
- Download the DisplayLink Support Tool for macOS
- Select the "DisplayLink Support Tool for macOS6.3.163-EXE.zip" from the downloads to extract the "DisplayLink Information.app" to the Downloads directory, a Finder window should open showing the extracted file
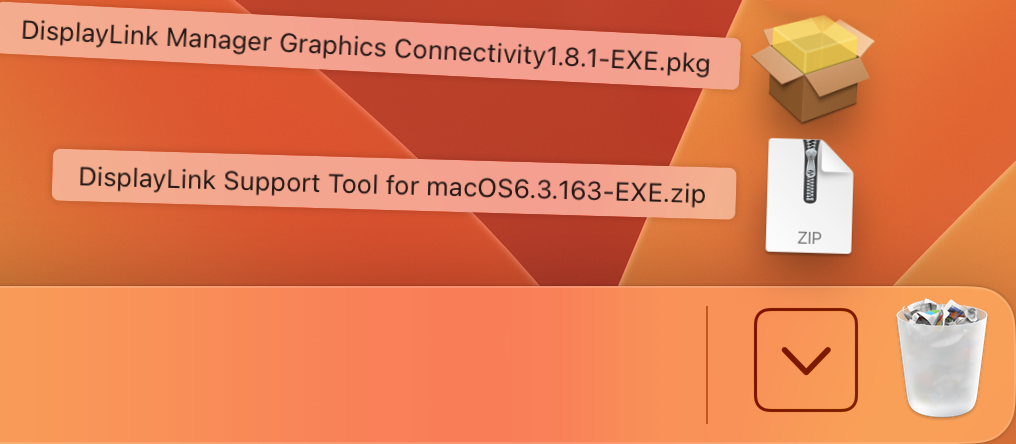
- Double-click on the "DisplayLink Information.app" from the Downloads folder to start the tool
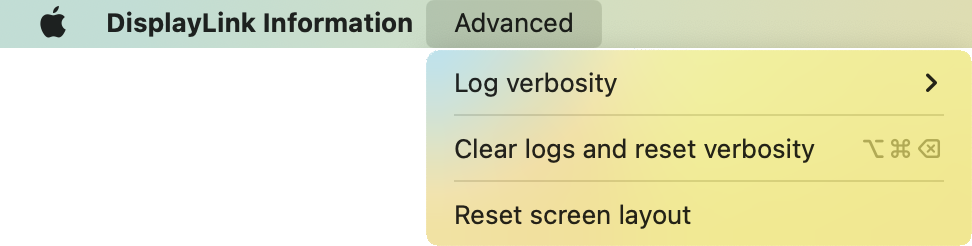
- This will open a window for the DisplayLink Information tool, however we can ignore this for now. From the macOS top bar, next to "DisplayLink Information" select "Advanced" then "Reset screen layout"
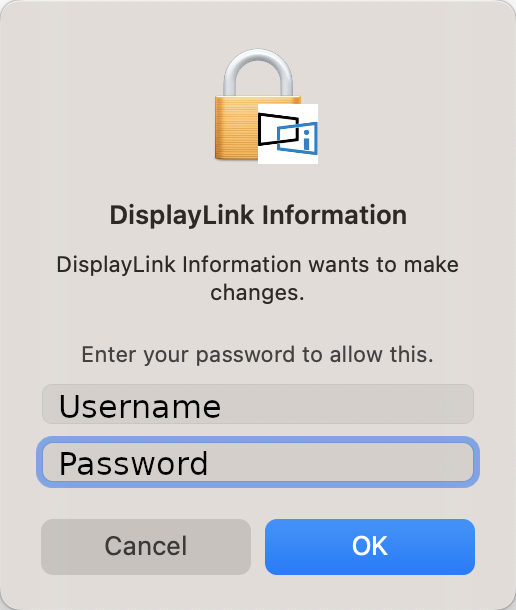
- You will be prompted for the account password to proceed, enter your password, then click the "OK" button
- Next you will be prompted to reboot the computer, save and close any open applications then click on the "Reboot" button to proceed
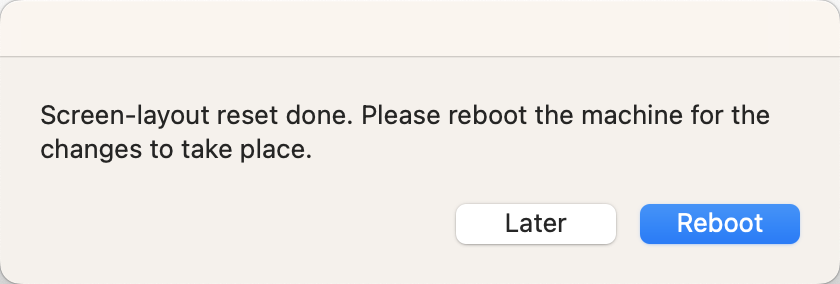
- After rebooting the computer, log into the desktop and reconnect the external display(s), you may need to rearrange the external displays through the Apple Menu > System Settings > Displays > Arrange settings panel
If you are experiencing this behavior, with the system logging in and back out, or logging out when connecting the DisplayLink based docking station or graphics adapter and the above does not help, please contact our support team via email at 'support@plugable.com' and we will be happy to help!
How to Configure/Adjust Multiple Monitors Using a Windows System
We have a produced a series of short videos that introduce the general concepts of multi-monitor setups in Windows, how to make changes to the way things behave, as well as how to solve common problems.
Direct links to the introductory videos our customers have found the most useful are:
- Introduction to Multiple Displays in Windows
- Common Multi-Monitor Problem—Spatial Orientation
- How To Make a Display the ‘Main’ Display in Windows
- Multi-Monitor Problem—Spatial Orientation Part Two
- Introduction to Display Scaling in Windows
We also maintain a playlist that contains all of the multiple monitor tutorial videos we have made .
Understanding and Troubleshooting Network Performance
Computer networking is a complex topic. In this article, we'll be taking a deep dive on the nuances of network performance for those who need some additional explanation while striving to be concise, and to educate users of various experience levels relating computer hardware and computer networking.
If you just need to know how to perform a network performance test/benchmark, jump down to configuring iPerf.
Core Network Concepts
LAN vs WAN
With regards to network performance, it is crucial to first separate whether an issue is with Wide Area Network (WAN) performance, or if the issue is with Local Area Network (LAN) performance.
Your LAN is essentially the network inside your home or business. Many homes use a combination modem/router device provided by their Internet Service Provider (ISP). In some cases, especially in businesses, you may have a separate modem and router, along with other equipment connecting to the router such as a network switch.
Your modem, and the connection it establishes to your ISP—whether through coaxial cable, fiber, phone lines, or long-range wireless—essentially marks the point between the WAN and the LAN. The connection your modem makes to your ISP is the WAN, and any devices you connect through your router behind that modem belong to the LAN.
Link Rate
Almost every type of connection your computer makes to any piece of hardware will have a link rate of some kind. The link rate establishes how fast data can possibly be transferred across any given connection, but it does not guarantee how fast the hardware on either end of the connection will actually transfer data.
The concept of link rates, and their related bottlenecks, is likely best conveyed by giving an example of what connections might be involved in transferring a file from one computer on your LAN to another.
- 800Mbps—The file source is a USB 3.0 thumb drive capable of 100MB/s (800Mbps) read/write.
- 480Mbps—The USB 3.0 thumb drive is plugged into a USB 2.0 port on the PC, which has a maximum throughput of 480Mbps
- 1000Mbps—PC1's Ethernet connection establishes 1Gbps (1000Mbps) link to the router via Ethernet
- 300Mbps—The router connects to a second PC (we'll refer to this as PC2) via Wi-Fi, and it has established a 300Mbps link to the Wi-Fi adapter on PC2
- 480Mbps—The Wi-Fi adapter on PC2 is connected via a USB 2.0 port. The link rate of the USB connection to PC2 is at 480Mbps
- 6000Mbps—PC2 is going to store the file on an internal hard drive with a link rate of 6Gbps
- 1600Mbps—File Destination: SATA hard drive capable of 200MB/s (1600Mbps) read/write.
Following this chain, we see that 300Mbps is the slowest link rate established. This means that, regardless of the link rates established elsewhere, the absolute maximum the data can possibly be transferred is 300Mbps.
if we were to change the Wi-Fi connection to a wired Ethernet connection capable of 1Gbps, our performance bottleneck would then become the USB 2.0 connection to the USB drive where the file is stored.
Ports and Interfaces
Interfaces
A network interface represents connections, whether wired or wireless, that are made to form a network between devices.
Ports
Some may refer to physical hardware connections as "ports". For the purposes of networking, ports are logical constructs that can also be referred to as "network ports". Each network interface has 65,535 of these logical ports. Each port on a network interface is a separate data connection.
Benchmarking Network Adapter Performance
To properly benchmark network adapter performance, we need to:
- Use a simple LAN configuration
- Eliminate bottlenecks, especially link rate bottlenecks
Websites like speedtest.net, fast.com, and other performance tools in your web browser are going to use your WAN connection, and are not appropriate for determining if a network adapter is working well.
Transferring files from one computer to another on your LAN is typically not the best way to benchmark a network adapter. File transfers are bottlenecked by a number of things, including performance limitations of the disk the data is on, and often times a lack of establishing parallel network connections to perform the task.
One of the most accurate ways to benchmark network performance on a LAN is by using iPerf . To more effectively benchmark network adapter performance, it is best to establish a point-to-point connection between two PCs, rather than connecting through a router or switch.
Configuring iPerf
To test a connection using iPerf, you'll need at least two network interfaces, and preferably two computers. You'll also need to know the IP (Internet Protocol) address assigned to each network interface . One network interface will function as an iPerf server, and the other network interface will function as an iPerf client. Lastly, you'll need to download the version of iPerf 3.x that's appropriate for your computer's operating system and extract/install it .
Windows
- Make sure the drivers for both network interfaces involved in the test are using up-to-date drivers. Drivers for Plugable products can be found here.
- Download and extract iPerf for Windows
- Open Command Prompt
- Press Windows Key + R or + R, then enter
cmdin the window that appears - Search the Start Menu for
Command Prompt, and open it
- Press Windows Key + R or + R, then enter
- Navigate Command Prompt to the directory the directory where iPerf is located
- The
cdcommand is for 'change directory'- If you have a folder named 'iperf' on your Windows desktop, you can reach it in command prompt with the command
cd %USERPROFILE%\Desktop\iperf
- If you have a folder named 'iperf' on your Windows desktop, you can reach it in command prompt with the command
- The
- Run iperf in server mode via Command Prompt
iperf3.exe -s
macOS
- Usually it is best to install iperf on macOS using brew in Terminal
- Make sure the drivers for both network interfaces involved in the test are using up-to-date drivers
- Open Terminal
- Run iPerf in server mode
iperf3 -s
Linux
- Usually it is best to install iperf using the package manager in your Linux distro. For example, in Ubuntu, use
apt: sudo apt install iperf3
- Make sure the drivers for both network interfaces involved in the test are using up-to-date Drivers
- Open Terminal
- Run iPerf in server mode
iperf3 -s
Next, you'll need to run iPerf in client mode, targeting the IP address of the server/interface where iPerf is running in server mode. Additionally, we'll run the test for 30 seconds using -t 30 and with four parallel connections using -P 4. Running 4 parallel connections is optimal for saturating a network link.
Windows
- Open Command Prompt
- Press Windows Key + R or + R, then enter
cmdin the window that appears - Search the Start Menu for
Command Prompt, and open it
- Press Windows Key + R or + R, then enter
- Navigate Command Prompt to the directory the directory where iPerf is located
- The
cdcommand is for 'change directory'- If you have a folder named 'iperf' on your Windows desktop, you can reach it in command prompt with the command
cd %USERPROFILE%\Desktop\iperf
- If you have a folder named 'iperf' on your Windows desktop, you can reach it in command prompt with the command
- The
- Run iperf in client mode via Command Prompt (replace 192.168.0.200 with the IP address of the server/interface where iPerf is running in server mode)
iperf3.exe -c 192.168.0.200 -t 30 -P 4
macOS / Linux
- Open Terminal
- Run iPerf in client mode (replace 192.168.0.200 with the IP address of the server/interface where iPerf is running in server mode)
iperf3 -c 192.168.0.200 -t 30 -P 4
iPerf should start performing a network performance test. If the test fails to start, make sure that iPerf is not being blocked by your PC's/Mac's firewall.
Why iPerf is Ideal for Benchmarking
Unlike a file transfer, iPerf runs in memory on the PC and generates data to send using the CPU directly. This alleviates potential bottlenecks generated by storage devices, and allows you to explicitly control how many parallel connections are being used to transfer data rather than being unsure if parallel network connections are being used by other means.
Conclusion
There's a lot more to networking that isn't covered in this article, but we hope this helps explain enough to get an accurate measure of your network performance.
If you need assistance with your Plugable product that features network connectivity, please contact us for further assistance.
No Sound? How to Change Your Default Audio Device to Your Plugable Product
Whether you're on Windows, macOS, or Linux, it's common to add new audio devices to your computer.
Some examples of additional audio devices you may want to switch to include:
- Bluetooth headsets, headphones, and speakers
- Speakers built into a display, such as a TV or monitor
- A USB sound card, digital audio converter (DAC), or analog to digital converter (ADC)
- USB microphones
- Audio jacks on a docking station
These steps don't apply to the Plugable Performance NIX HDMI Capture Card (USBC-CAP60).
Here are the steps that you need to set a new default audio recording or output device on different operating systems.
Set Audio Output Device
Set Audio Recording Device
Set Default Playback Device in Windows
- Check that your device is properly connected, and that any necessary drivers are installed
- It is also a good idea to make sure that your sound device is turned on, and that the device's volume control is not at the absolute minimum setting
- Right-click on the speaker symbol in the Windows taskbar/system tray
-
Windows 7/8.x—Select Playback Devices. The Sound window will open with the Playback tab highlighted
-
Windows 10/11—Select Open Sound Settings then click the link under 'Related Settings' for Sound Control Panel, then click the Playback tab
- Alternatively, after selecting Open Sound Settings, use the dropdowns under the Output header
-
Windows 7/8.x—Select Playback Devices. The Sound window will open with the Playback tab highlighted
- Find your device in the window
- A Plugable USB 3.0 docking station or sound-enabled display adapter will appear as Plugable Audio
- A Plugable USB 3.0 Silicon Motion docking station or sound-enabled display adapter will appear as SMI USB Audio
- A Plugable USB 2.0 docking station will appear as USB Multimedia Audio Device
- A Plugable USB Audio adapter will appear as USB Audio Device
- Right-click on the device you found in step 3 and select Set as Default Device. A check mark should appear next to your device, and sound should now play through it
- Click OK to exit the window
Additional Configuration for Bluetooth
Please see our pairing and configuration guide for Bluetooth devices.
Set Default Playback Device in macOS
- Open System Preferences
- Click Sound
- Select Output
- Select the most appropriate device
- A Plugable USB Audio adapter will appear as USB Audio Device
Set Default Playback Device in Linux
- Ensure that you audio device is connected to the PC
- If the audio device is self-powered, it is a good idea to make sure that it is powered on, and that the device's volume control is not at the absolute minimum setting
- Launch the 'Settings' application in your distro
- Go to the 'Sound' option
- Find the dropdown for your 'Output Device', and change it to your preferred output device
- For additional sound device controls, you may want to consider using Pulseaudio Volume Controls (package name pavucontrol)
Set Default Recording Device in Windows
- Check that your device is properly connected, and that any necessary drivers are installed
- It is also a good idea to make sure that your sound device is turned on, and that the device's volume control is not at the absolute minimum setting
- Right-click on the speaker symbol in the Windows taskbar/system tray
-
Windows 7/8.x—Select Recording Devices. The Sound window will open with the Recording tab highlighted

-
Windows 10/11—Select Open Sound Settings then click the link under 'Related Settings' for Sound Control Panel, then click the Recording tab

- Alternatively, after selecting Open Sound Settings, use the dropdowns under the Input header
-
Windows 7/8.x—Select Recording Devices. The Sound window will open with the Recording tab highlighted
- Find your device in the window
- A Plugable USB 3.0 DisplayLink docking station or sound-enabled display adapter will appear as Plugable Audio
- A Plugable USB 2.0 docking station will appear as USB Multimedia Audio Device
- A Plugable USB Audio adapter will appear as USB Audio Device
- Right-click on the device you found in step 3 and select Set as Default Device. A check mark should appear next to your device, and sound should now play through it
- Click OK to exit the window
Additional Configuration for Bluetooth
Please see our pairing and configuration guide for Bluetooth devices.
Set Default Recording Device in macOS
- Open System Preferences
- Click Sound
- Select Input
- Select the most appropriate device
- A Plugable USB Audio adapter will appear as USB Audio Device
Set Default Recording Device in Linux
- Ensure that you audio device is connected to the PC
- If the audio device is self-powered, it is a good idea to make sure that it is powered on, and that the device's volume control is not at the absolute minimum setting
- Launch the 'Settings' application in your distro
- Go to the 'Sound' option
- Find the dropdown for your 'Input Device', and change it to your preferred input device
- For additional sound device controls, you may want to consider using Pulseaudio Volume Controls (package name pavucontrol)
Why Isn’t My Plugable Dock Charging My Laptop?
Please note that not all USB-C ports on a computer support charging. Verify if your computer supports Power Delivery (PD) over USB-C and also identify which port has this functionality (if multiple USB-C ports are available).
Otherwise, please check that the docking station is powered on. Depending on the model of the dock, you should see a blue or white light which indicates the dock is powered.
Please contact us at support@plugable.com for further assistance.
My Docking Station/Adapter Works Well With My Windows Laptop, but When I Close the Lid the Displays and Laptop Turn Off or Sleep. How Do I Fix This?
Most Windows notebook computers power management settings will default to putting the computer to sleep with the lid closed, regardless of any external displays, keyboard, or mouse connected to the computer. If this is happening but you would prefer the system to remain active with the lid closed utilizing the external display or displays, these settings can be changed by performing the following:
For Windows 10:
- Start by right-clicking on the Start button and select Power Options from the menu.
- From the right side of the Power Options settings page, select the blue link for Additional power settings
- From the choices present on the left-hand side of the Power Options window, please click on Choose what closing the lid does
- Make sure the setting for When I close the lid under the Plugged In column is set to Do Nothing
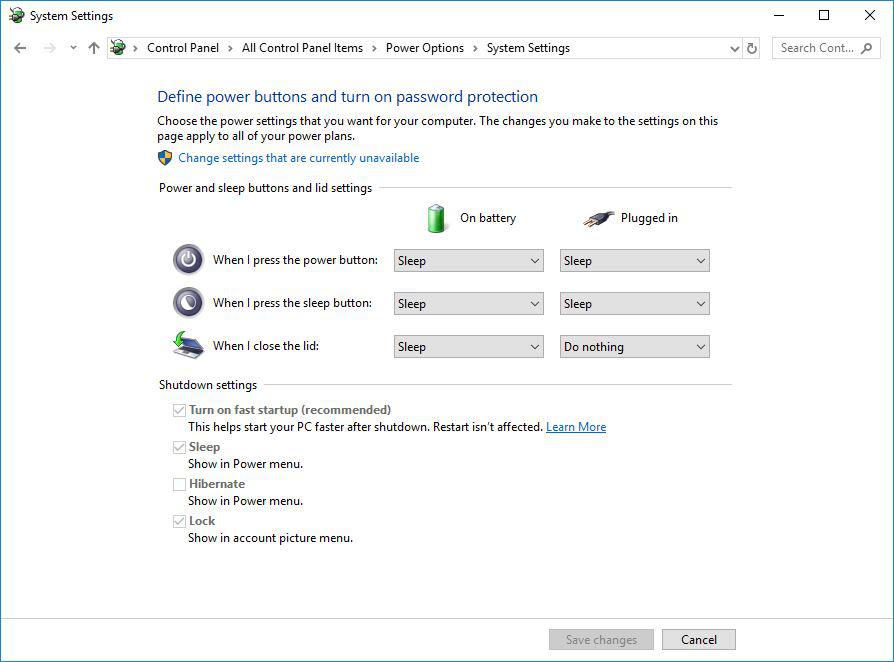
- Click the Save Changes button and restart the system (making sure that the laptop’s power adapter is also connected) and test the behavior again.
For Windows 11:
- Start by right-clicking on the Start button and select Power Options from the menu.

- In the upper left corner of the settings window, in the search box, type "lid" then select Change what closing the lid does from the search results
- Make sure the setting for When I close the lid under the Plugged In column is set to Do Nothing
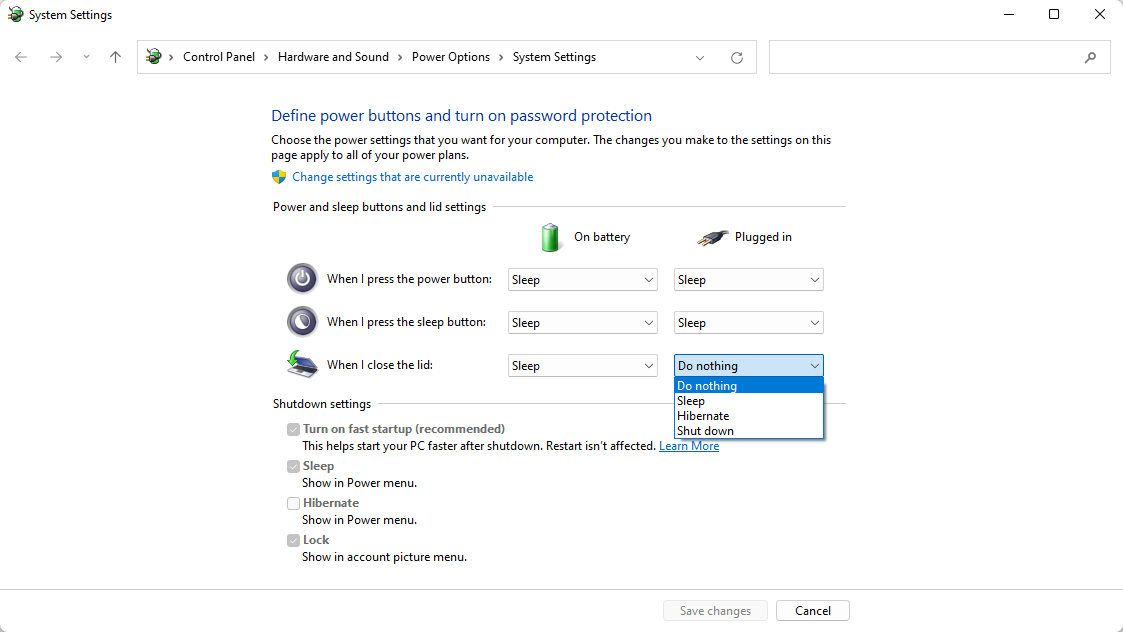
- Click the Save Changes button to apply the new settings.
Closing the lid should no longer put the computer into sleep mode when an external display and power source is connected, instead one of the external displays should now become the Primary display with the desktop icons instead of the laptop's built-in display.
The lid may still need to be opened to perform the following tasks:
- To power on the computer from a fully powered off state
- To log into the computer if logged out or if the computer is restarted with the lid closed
- To wake the computer from a deep sleep state ( hibernation, or Windows hybrid sleep states )
Legacy macOS DisplayLink Driver Installation Instructions for macOS 10.14 Mojave or 10.15 Catalina
Unsure which version of macOS you have installed? Click on the ‘Apple’ icon in the menu bar on your desktop and select ‘About this Mac’. A new window will open and display the system’s macOS version.
'Legacy' DisplayLink Driver installation for macOS 10.15 Catalina
We also have a video that demonstrates this process here –> https://youtu.be/ixWKrd5SLKs
Before you begin
If have installed a previous version of the DisplayLink driver, please uninstall it and then reboot your system before proceeding.
1. Download the latest driver for macOS 10.15 Catalina from here -> Link
2. Navigate to your Downloads folder and double-click on the DisplayLink driver download
3, The disk image of the driver will mount, and automatically open the DisplayLink Installer main landing page.

4. Double-click on the ‘DisplayLink Software Installer.pkg’ file. The Install DisplayLink Driver page will open.
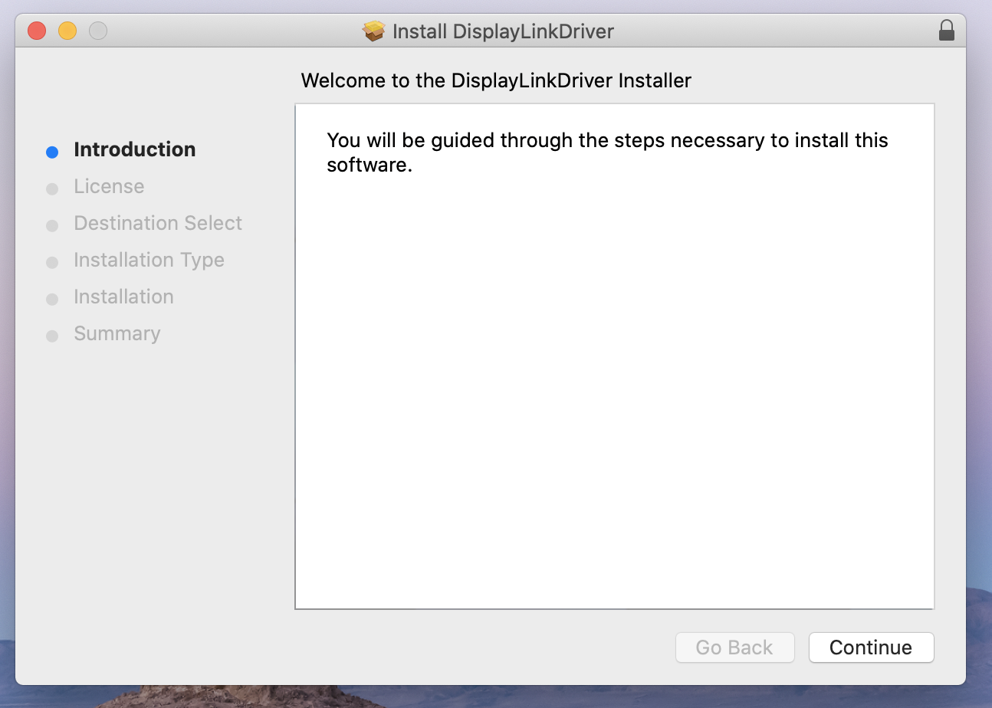
*** Depending on your system’s security settings, the installer may not open and instead present you with a warning ***
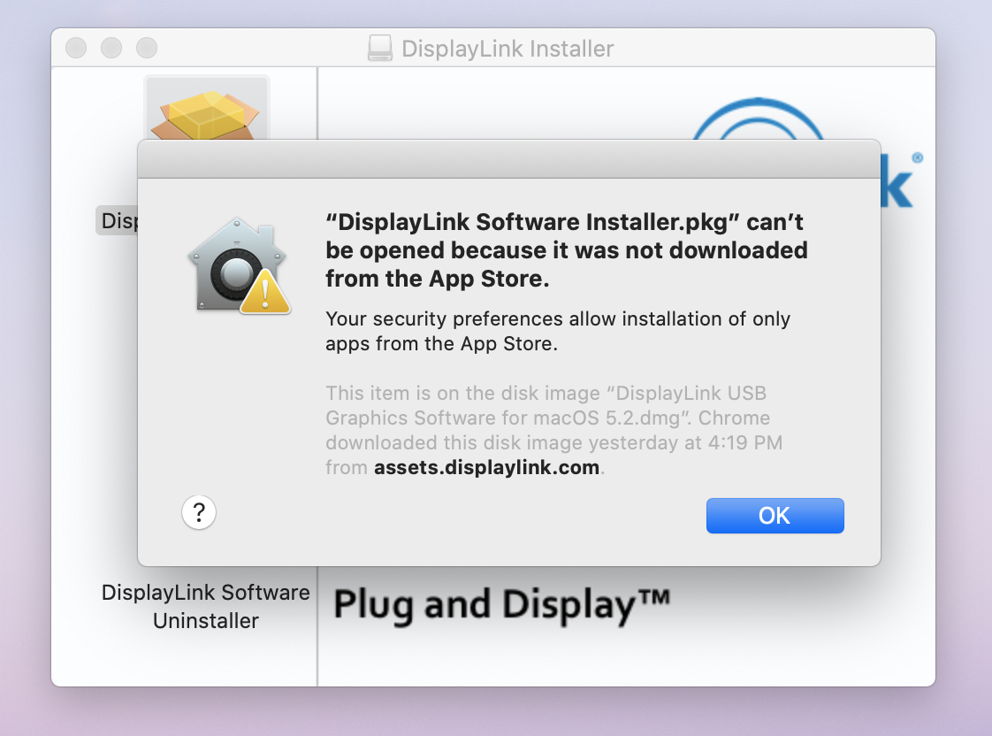
Click on the ‘OK’ button to dismiss the warning, and then open ‘System Preferences’ (gear icon) and then open the ‘Security & Privacy’ application.
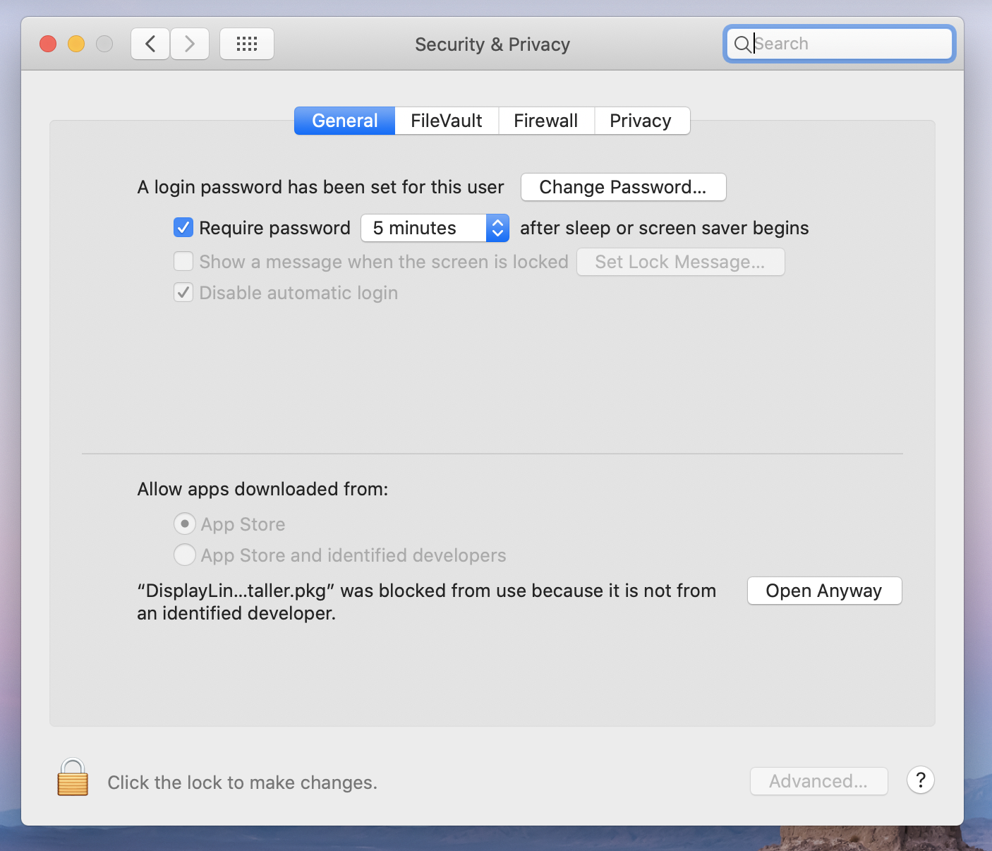
Click on the ‘Open Anyway’ button in the lower right-hand portion of the application window. Then click the ‘Open’ button within the next prompt.
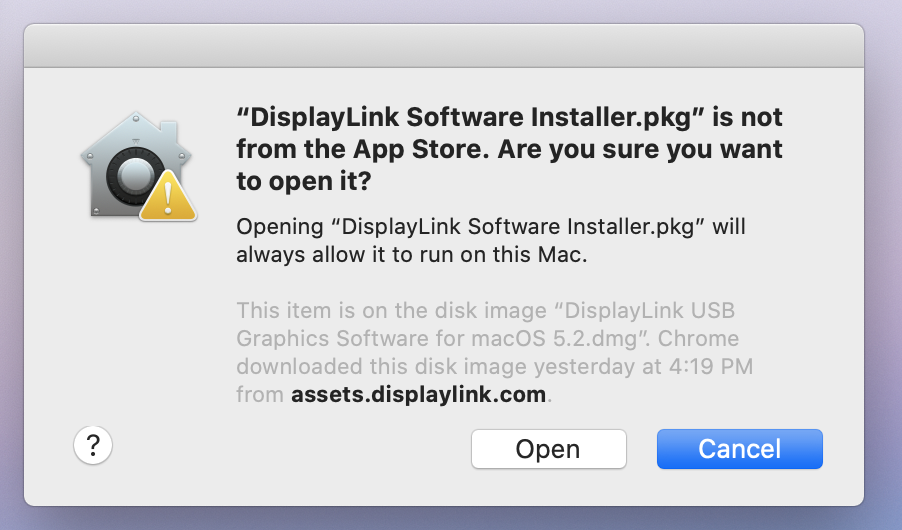
5. Click the ‘Continue’ button shown within the installer’s ‘Introduction’ screen.

6. Click the ‘Agree’ button to accept the license.
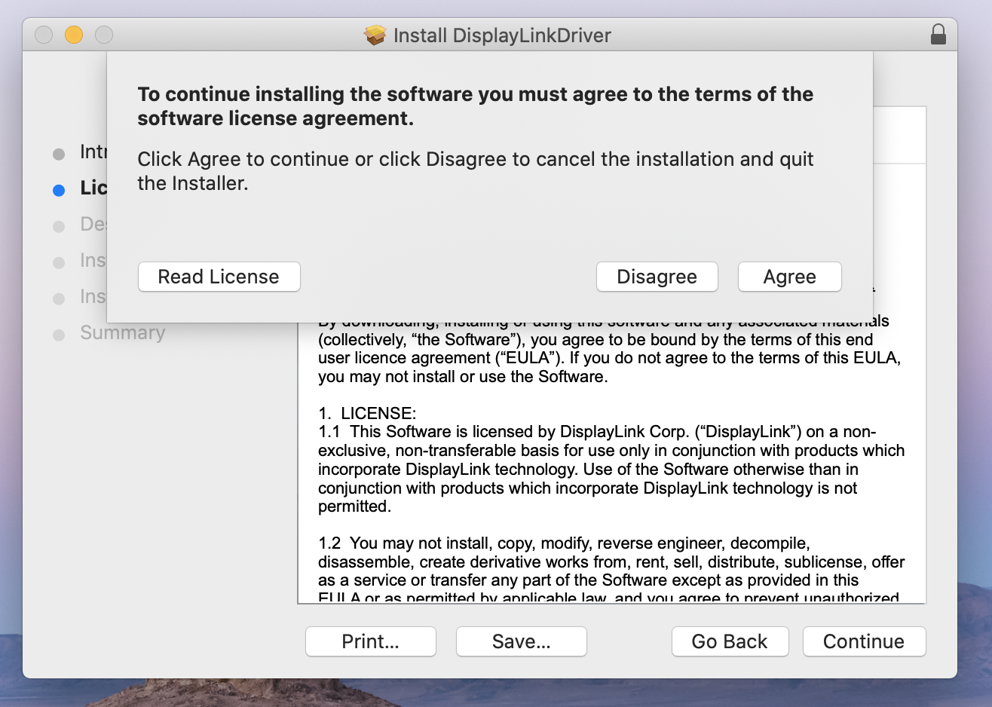
7. Click the ‘Install’ button.
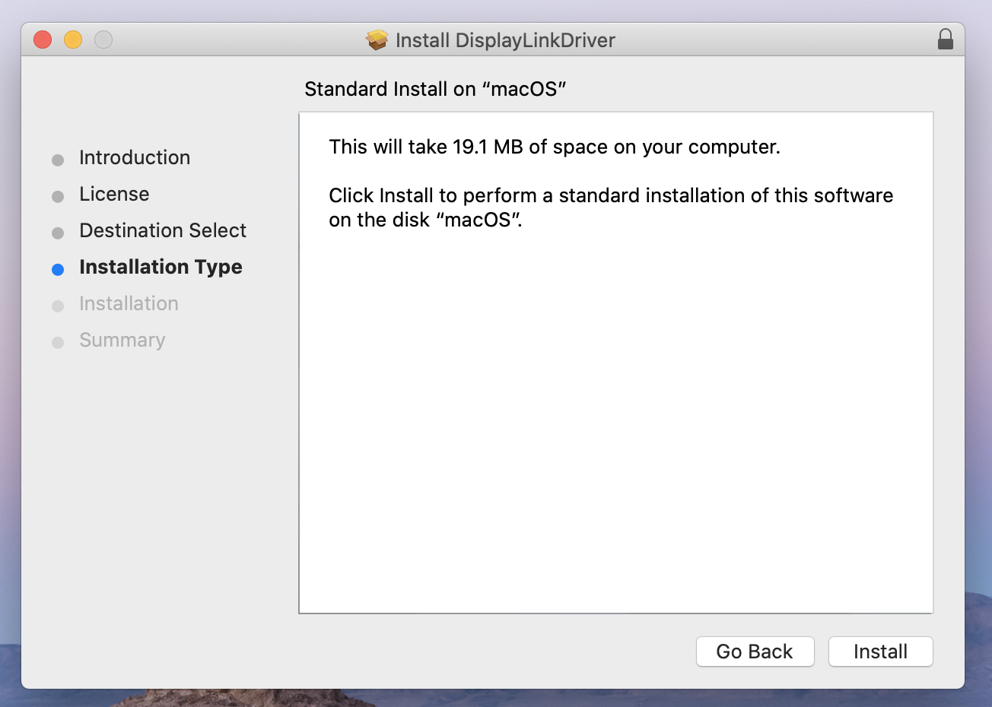
8. Click the ‘Continue Installation’ button. The system will need to be restarted when the installation is complete.
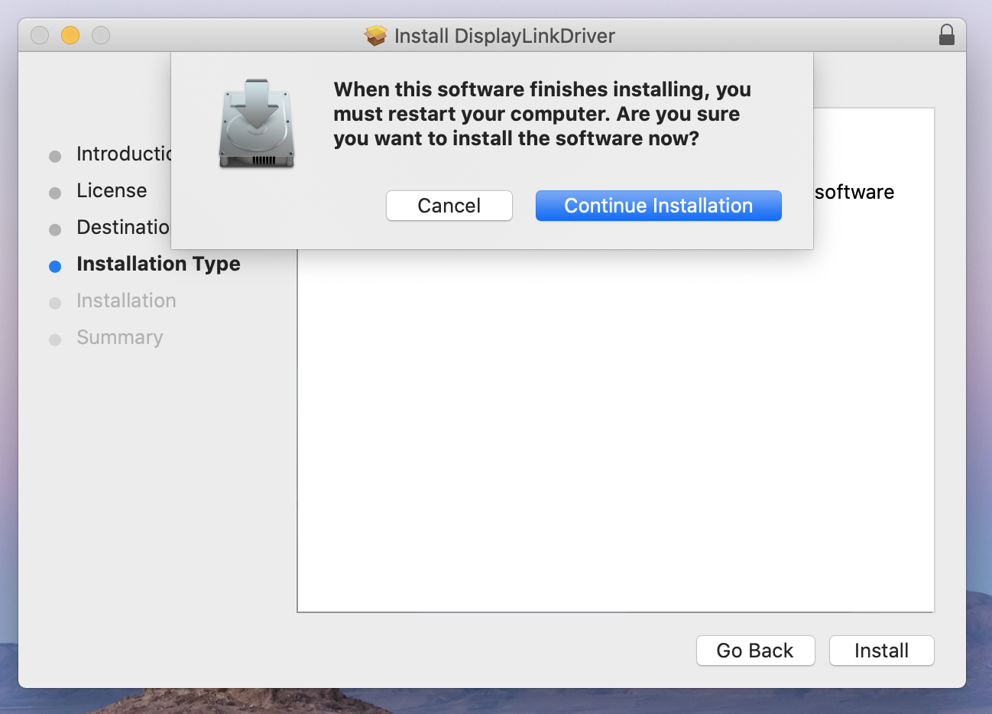
9. Enter your system password and click the ‘Install Software’ button.
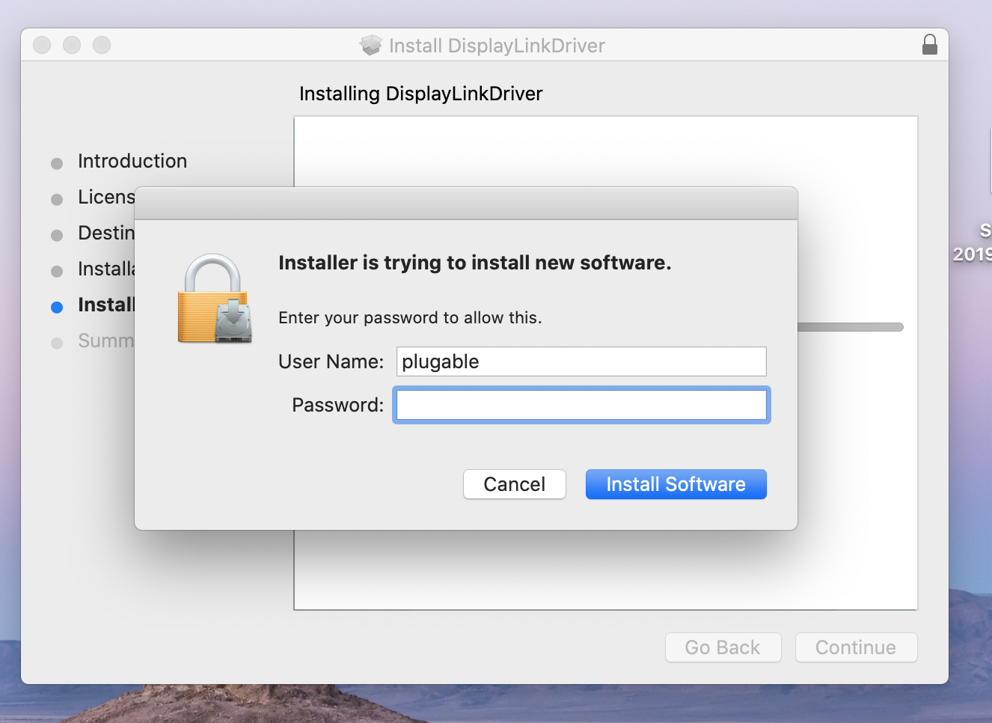
10. After a few moments, the installer should report a successful installation.
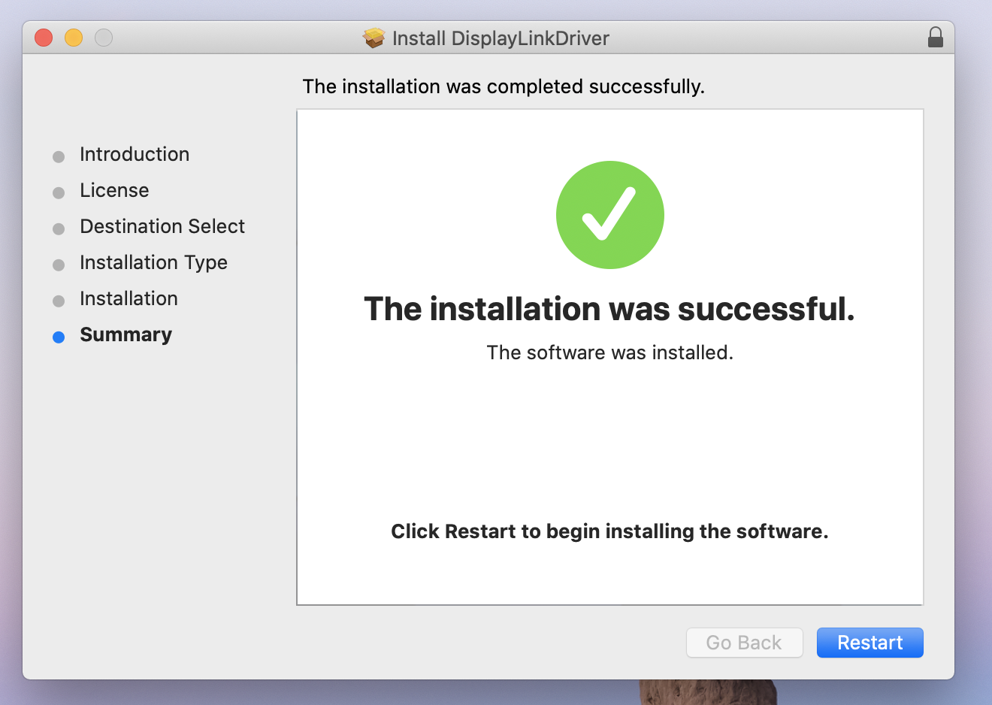
11. The system should also prompt you to access the System Preferences to grant necessary permissions to the DisplayLink driver. Click on the ‘Open System Preferences’ button.
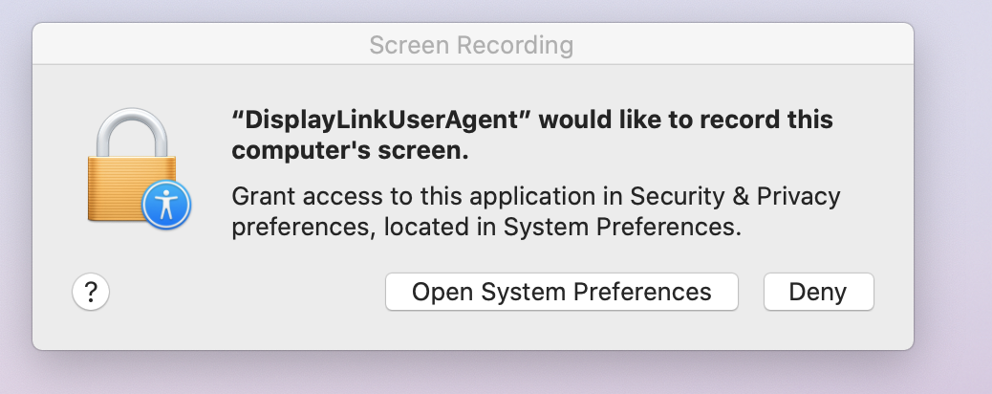
*** If the prompt described above did not appear automatically, manually open the ‘System Preferences’ application (gear icon in the macOS dock at the bottom of the screen) and select the ‘Security & Privacy’ application. Within the ‘Security & Privacy’ application click on the ‘Privacy’ tab. Scroll down in the list of items on the left-hand side of the application window and click to select ‘Screen Recording’. The proceed to the next step ***
12. The ‘Security & Privacy’ application should open and default to showing the ‘Privacy’ tab. On the right-hand side of the application window there should be a single entry entitled, ‘DisplayLinkUserAgent’. Click to place a checkmark next to this entry.
*** Important note – the contents of your screens (displays) are not being recorded. This setting just enables the DisplayLink driver to access the information generated by the system’s built-in graphics adapter to generate the image shown on the DisplayLink-connected displays. ***
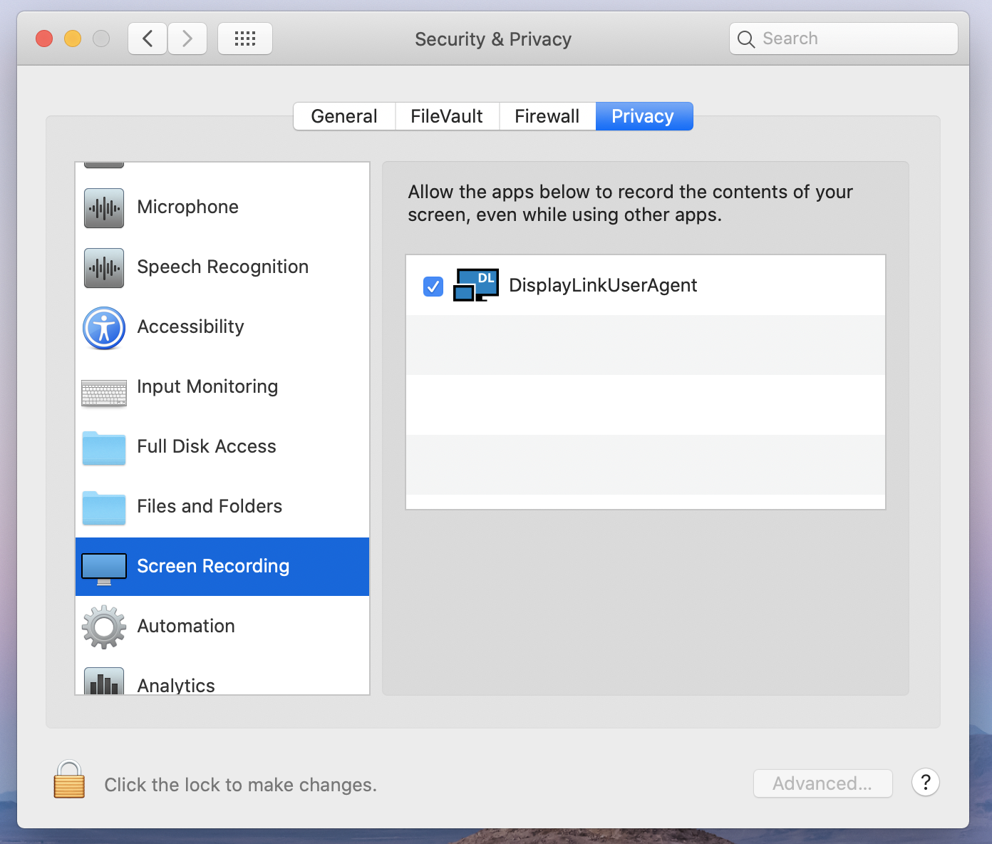
13. After having placed a checkmark next to the ‘DisplayLinkUserAgent’ entry, click the ‘Quit Now’ button in the prompt that appears.
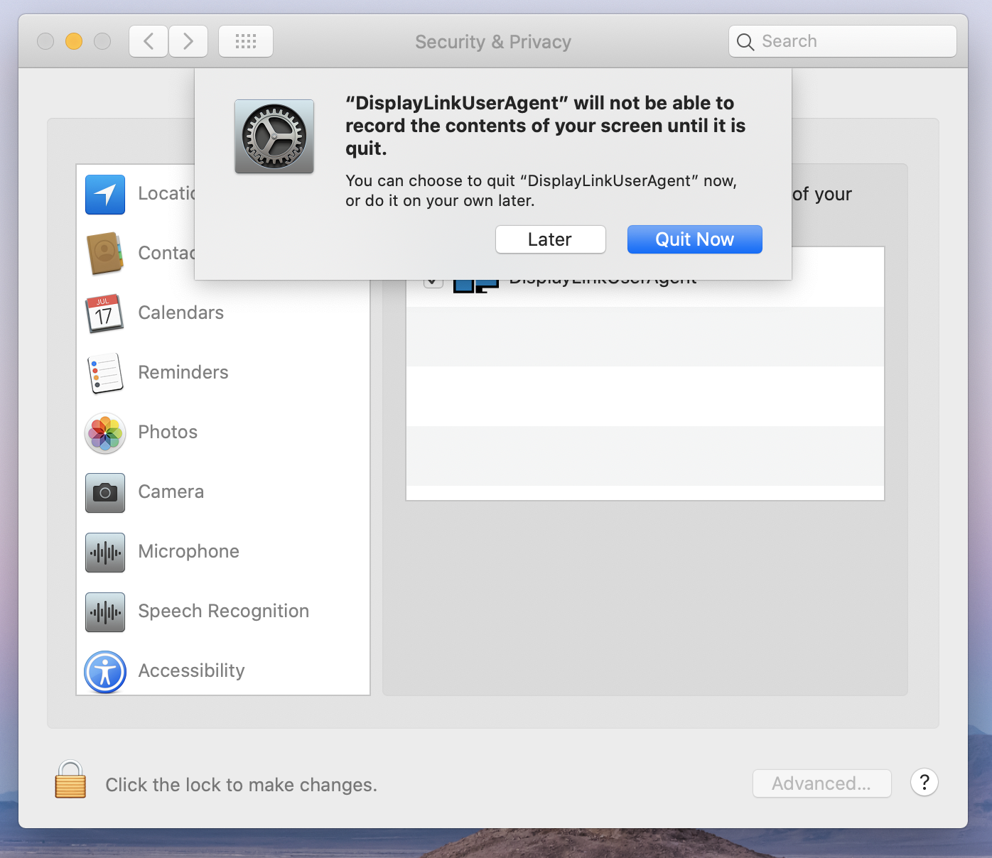
14. Close the ‘Security & Privacy’ application, and then restart your system. The DisplayLink device should start working after the restart is complete.
'Legacy' DisplayLink Driver installation for macOS 10.14 Mojave
** Before you begin **
If have installed a previous version of the DisplayLink driver, please uninstall it and then reboot your system before proceeding.
1. Download the latest driver for macOS 10.14 Mojave from here -> Link
2. Navigate to your Downloads folder and double-click on the DisplayLink driver download
3. The disk image of the driver will mount, and automatically open the DisplayLink Installer main landing page

4. Double-click on the ‘DisplayLink Software Installer.pkg’ file. The Install DisplayLink Driver page will open
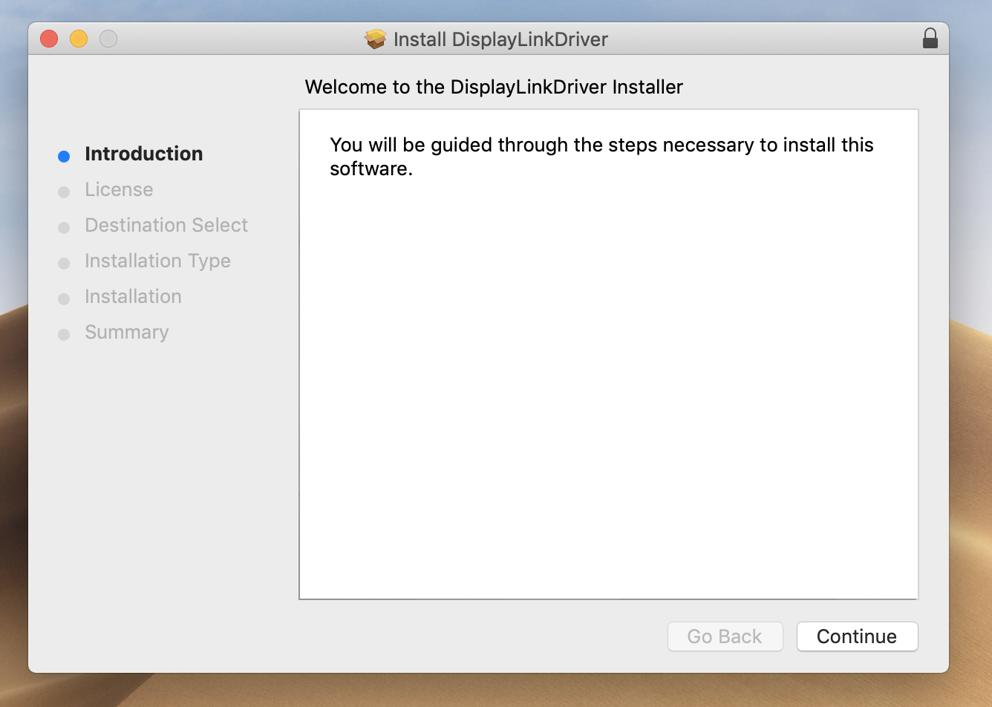
5. Click ‘Continue’
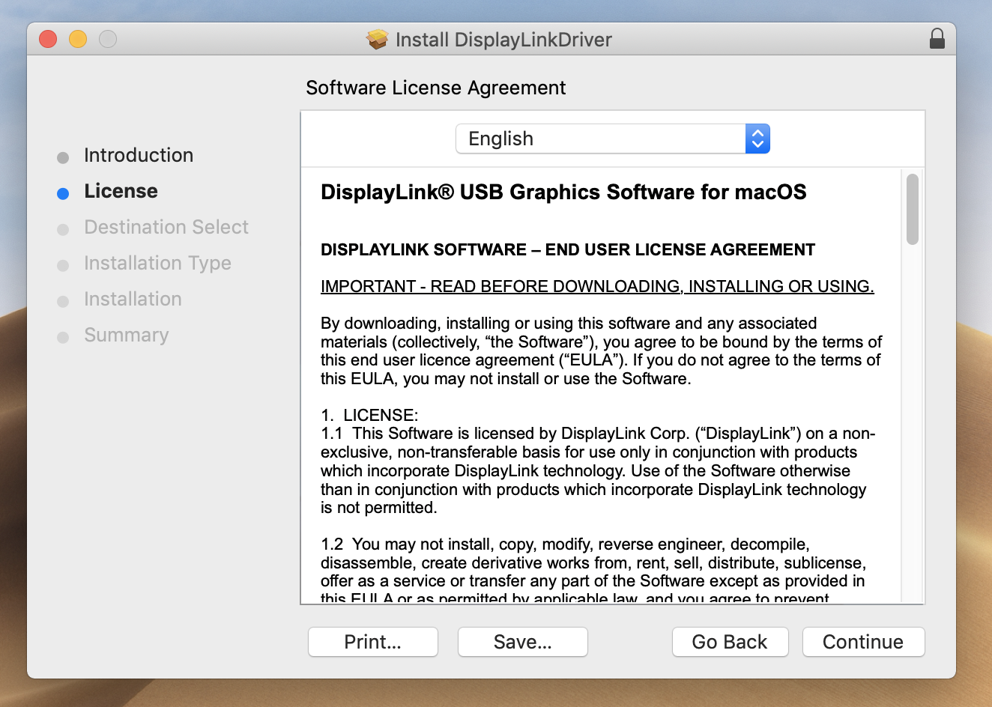
6. Click the ‘Agree’ button
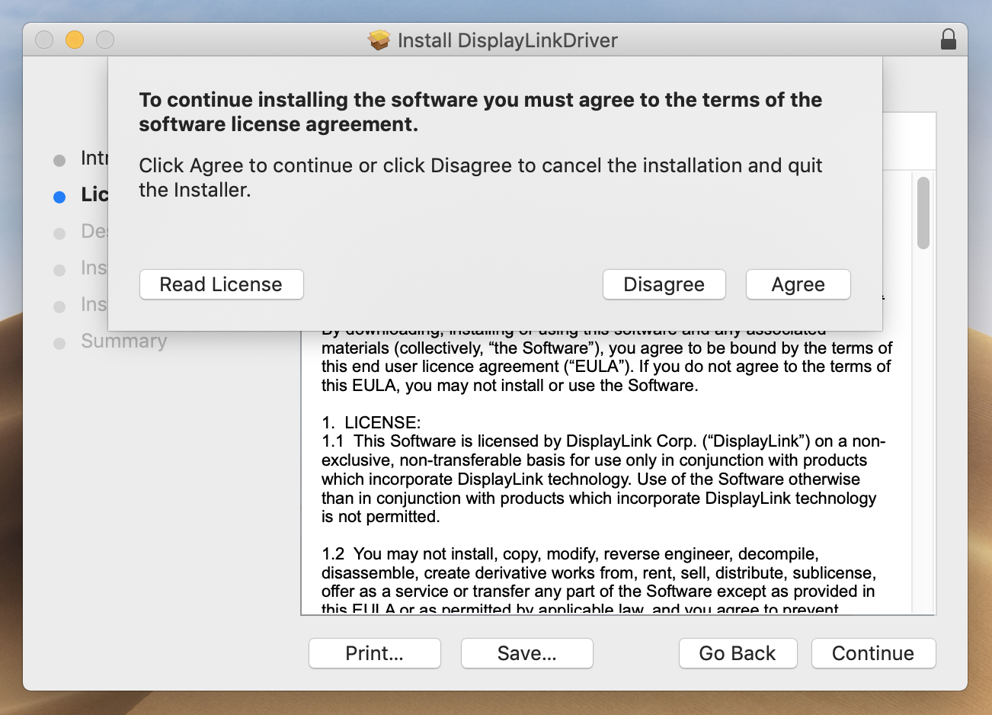
7. Click ‘Install’
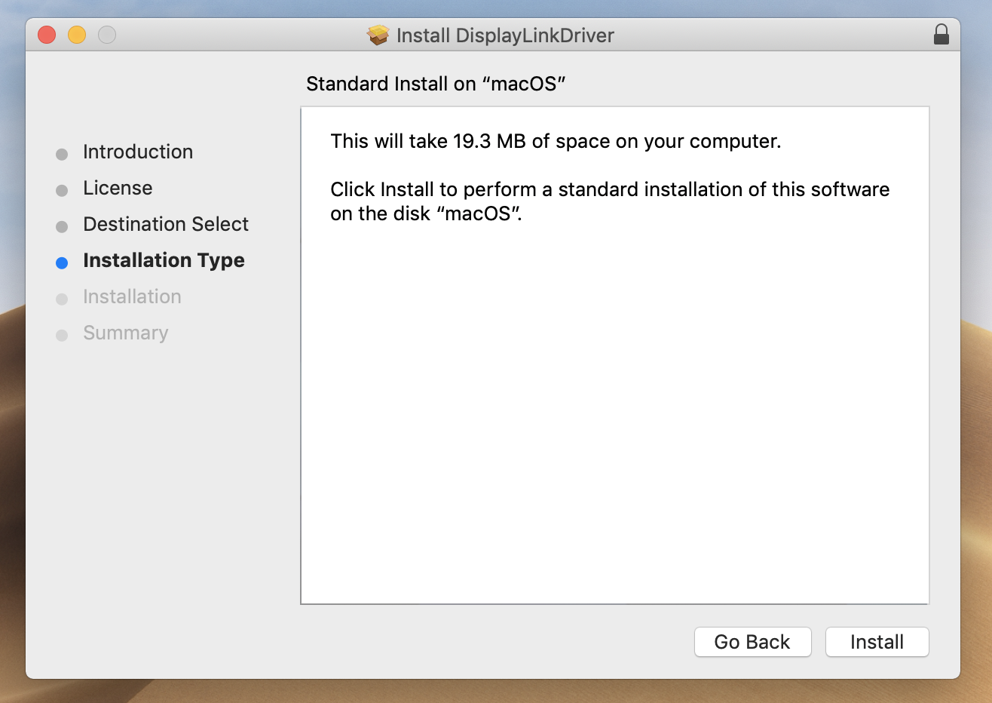
8. Click ‘Continue Installation’ The system will need to be restarted when the installation is complete
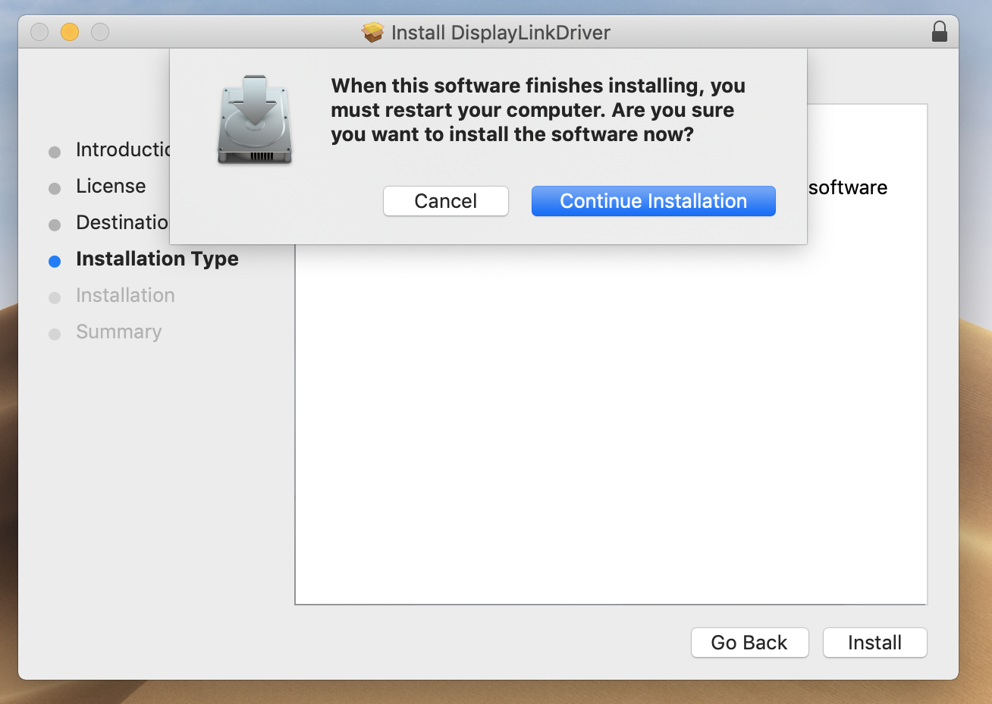
9. Enter your system password and click the ‘Install Software’ button
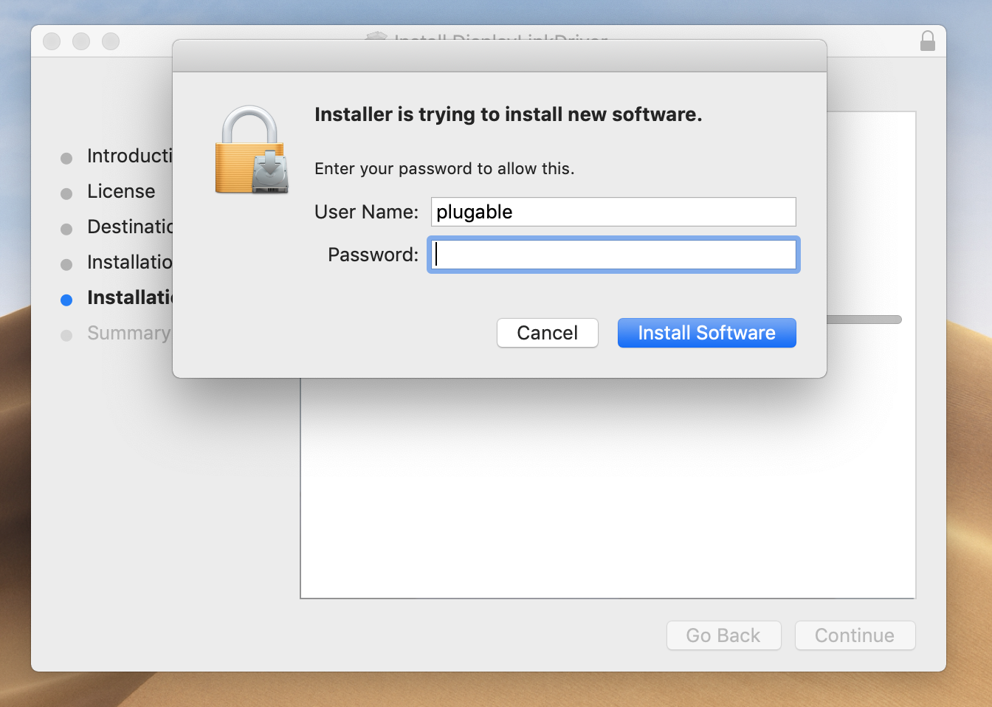
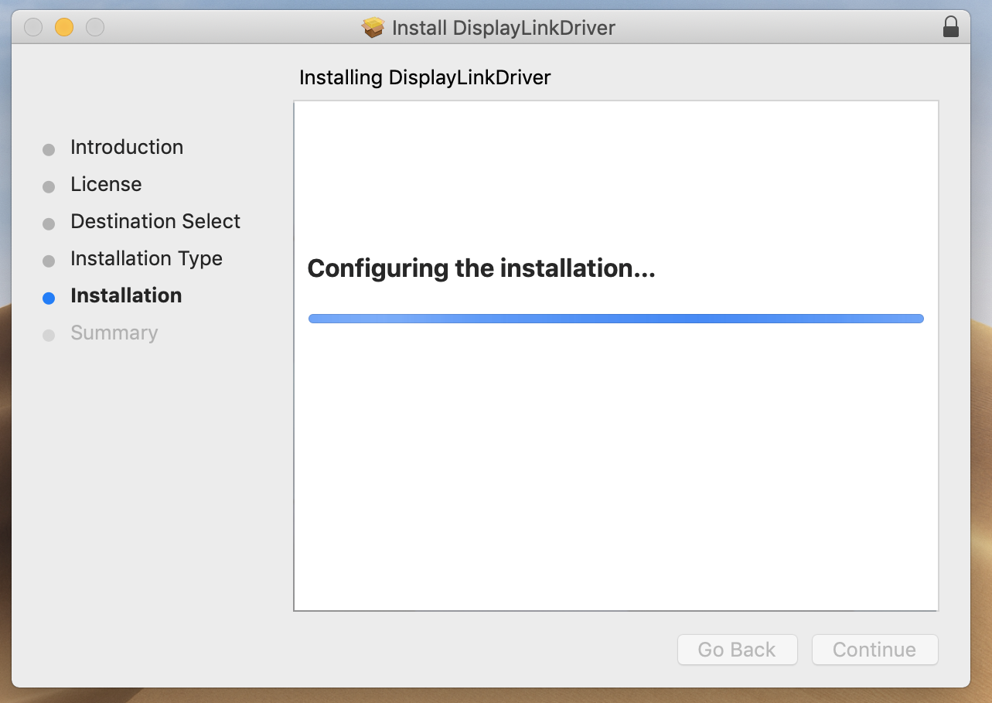
10. There is a chance that the security settings in macOS may block the installation of the DisplayLink extension
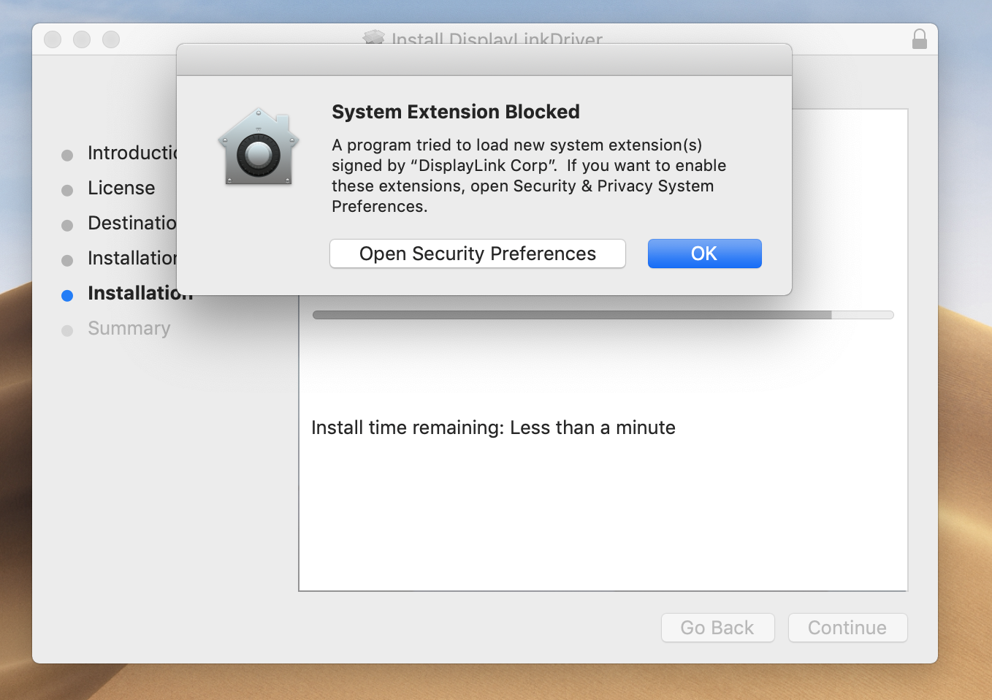
11. If that occurs, click on the ‘Open Security Preferences’ button and click the ‘Allow’ button at the bottom of the window to grant permission for the extension to be loaded. ** Important note – this approval must be granted within 30 minutes of the driver installation or the process will not work. A fresh installation must be performed to reset this timer. **
There is also a chance that the warning message about the blocked System Extension will not appear, but macOS may still block the extension. After the driver installation completes, please double-check that the necessary approval was granted by clicking the ‘System Preferences’ icon (the gear) and then clicking on the ‘Security & Privacy’ icon. From the window that appears please ensure the DisplayLink driver is Approved by clicking the ‘Allow’ button.
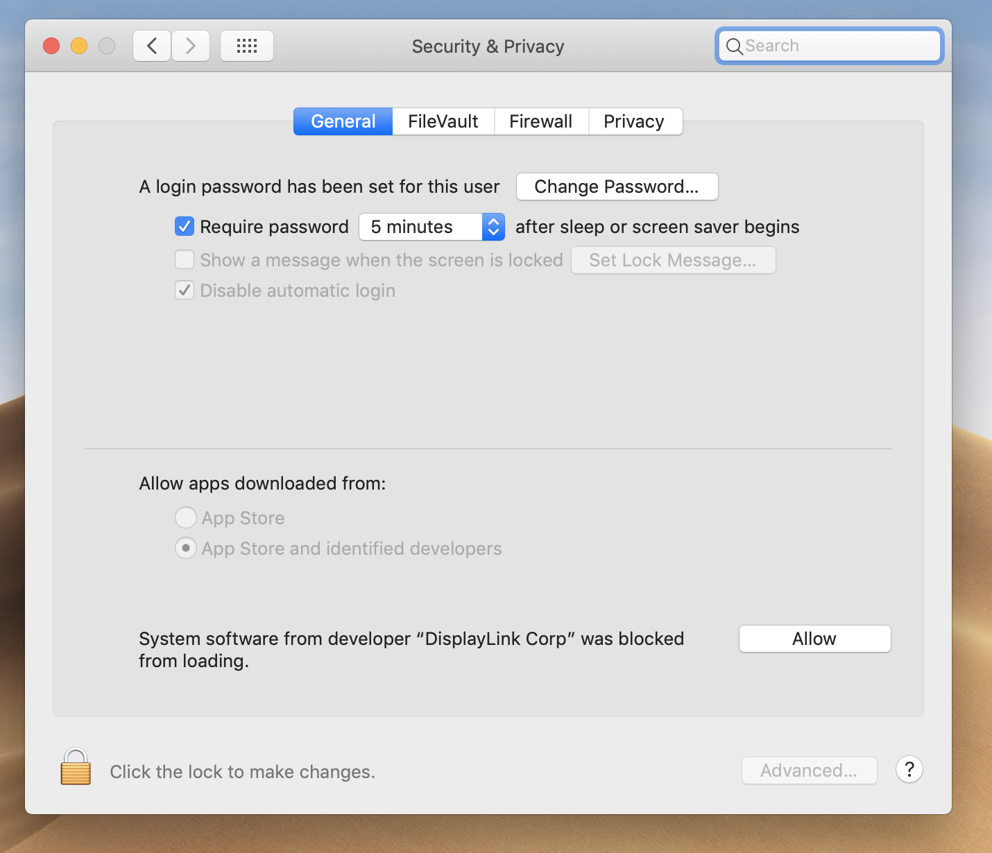
12. Close the ‘Security and Privacy’ window. The DisplayLink installation should now complete
13. Click on the ‘Restart’ button to restart your system. The DisplayLink device should start working after the restart is complete.
'Legacy' DisplayLink Driver removal for macOS 10.14 Mojave and 10.15 Catalina
We also have a video that demonstrates this process here –> https://youtu.be/VRRLJf6D7vc
1. Click the Spotlight magnifying glass icon in the Apple Menu, and search for ‘DisplayLink Software Uninstaller’. Double-click on the result
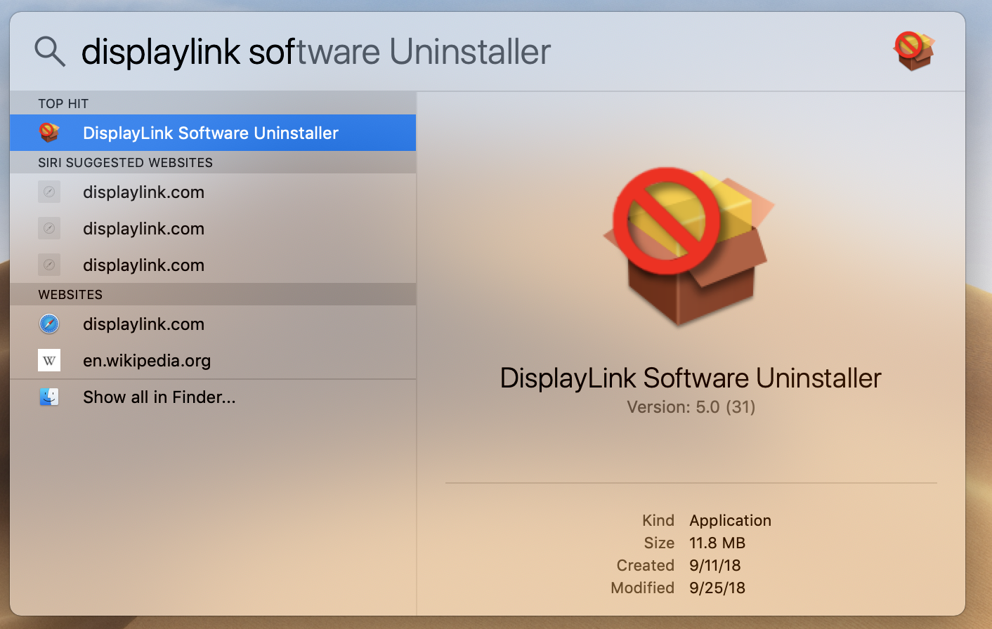
2. The uninstall window will appear
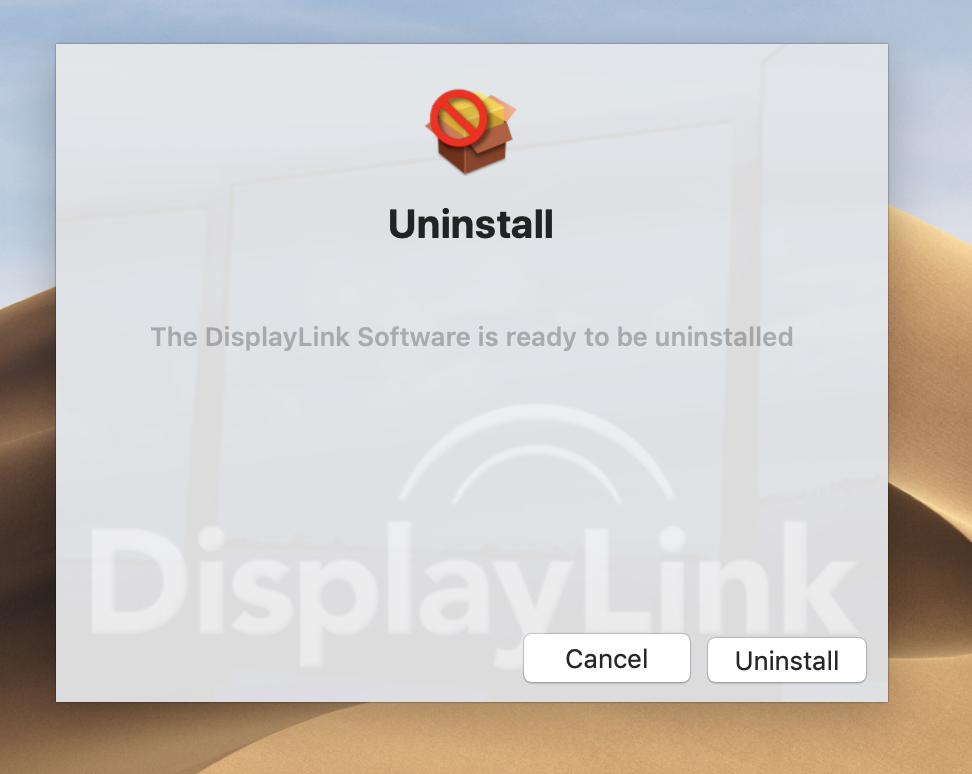
3. Click the ‘Uninstall’ button
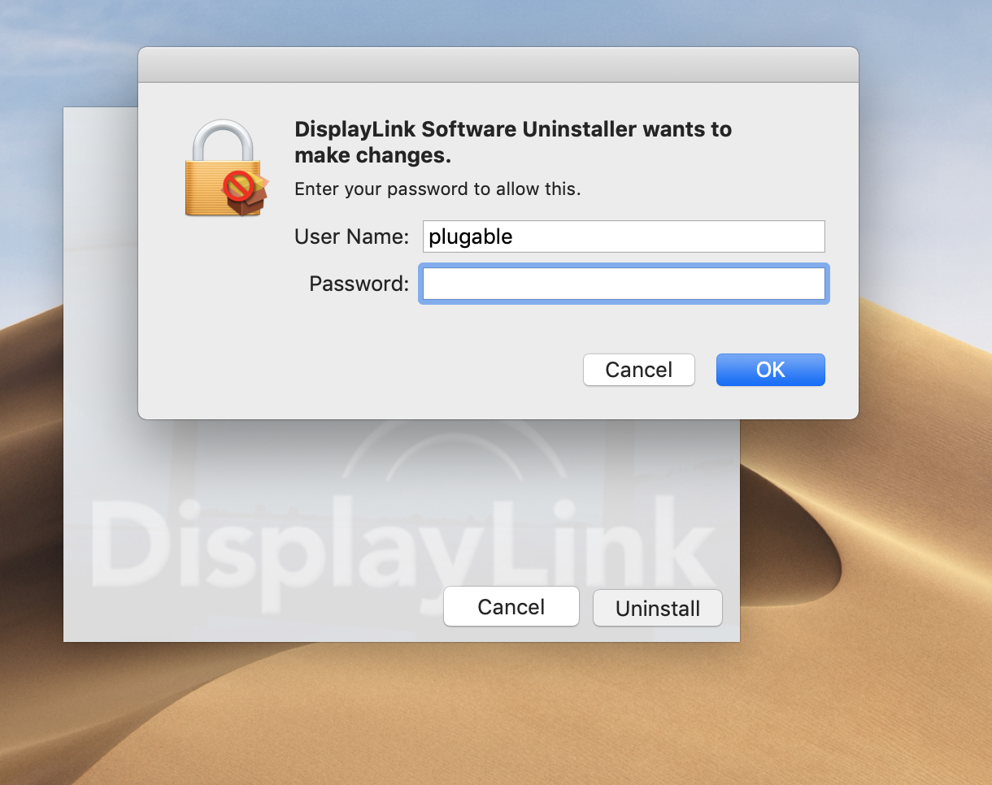
4. Enter your account password and click ‘OK’
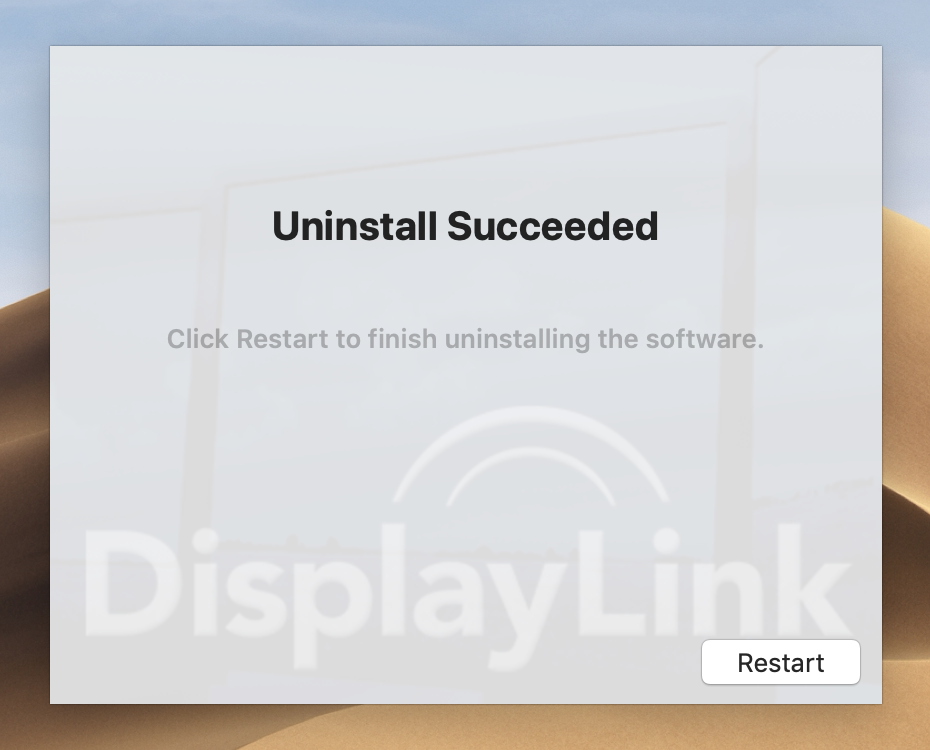
5. After a few moments the process will complete. Click the ‘Restart’ button to complete the removal process.
My Windows Laptop Will Not Boot Properly When My Docking Station Is Connected
If your Windows laptop will not boot properly when a docking station is connected to the laptop, most often the cause is an external device connected to the docking station (for example an external USB storage drive) as opposed to the dock itself.
If you are affected by this condition, please follow these steps in order to isolate the behavior further:
- Disconnect all USB devices from the docking station and put them aside for the moment.
- Disconnect any displays connected to the dock's video outputs.
- Disconnect any audio devices connected to the dock's audio ports (if present).
- Disconnect the Ethernet network cable from the dock's Ethernet port (if present).
- The only remaining connections should be the dock's power adapter cable and the USB cable used to connect it to the laptop. No other external devices should be connected to the dock.
- While in this state, reboot the laptop to test the behavior.
- Assuming the laptop boots as expected, please reconnect each device back to the dock one at a time and reboot after each one to test the behavior again. Please reconnect the displays first, then the audio devices, then the Ethernet cable. Please reconnect any USB devices to the dock last, again rebooting after each one is added to test the behavior.
In our experience helping others, the most common cause of this behavior is an external USB storage drive connected to one of the dock's USB ports. In some cases, a laptop may try to boot from an external storage drive by mistake as opposed to the laptop's built-in storage drive. Since most external USB storage drives are not 'bootable', this can interrupt the boot process.
If this behavior occurs, the most common way to mitigate the behavior is to access the laptop's System BIOS (also known as UEFI firmware) to change the 'boot order' settings to ensure that the laptop's internal storage drive is the first boot option. Doing so helps ensure that the laptop will not try to boot from an external USB storage device.
Every laptop system is different, so the best resource for accessing the System BIOS and changing the settings is the manual for the laptop provided by the laptop manufacturer.
Applications That Use OpenGL Such As Google Sketchup or Google Earth Do Not Work As Expected When Connected to a DisplayLink-Based Docking Station
Docking stations based on DisplayLink USB video technology are in essence a 'virtual' graphics adapter that relies on the host laptop's CPU and internal physical graphics processing unit (aka as GPU) to generate the information shown on the dock-attached displays.
In rare instances, Windows applications that use a technology known as OpenGL to draw the image shown on the display will attempt to direct OpenGL related tasks to the DisplayLink-based docking station's virtual graphics adapter, and not to the 'real'/'physical' GPU within the laptop.
Since the dock is not a physical GPU that supports OpenGL, this can sometimes cause applications that make use of OpenGL (such as Google Earth or AutoCAD) to not work as expected or result in various types of error messages.
The true root cause of this behavior can vary, and ultimately lies outside of the docking station or its associated DisplayLink driver. In some cases the root cause lies within the Windows driver for the host system's physical GPU and in rarer cases within the Windows operating system itself.
In some cases updating either the driver for the system's internal GPU or updating Windows itself (when Microsoft provides such updates) can help, however that is unfortunately not always the case.
If updating those components does not help, in most cases there are two possible workarounds.
The first is to configure Windows to have the ‘Main’ display set to a display directly connected to the host system's built-in internal GPU, whether that is an internal laptop display or another external display connected to one of the system's built-in video outputs (a quick guide to doing so is here -> https://youtu.be/7nnKztRZXsw).
If the first option does not prove a suitable workaround, the second option is to boot the system without the dock connected, launching the affected application, and then connecting the dock may also help.
Why Aren’t My Monitors Working Within macOS After Upgrading to a Newer Version of the DisplayLink Manager Graphics Connectivity App?
When upgrading the DisplayLink Manager Graphics Connectivity App to new version within a macOS system, the update process will cause the older version of the App to quit. As a result, any monitors connected to a DisplayLink-based USB video adapter or docking station will stop working.
The solution is to manually start the new version of the DisplayLink Manager Graphics Connectivity App by double-clicking on the App's icon within the macOS 'Applications' folder within the macOS Finder. This will restart the DisplayLink Manager Graphics Connectivity App, which in turn will enable any monitors connected to a DisplayLink-based USB video adapter or docking station to start working again.
My Docking Station and/or connected devices are not detected by my Apple Silicon M1 or M2 based Mac computer
Some users have reported after macOS Big Sur version 11.1 and newer that their USB-C Triple Display Docking Stations may not be correctly detected by Apple’s MacBook Air, MacBook Pro, Mac Mini, iMac, and Mac Studio computers with Apple Silicon processors after being restarted, when powered on after being turned off, or after being in sleep mode and then woken up. Older Intel processor based Macs are not affected.
This issue affects the UD-ULTCDL (original version), UD-ULTC4K (original version), and UD-3900PDZ docking stations along with any connected USB 2.0 and 3.0 devices, including the two DisplayLink based video outputs, Ethernet, and audio controlled by the DisplayLink USB Graphics chipset. The primary USB-C DisplayPort Alternate Mode based video output and connected display should remain functional after reboot. Charging should also be unaffected.
For most users simply unplugging the docking station from the computer, waiting 10-15 seconds, then reconnecting the docking station will restore the functionality, if this does not help please try these additional steps to fully reset the docking station and computer:
- Unplug the dock from the Mac and unplug power from the dock. Please leave the dock disconnected until the final step.
- Fully shutdown the Mac. (On your Mac, click the "Apple" menu and select "Shut Down")
- After the Mac has shutdown, wait for 60-90 seconds, then turn the Mac back on.
- After logging back in, wait for an additional 30-60 seconds, then plug power back into the dock first and plug the dock into the Mac next (using the provided USB-C to USB-C cable the dock shipped with) and see if the behavior has improved.
We are hopeful this issue may be resolved by a future update to macOS but do not have a timeline for such a resolution. We will update this article periodically as we learn more. As of macOS 14.x Sonoma we are still seeing occasional reports of this issue.
If these initial troubleshooting steps do not help, please contact us at support@plugable.com and we'll be happy to assist you.
DisplayLink Products Recommended for macOS
This article intends to provide a list of Plugable products that utilize DisplayLink technology that we currently recommend for use with macOS Mojave 10.14 and newer versions of the macOS operating system. For additional information regarding the current limitations with DisplayLink adapters and docks with macOS, please look at our KB article here: https://kb.plugable.com/question/724337
DisplayLink docks that are recommended with USB 3.0 Type-A and USB 3.0 Type-C connection to laptop:
Plugable UD-3900 Dual Display Universal Docking Station (UD-3900)
- USB-C connection achievable with purchase of a separate adapter, USBC-AF3
Plugable USB 3.0 Dual Monitor Horizontal Docking Station (UD-3900H)
Plugable Dual HDMI USB Universal Docking Station For Windows (UD-3900Z)
Plugable Dual 4K Display HDMI or DisplayPort Universal Docking Station (UD-6950Z)
Plugable UD-6950 USB 3.0 Dual DisplayPort 4K Docking Station (UD-6950)
Plugable UD-6950H USB 3.0 Dual 4K Display Horizontal Docking Station with DisplayPort and HDMI (UD-6950H)
DisplayLink docks that are recommended that support USB-C power delivery to the laptop:
Plugable USB-C Triple HDMI Display Docking Station (UD-3900PDZ)
Plugable USB-C Triple 4K Display Docking Station (UD-ULTC4K)
- Note: upon restart of a M1 Mac host system, USB and DisplayLink devices may not reconnect automatically. Please see our article here: https://kb.plugable.com/question/825145
DisplayLink adapters that are recommended:
Plugable USB 3.0 and USB-C 4K DisplayPort and HDMI Dual Monitor Adapter (USBC-6950U)
Plugable USB 3.0 and USB-C 4K DisplayPort and HDMI Dual Monitor Adapter with Ethernet (USBC-6950UE)
DisplayLink docks and adapters that are not compatible or recommended for macOS:
Plugable USB-C Triple Display Docking Station (UD-ULTCDL)
I Lost the Power Adapter for My UD-ULTC4K. Where Can I Buy a New One?
We sell replacement power adapters for use in the US, UK, AU and EU via our eBay Store .
Direct links:
Replacement Docking Station Power Adapters
Below is a list of pre-tested power adapters and corresponding power prongs/cables for Plugable docking stations that can be purchased on eBay if a replacement is needed.
If the power adapter for your docking station or region is not listed or if it out of stock on eBay please contact us at support@plugable.com and we will be happy to assist further.
We offer a 30-day return period for our replacement power adapters listed on eBay.
| Dock Models | Power Supplies |
|---|---|
| USB Products | |
| UD-3900 UD-3000 UD-5900 UD-PRO8 |
|
| UD-3900H | |
| UD-3900PDZ | |
| UD-3900Z | |
| UD-6950 | |
| UD-6950H | |
| UD-6950Z | |
| UD-CA1 UD-CA1A |
|
| UD-ULTCDL (MK1 original and MK2 updated version) |
|
| UD-ULTC4K (MK1 original and MK2 updated version) | |
| USB4-HUB3A | |
| Thunderbolt Products | |
| TBT4-UDZ |
North America plug |
| TBT3-UDC1 | |
| TBT3-UDV | |
| TBT3-UDZ | |
| TBT3-UDC3 | |
| TBT4-HUB3C | |
Why do I not see any video when using a USB-C to DisplayPort cable?
When connecting to a monitor that accepts a USB-C input, from a docking station that outputs DisplayPort (such as the UD-6950, UD-6950Z, UD-6950H, TBT3-UDZ, TBT3-UDC3), you will need to use a DisplayPort to USB-C "Bi-Directional" cable. This is because many USB-C to DisplayPort cables are unidirectional and only send data in one direction, from USB-C source device to a DisplayPort input port on a monitor.
Additional information:
- Be sure to use a DisplayPort to USB-C cable that supports the 1.2 DisplayPort standard (or higher).
- To ensure optimal performance the maximum recommended cable length should be no longer than 1.8 meters (6 feet).
An example of a DisplayPort to USB-C "Bi-Directional" cable can be seen here: https://www.amazon.com/dp/B081VK1KHV
When My DisplayLink-Based Product Is Connected to My Mac Running macOS 12 Monterey or macOS 13 Ventura, I Do Not See ‘Notifications’ From the Operating System. When I Disconnect the DisplayLink-Based Product From My Mac, Notifications Work As Expected. Why Is This?
Plugable has received reports of Notifications not working as expected when a DisplayLink-based product (such as our UD-3900 or UD-6950Z docking stations) is connected to a Mac running macOS 12 Monterey.
The cause of this behavior is still being investigated, however in our experience making a small change within the ‘Notifications & Focus’ preference settings can help.
For macOS 12 Montery, please follow these steps:
- Click on the ‘System Preferences’ icon (looks like a gear) in the macOS Dock at the bottom of your screen
- Click on the ‘Notifications and Focus’ application
- At the bottom of the ‘Notifications and Focus’ application window, click to place a checkmark in the ‘When mirroring or sharing the display’ option under the ‘Allow notifications’ section. An example screenshot with this option highlighted is included below:
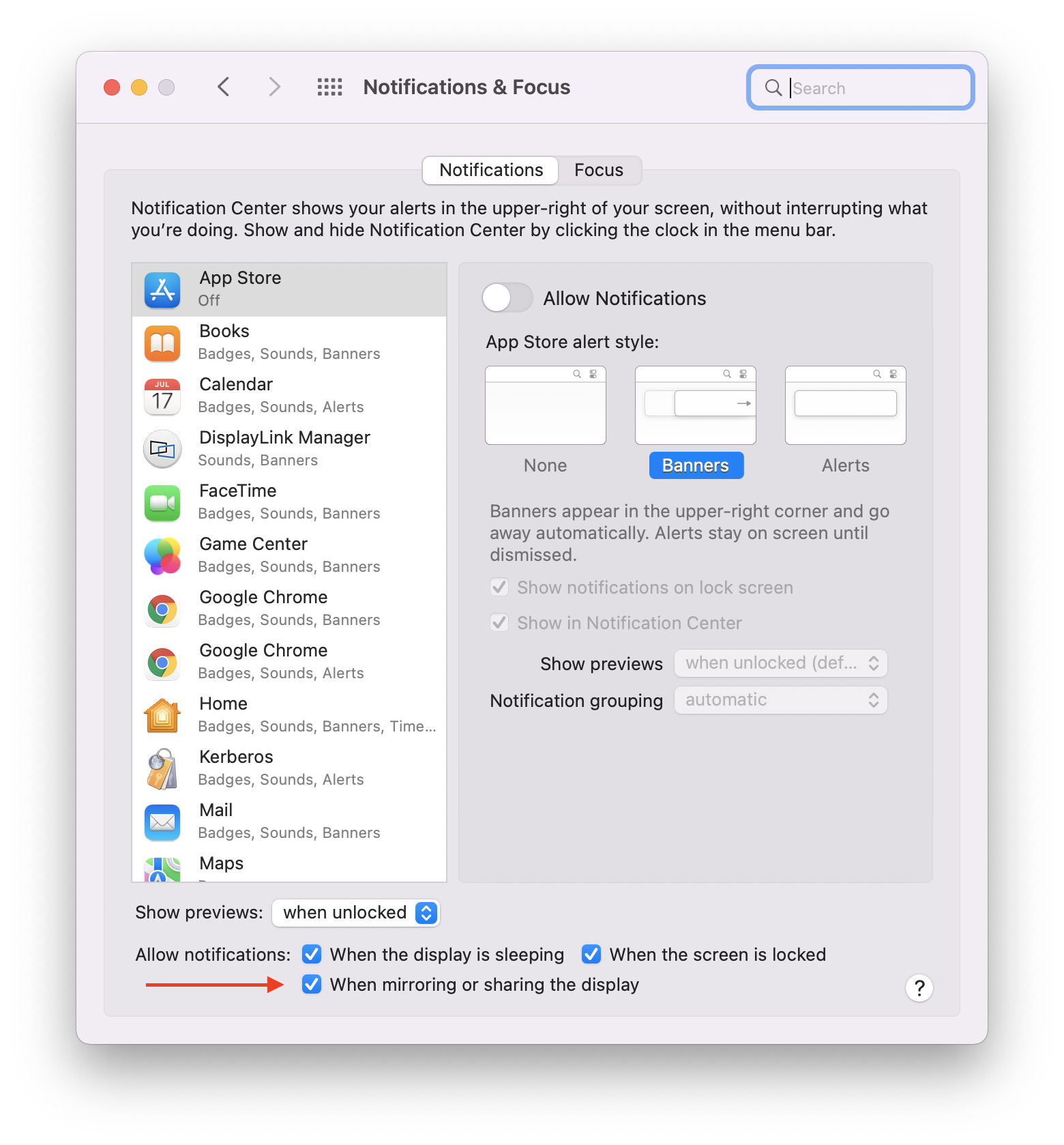
For macOS 13 Ventura, please follow these steps:
- From Finder, click on the Apple Menu then select System Settings
- On the left side select "Notifications"
- On the right side select the option to "Allow notification s when mirroring or sharing the display"
- Under Application Notifications select "DisplayLink Manager"
- Toggle on the "Allow notifications" option at the top
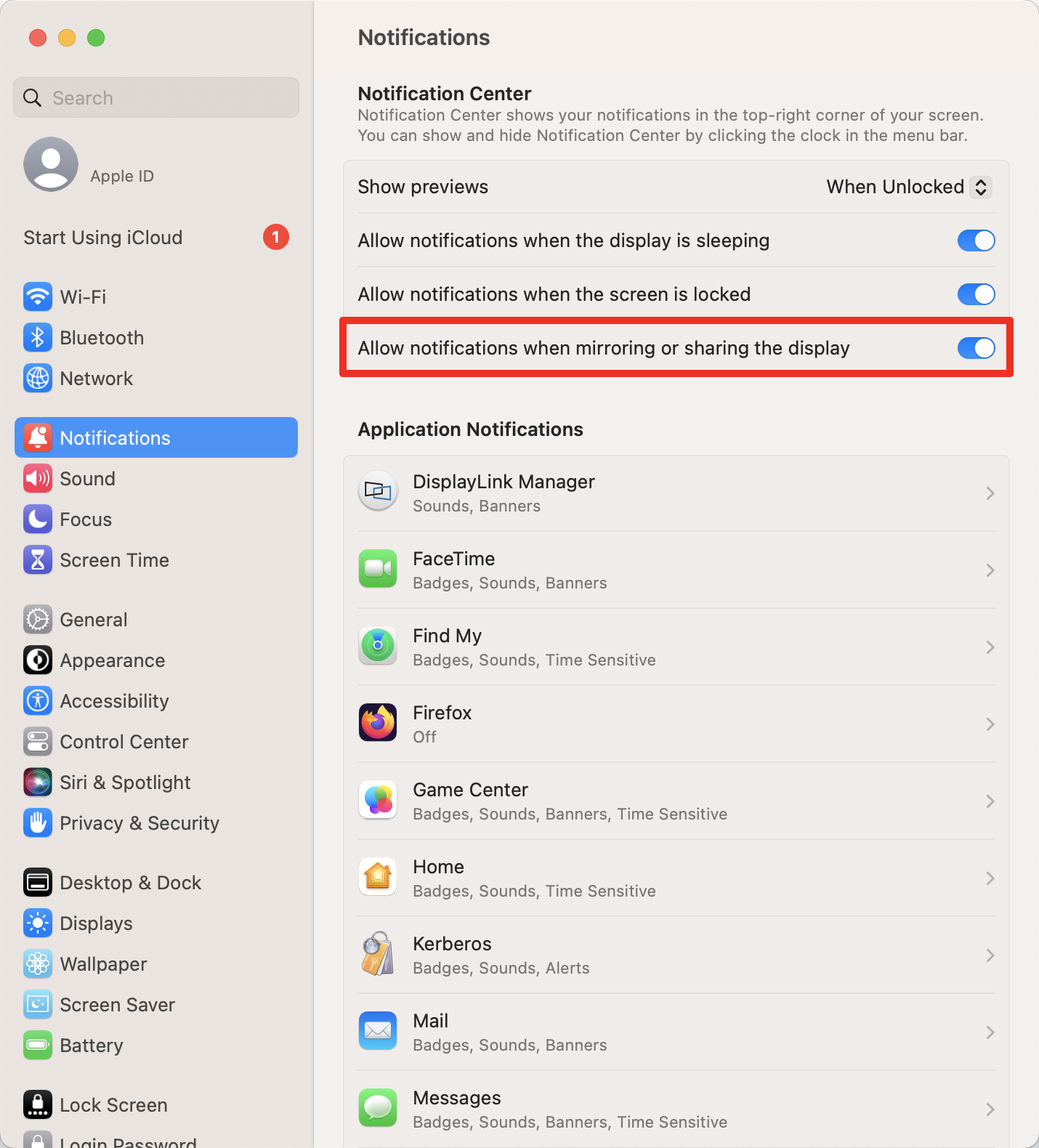
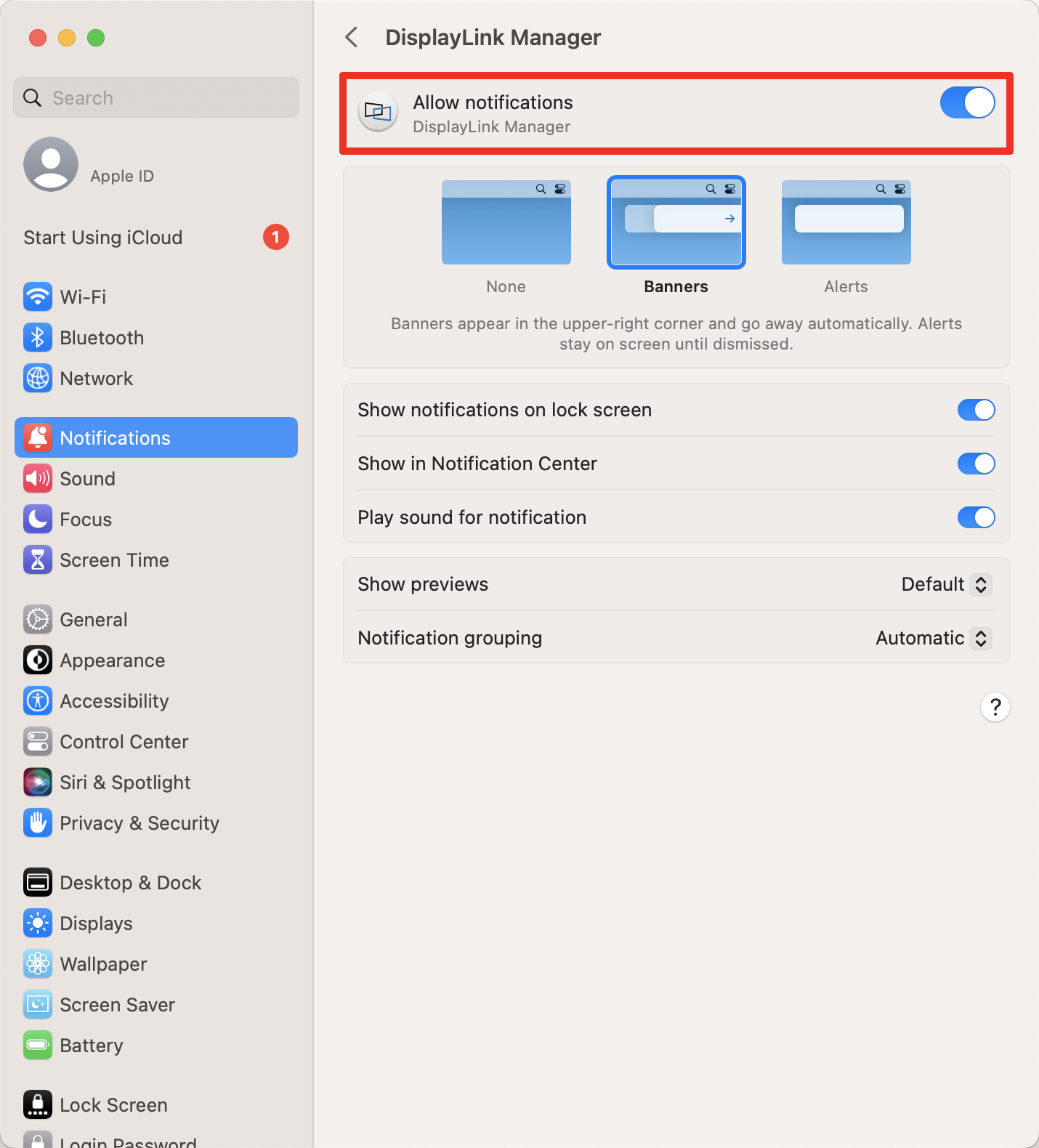
The Audio Output From My DisplayLink-Based USB Docking Station or USB Video Adapter Is Not Working Fully As Expected When Used With macOS 12 Monterey. Why Is This Happening, and How Do I Fix This?
UPDATE 5/24/2022 - To the best of Plugable's knowledge, the unexpected behavior described below has been resolved by the macOS 12.4 update. While the issue has been resolved, the information below has been retained for historical reference.
Plugable’s products based on DisplayLink technology have the ability to send an audio signal out via their 3.5mm analog audio jacks or via their HDMI or DisplayPort video output ports (which can also carry an audio signal).
Examples of Plugable products based on DisplayLink technology are the UD-3900, UD-6950Z, or USBC-6950U. Any Plugable product based on DisplayLink technology will have a 'DisplayLink' logo printed somewhere on the product. If a Plugable product does not have this logo, then it does not use DisplayLink technology.
In some cases, when DisplayLink-based products are used with a Mac running macOS 12 Monterey the audio signal may not be heard when switching to the DisplayLink-based device.
This behavior appears to be tied to the order in which an audio output device is selected and used within macOS. For reference, the macOS driver used for the audio device within any DisplayLink-based product is provided by Apple and built-in to macOS.
To expand further, consider the following two examples:
‘Working’ example
- A Mac system is powered on with a DisplayLink device already connected.
- The DisplayLink device is set to the default audio output device within the ‘Sound’ macOS System Preferences application.
- An application plays a file that contains audio.
- The audio signal is heard properly via the DisplayLink device.
‘Not working’ example
- A Mac system is powered on without a DisplayLink device connected
- The Mac’s built-in audio output device is set as the default audio output device within the ‘Sound’ macOS System Preferences application.
- An application plays a file that contains audio.
- The audio signal is heard properly via the Mac’s built-in audio output device.
- A DisplayLink device is connected to the Mac
- The default audio output device within the ‘Sound’ macOS System Preferences application is changed to the DisplayLink device.
- An application plays a file that contains audio.
- An audio signal is NOT heard via the DisplayLink device.
At this time, there are three potential workarounds for this behavior:
- Restart the Mac
- Completely close the application that is affected by the behavior, and then restart the application
- Execute this command from within the macOS Terminal application (without the quotes) --> 'sudo killall coreaudiod'
Can Silicon Motion and DisplayLink-based Docking Stations and Graphics Adapters Work Together?
Yes! As long as the software drivers for both Silicon Motion and DisplayLink-based products are installed on the same computer these two USB graphics solutions can work together and be used at the same time.
I Have a Plugable Product That Is Based on DisplayLink USB Video Technology. What Options Are Available To Install the Required DisplayLink Software Within an Enterprise or Corporate Environment?
The DisplayLink software is not developed by Plugable. The DisplayLink software is developed by a separate company called DisplayLink --> https://www.synaptics.com/products/displaylink-graphics (which is itself part of the Synaptics Corporation).
DisplayLink has a 'Corporate Deployment' section within their online knowledge base that speaks to all of the corporate deployment options available for the software --> https://support.displaylink.com/knowledgebase/topics/92322-corporate-deployment
Plugable does not support any of the 'Corporate' installation methods of the DisplayLink software.
Should you require assistance with a corporate deployment method of the DisplayLink software, we would suggest contacting DisplayLink directly for assistance --> https://support.displaylink.com/knowledgebase
Is the Playback of Copy-Protected or Encrypted Video Content Supported While Using My DisplayLink-Based Product?
Plugable’s USB video adapters or USB docking stations based on DisplayLink technology do not support the playback of copy-protected or encrypted video content, and we do our best to call this out in our product listings.
Examples of this type of video content are:
- Video content that is protected by High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection (also known as HDCP), for example Blu-ray discs
- Copy-protected video content provided by various online streaming services, for example Netflix, Hulu, Amazon Prime Video, iTunes, Disney+, YouTubeTV, etc.
As a result, copy-protected video content may not display an image on-screen while using a DisplayLink-based product.
In some cases (such as when using a streaming service) the copy-protected video content may display an image on-screen, however the resolution of the image may be lower than expected.
My Plugable Dock Is Missing a Component Such As the Power Supply, USB Cable, or Other Adapter.
If your package is missing one or more of the items that should be included with your Plugable dock (included items are listed on a chart on the side of the box), start by double checking if the part is still in the packaging. Pieces can occasionally get stuck in the corners under the main insert in the box.
If you are still unable to locate the piece, please contact support@plugable.com with the following information:
1. Amazon Order ID (or other proof of purchase) associated with your Plugable device.
2. A description of the parts that are missing from your order.
3. Your preferred shipping address (and a phone number associated with that address).
4. The serial number of your Plugable Dock.
Can I Connect My High Refresh Rate Monitor (e.g. 120Hz, 144Hz) to a Plugable Dock?
Most Plugable docks do not officially support monitors over 60Hz including 120Hz or 144Hz refresh rate unless otherwise specified on the Plugable product page or listing.
DisplayLink USB Graphics technology and Silicon Motion based docking stations and graphics adapters, like our USB 3.0 dual display and USB Type-C triple display docking stations, are limited to 60Hz fresh rate by the USB graphics controller hardware.
USB Type-C DisplayPort Alternate Mode docking station and ports on our USB Type-C Triple Display Docking Stations can support higher refresh rates, but may be limited by the computer's capability and available bandwidth to the docking station. Additionally, when paired with DisplayLink or Silicon Motion USB graphics, having displays at different refresh rates may reduce overall system performance. Due to this we normally recommend limiting all connected displays to 60Hz refresh rate when using DisplayLink and Silicon Motion graphics technology with directly connected, or USB Type-C DisplayPort Alternate Mode controlled displays.
Monitors with refresh rates higher then 60Hz may be connected to a docking station operating at up to 60Hz, or connected directly on the computer's HDMI or DisplayPort to ensure the display is powered by the system's native GPU.
My UD-UTLC4K appears to be different than what is currently pictured, why?
The original UD-ULTC4K docking station was released in November 2017 and was sold until May 2022. It offered the following features:
- 1x USB-C Port (5Gbps) (Front)
- 1x Audio In (3.5mm) and 1x Audio Out (3.5mm)
- 2x DisplayPort 1.2 (DisplayLink)
- 1x HDMI 1.4 (Alt Mode)
- 4x 3.0 Ports (5Gbps) (1x Front, 3x Rear)
- 1x Gigabit Ethernet
- 1x 5Gbps USB-C connection to host with 60W Power Delivery

As of June 2022 we have now introduced a new version of the UD-UTLC4K with updated features based on customer feedback. The updated version now offers the following features:
- 1x USB-C (10Gbps, 20W PD) (Front)
- 1x SD Card Reader
- 1x Audio In (3.5mm) and 1x Audio Out (3.5mm)
- 2x DisplayPort 1.2 or HDMI 2.0 (DisplayLink)
- 1x DisplayPort 1.2 or HDMI 2.0 (Alt Mode)
- 4x USB 3.0 (5Gbps) (Rear)
- 1x Gigabit Ethernet
- 1x 10Gbps USB-C connection to host with 100W (96W Certified) Power Delivery
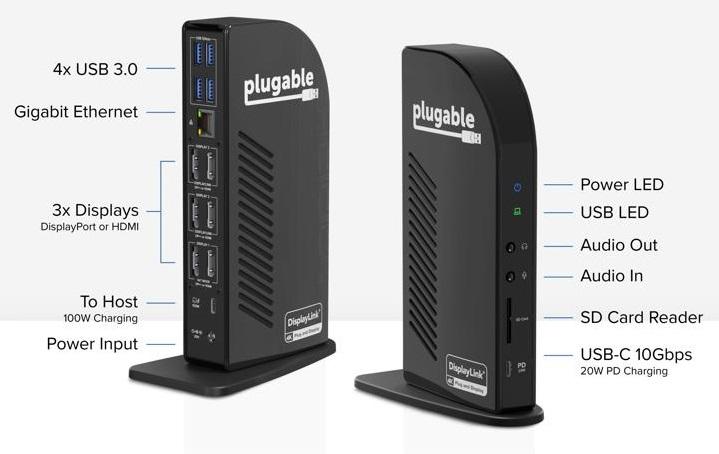

If you have any questions about the different versions or are unsure which version you have please contact us at support@plugable.com and we'll be happy to assist.
Do Plugable products support the Apple SuperDrive?
Unfortunately Plugable products do not support the Apple SuperDrive.
The Apple SuperDrive has stringent power requirements that can only be met by directly connecting the SuperDrive to your host laptop. As a result at this time Apple recommends only using their USB-C adapter cables. You can find more information on that here → How to connect the Apple USB SuperDrive
If you have purchased a Plugable product to use with your Apple SuperDrive, and would like some additional assistance please do not hesitate to reach out. You can do so by emailing support@plugable.com, or going to Plugable.com/Support.
My Plugable product with wired Ethernet is no longer working on macOS. What can I do?
Please Note
The below guide is an advanced troubleshooting step, and we do not recommend doing so unless you are comfortable manually altering files on your Apple product running macOS. You may not be able to perform the below troubleshooting step if you are unable to execute administrative credentials on your laptop. Please reach out to our support first if you do not wish to attempt the below instructions. You can do so at Plugable.com/Support
How to delete a specific Ethernet adapter from your Network devices on macOS
- Click on the Apple logo in the top left corner of your primary monitor, and select ‘System Preferences’
- Next select ‘Network’ in the ‘System Preferences' window.
- In the now visible list, please select the Plugable Ethernet, or Thunderbolt Ethernet device that may not be working as expected.
- Once selected click on the minus button in the bottom left of the network window.
- Click on Apply in the bottom right.
- Next click on the plus button in the bottom left of the network window, and add the previously removed device.
- Click on Apply in the bottom right.
- Test to see if this has resolved the unexpected behavior, and assure that your Ethernet is now working.
- If this does not resolve the problem, please proceed to the next section (As noted previously the next section is for advanced users only!)
Manually erase your macOS Network Settings to fully reset the Network configuration
(Advanced! Click to reveal)
Warning!
This will fully erase all of your Network configuration! Do not skip any steps, and proceed only if you are comfortable with each step!
- Open the ‘Finder’ app, then in the ‘Go’ menu at the top of your screen select ‘Computer’
- Click on ‘Macintosh HD’ then Library, Preferences, SystemConfiguration
- Copy the file named ‘NetworkInterfaces.plist’ to your desktop as a backup of your current configuration.
- Delete the original version of the ‘NetworkInterfaces.plist’ located in the SystemConfiguration directory.
- Restart your Mac
- Login to your Mac, and return to System Preferences → Network
- If the list is now empty, please re-add the Plugable or Thunderbolt network adapter by clicking on the plus button in the bottom left of the Network window. Once done click on 'Apply'.
- Test to see if this has resolved the unexpected network behavior
I am still unable to get my Ethernet connection working on my Mac
If this is the case please reach out to our support team. When you do please include a diagnostic log gathered using our PlugDebug tool (instructions are provided on the PlugDebug page). If you are not able to gather the PlugDebug diagnostics do not worry we are still here to help! Please reach out to our support team at support@plugable.com or Plugable.com/Support with a detailed description of your problem, and the model of Plugable product you are using.
Does Plugable support ChromeOS with our DisplayLink-based products?
Plugable’s DisplayLink-based products are supported with ChromeOS (the operating system used in Chromebook laptops), however there are some potential limitations.
In brief:
1. Plugable recommends using our DisplayLink-based products with Chromebooks that have an Intel central processing unit (CPU) or an AMD CPU. Chromebooks with ARM CPUs are not recommended due to ARM CPU performance limitations.
2. Most Chromebooks meet the minimum hardware specifications we recommend for use with products based on the DL-3900 chipset.
The DL-6950 chipset has higher recommended hardware specifications which may not be met by some Chromebooks, which in turn may result in lower than expected performance.
As of this writing, Plugable makes products based on the DisplayLink DL-3900 (https://www.synaptics.com/products/displaylink-graphics/integrated-chipsets/dl-3000) and DL-6950 chipsets (https://www.synaptics.com/products/displaylink-graphics/integrated-chipsets/dl-6000). You can determine which DisplayLink chipset is in use within a Plugable product by its model name. For example, a ‘UD-3900’ docking station uses the DL-3900 chipset and a ‘UD-6950Z’ docking station uses the DL-6950 chipset.
3. For best performance, Plugable recommends using our DisplayLink-based products with Chromebooks that were released in the year 2020 or later.
4. Plugable recommends that a Chromebook have ChromeOS version 100 or later installed. Earlier versions of ChromeOS are not officially supported. Only the 'Stable' release channel of ChromeOS is supported. The 'Beta', 'Dev', or 'Canary' release channels of ChromeOS are not supported.
5. In some cases, the wired Ethernet network adapter within a Plugable DisplayLink-based product may perform at a lower than expected level of performance when used with a Chromebook as compared to when the same device is used with a Windows or Mac computer.
As a result, the Ethernet adapter may not support Gigabit Ethernet speed. This is due to a limitation of the Ethernet network driver built-in to ChromeOS, it is not a limitation of Plugable’s DisplayLink-based products.
6. Google exercises complete control over ChromeOS. As a result of this control, there can be cases where a ChromeOS update could cause unexpected behavior of a Plugable DisplayLink-based device.
It is not possible for a 3rd-party to install driver updates or apply fixes to ChromeOS. All driver updates or fixes are provided by Google as Google publishes updates to ChromeOS.
7.. Plugable offers a diagnostic utility called PlugDebug → https://plugable.com/pages/plugdebug which helps simplify the process of assisting our customers using Windows, macOS, or Linux.
Unfortunately due to the control Google exercises over ChromeOS, it is not possible to use a diagnostic tool like PlugDebug with a Chromebook.
More detail:
To expand further on some of the items listed above…
Plugable products based on DisplayLink USB video technology (https://www.synaptics.com/products/displaylink-graphics) are in essence ‘virtual’ graphics processing units that rely on the host computer’s central processing unit (CPU) and physical graphics processing unit (GPU) in order to generate the image shown on the DisplayLink-attached displays.
Because ChromeOS is quite efficient, it does not generally require a powerful CPU in order to work well. As a result, many Chromebooks have lower powered CPUs as compared to their Windows and Mac counterparts.
This is a boon in that Chromebooks can be made comparatively cheaper and have excellent battery life, however when it comes to using Plugable products based on DisplayLink technology some lower powered processors may not provide the same level of performance as compared to a system with a more powerful CPU and GPU.
This drives our recommendation that for best performance, Chromebooks made in 2020 or later that have either Intel CPUs or AMD CPUs be used in conjunction with Plugable’s DisplayLink-based products.
This symbiotic relationship is also what informs the potential performance differences between products based on the DL-3900 and DL-6950 chipset.
Some Chromebooks are based on an ARM CPU, and speaking in general the ARM CPUs are not as powerful as an Intel CPU or AMD CPU. As a result, we do not recommend using Plugable’s DisplayLink-based products with Chromebooks that have an ARM CPU.
If you are unsure which type of CPU your Chromebook has within it, you can consult the Chromebook manufacturer’s specifications.
If the manufacturer’s information does not help, Google maintains a list of all Chromebooks and the type of CPU they have here → https://www.chromium.org/chromium-os/developer-information-for-chrome-os-devices/
Within Google’s list, the column ‘User ABI’ refers to the type of CPU, where ‘x86_64’ refers to an Intel or AMD CPU while ‘arm’ refers to an ARM CPU.
Further to this, a Chromebook should have ChromeOS version 100 or higher installed in order to be used with a Plugable DisplayLink-based product. Google has a guide for determining the ChromeOS version as well as updating ChromeOS here → https://support.google.com/chromebook/answer/177889
Does my DisplayLink-based product support color adjustment such as Night Light or Night Shift via the host operating system?
Modern operating systems support adjusting the color of the image shown within external displays in order to make the image more pleasing depending upon the time of the day.
In Windows 10 and Windows 11, this feature is known as ‘Night Light’ → https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/set-your-display-for-night-time-in-windows-18fe903a-e0a1-8326-4c68-fd23d7aaf136
In ChromeOS, this feature is also known as ‘Night Light’ → https://support.google.com/chromebook/answer/9145848?hl=en
In macOS, this feature is known as ‘Night Shift’ → https://support.apple.com/en-us/HT207513
When using a DisplayLink-based product based on the DL-3xxx, DL-5xxx, or DL-6xxx chipsets, as of today the level of support for color adjustment is as follows:
| Operating System | Color adjustment feature name | Level of support when using DisplayLink-based product |
Windows 10 & 11 |
Night Light |
- Supported when using DisplayLink driver version 10.3 M0 or newer - The 3rd-party utility f.lux also has native support for DisplayLink-based devices |
| ChromeOS (version 100 or newer) |
Night Light |
Supported |
| macOS 11, 12, 13 |
Night Shift |
- Not Supported - Experimental support for color adjustment via the 3rd-party utility f.lux is available when using DisplayLink Manager version 1.8.0*** |
*** More information about this feature is available here → https://support.displaylink.com/knowledgebase/articles/1990237-displaylink-manager-app-f-lux-support-option
I tried to install the DisplayLink Manager Application on my Mac, however the process ended in an ‘Unexpected Error’. How do I fix this?
In order to use one of our DisplayLink-based products with a Mac, the DisplayLink Manager Application must be installed.
We have found that in most cases the initial installation of the application completes without any issues.
With that said, there can be rare cases where the initial installation of the application may not complete successfully, and result in an ‘Unexpected Error’.
While each support case is unique, in our experience helping others we have found that there can be a few potential causes for this condition:
A. The end-user does not have the authority or permission in order to install software applications on the host computer.
In some enterprise or corporate environments there are security restrictions in place that prevent the end-user of the Mac from installing software applications.
If your Mac has been provided to you by your company or enterprise, please reach out to your organization’s IT support department in order to determine if you have both the necessary permission and authorization in order to install software on your Mac
B. The destination for the installation of the DisplayLink Manager Application software is not a valid location.
The DisplayLink Manager Application must be installed to the Mac’s built-in internal storage drive, and the drive must have the required amount of available storage space to accommodate the installation.
The DisplayLink Manager Application should not be installed on an external storage drive, or to any type of cloud storage drive (such as Microsoft OneDrive, DropBox or Google Drive) mounted as a local physical storage volume.
In addition, the DisplayLink Manager Application installation process should not be executed while the installation file is located within any type of cloud storage drive (such as Microsoft OneDrive, DropBox or Google Drive) mounted as a local physical storage volume.
C. macOS does not have permission to access the location of the DisplayLink Manager Application installation file.
The macOS ‘Installer’ application must have permission to access the location of the DisplayLink Manager Application installation file in order for the installation process to complete successfully. If this permission is not granted, then the installation process will not complete successfully.
In our experience helping others, we have found that some of our customers using macOS 13 Ventura may encounter an error during the installation process if this permission has not been granted.
To expand further and as an example, the first time you download an application to your Mac’s ‘Desktop’ folder and attempt to install the application macOS 13 Ventura will prompt you to grant permission to the macOS Installer application to access the ‘Desktop’ folder.
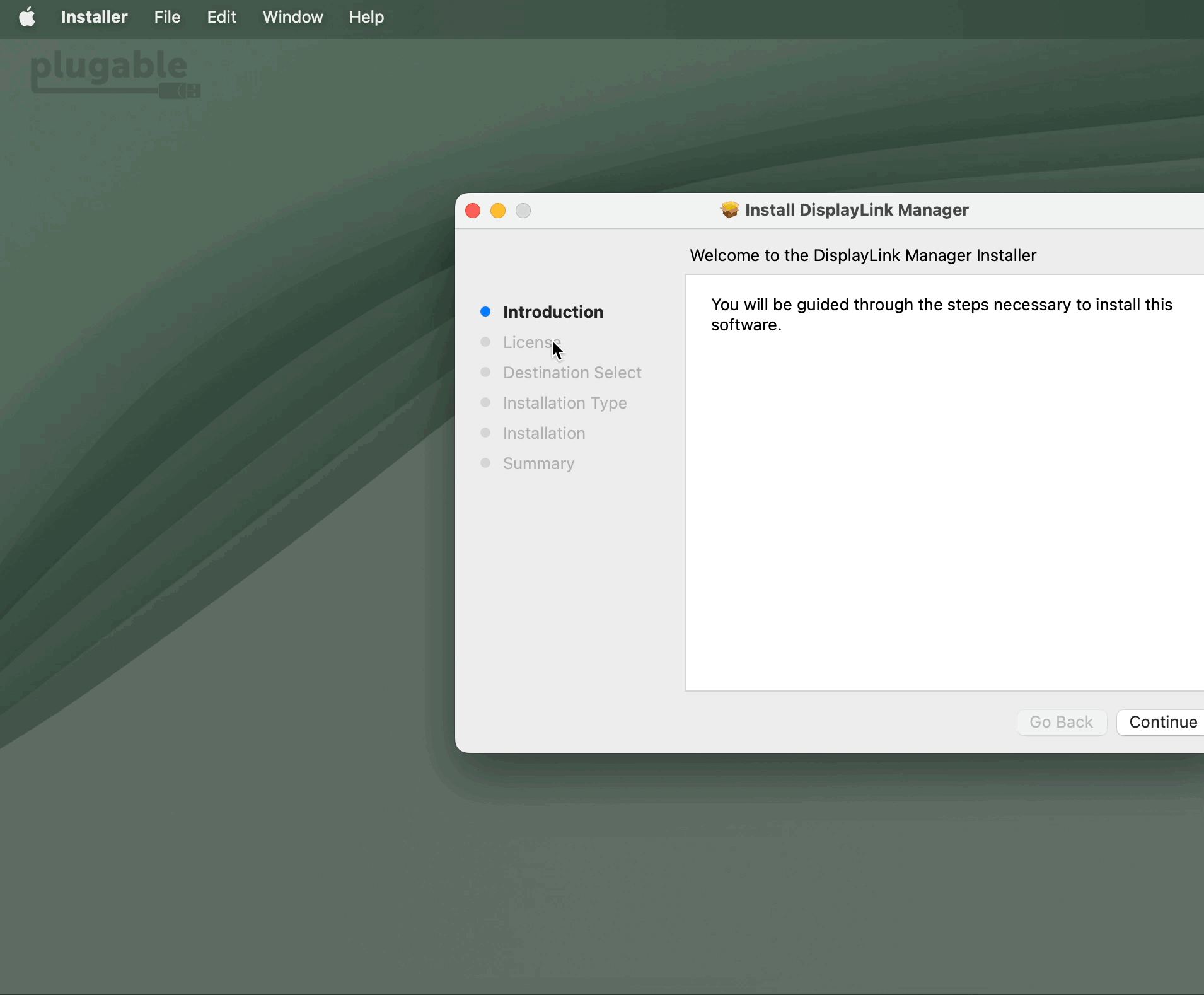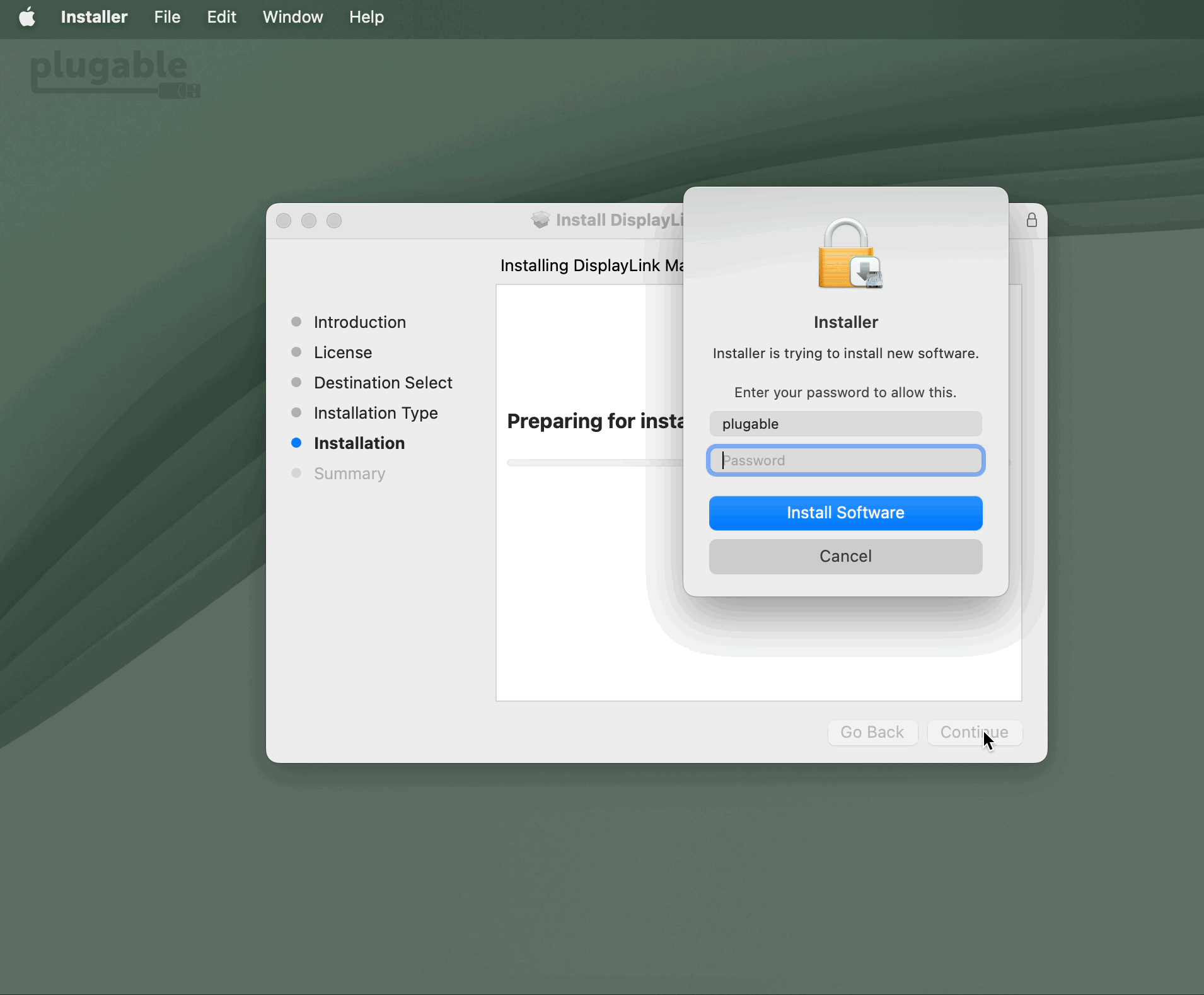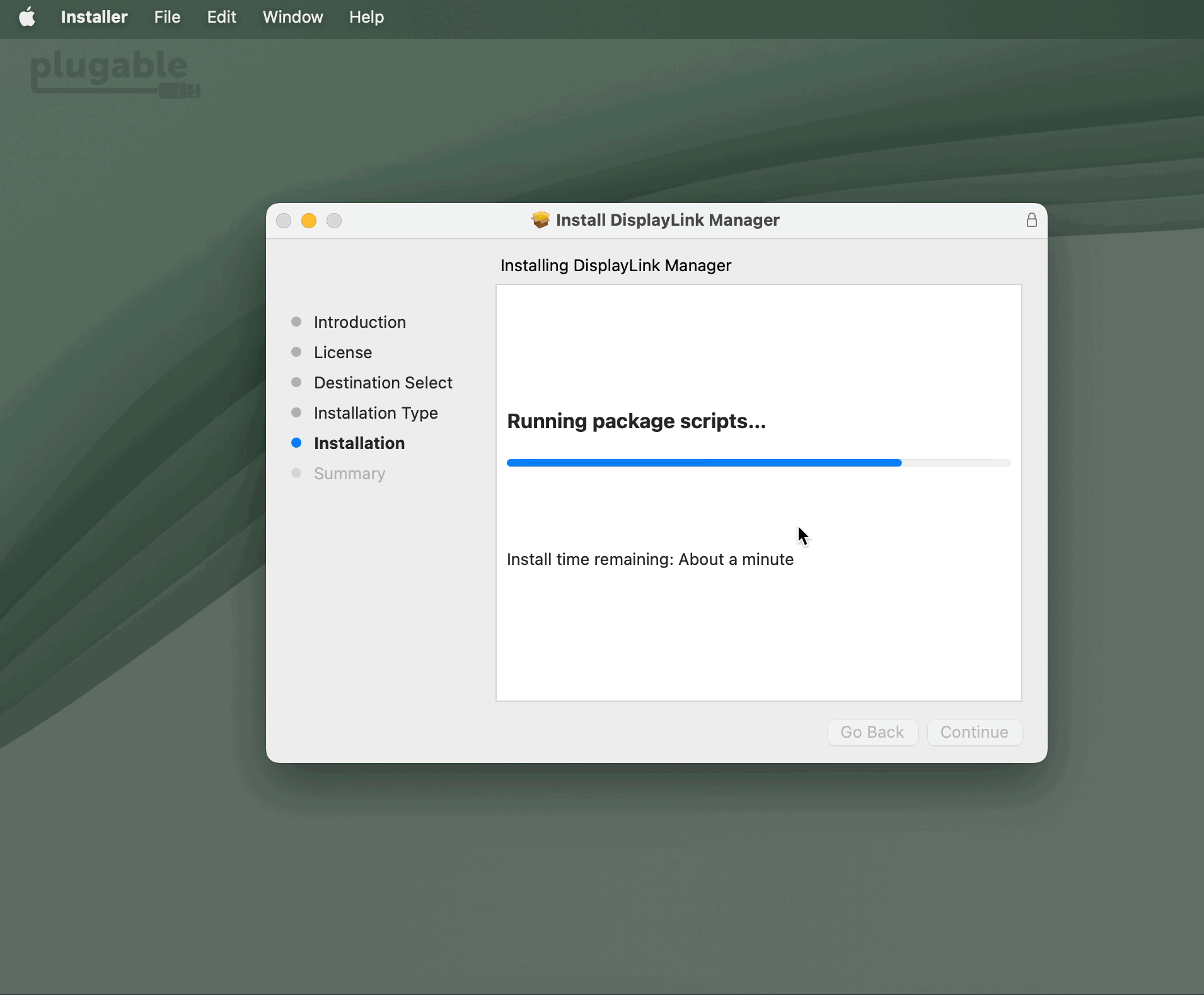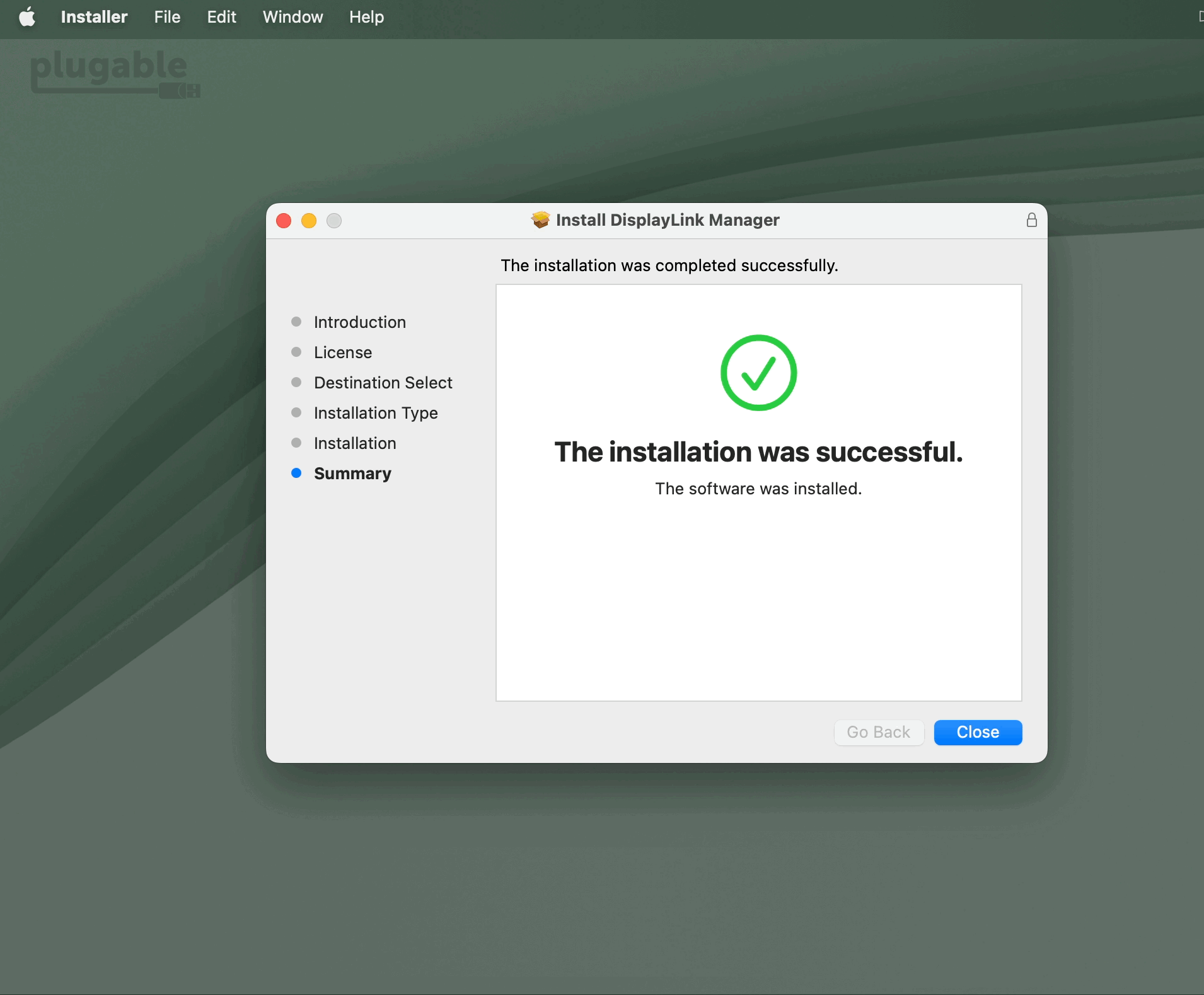
If this permission is granted, then the application installation process should complete successfully. If the permission is not granted, then the application installation will not complete successfully. If the permission is not granted and you attempt the installation process a second time, macOS will NOT prompt you to grant permission because of the previous denial.
The most straightforward way to ‘reset’ these permissions is as follows:
1. Click on the Apple Menu item at the top of your screen and select ‘System Settings’ from the menu that appears
2. In the list of items presented on the left-hand side of the ‘System Settings’ application window, click on the ‘Privacy & Security’ item.
3. Within the ‘Privacy & Security’ section, scroll down in the list and click on the ‘Files and Folders’ item.
4. Within the ‘Files and Folders’ section, there should be an entry for ‘Installer’. Click on the ‘Installer’ entry in order to select it. Once the item is selected, it should appear blue in color.
5. At the bottom of the list of items within the ‘Files and Folders’ section, there will be a small horizontal line that looks like a dash or a minus sign (-). Click on the horizontal line, which will remove the ‘Installer’ entry from the list.
*** Important note - please do not make any other changes in this location, other than what we describe above ***
6. Close the ‘Systems Settings’ application
7. Attempt the installation of the DisplayLink Manager Application again.
To help provide more context, an animated example of this process is below:
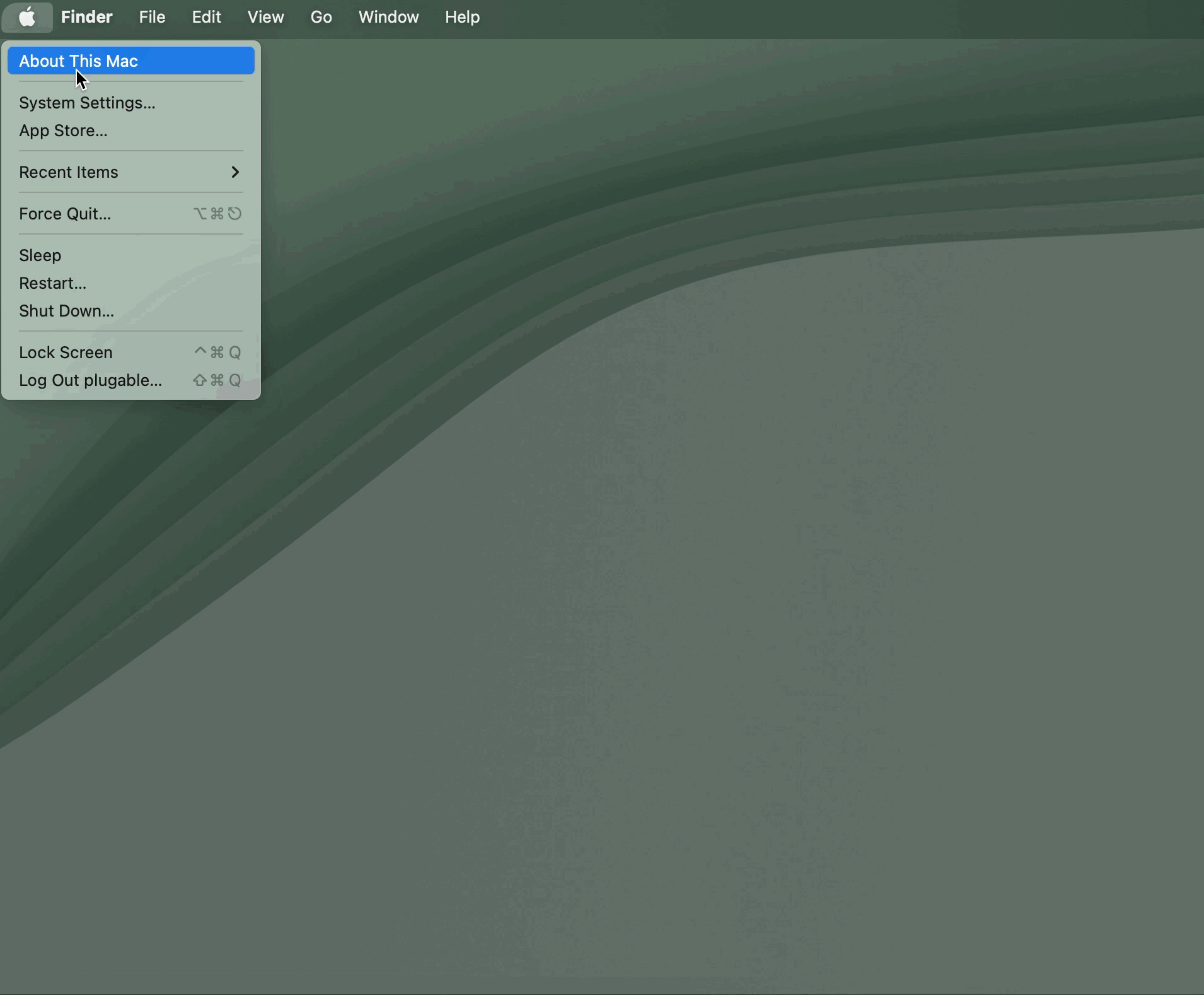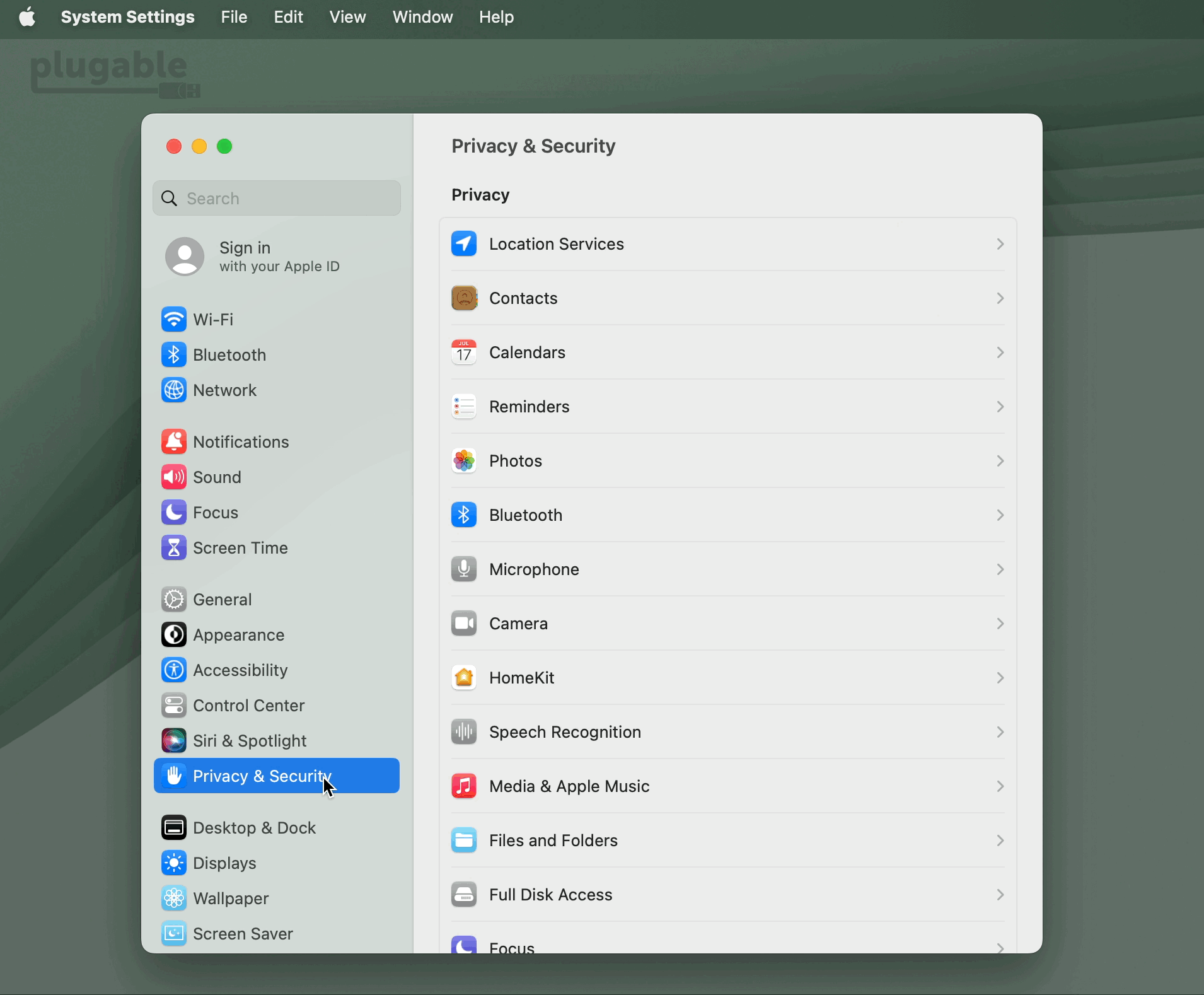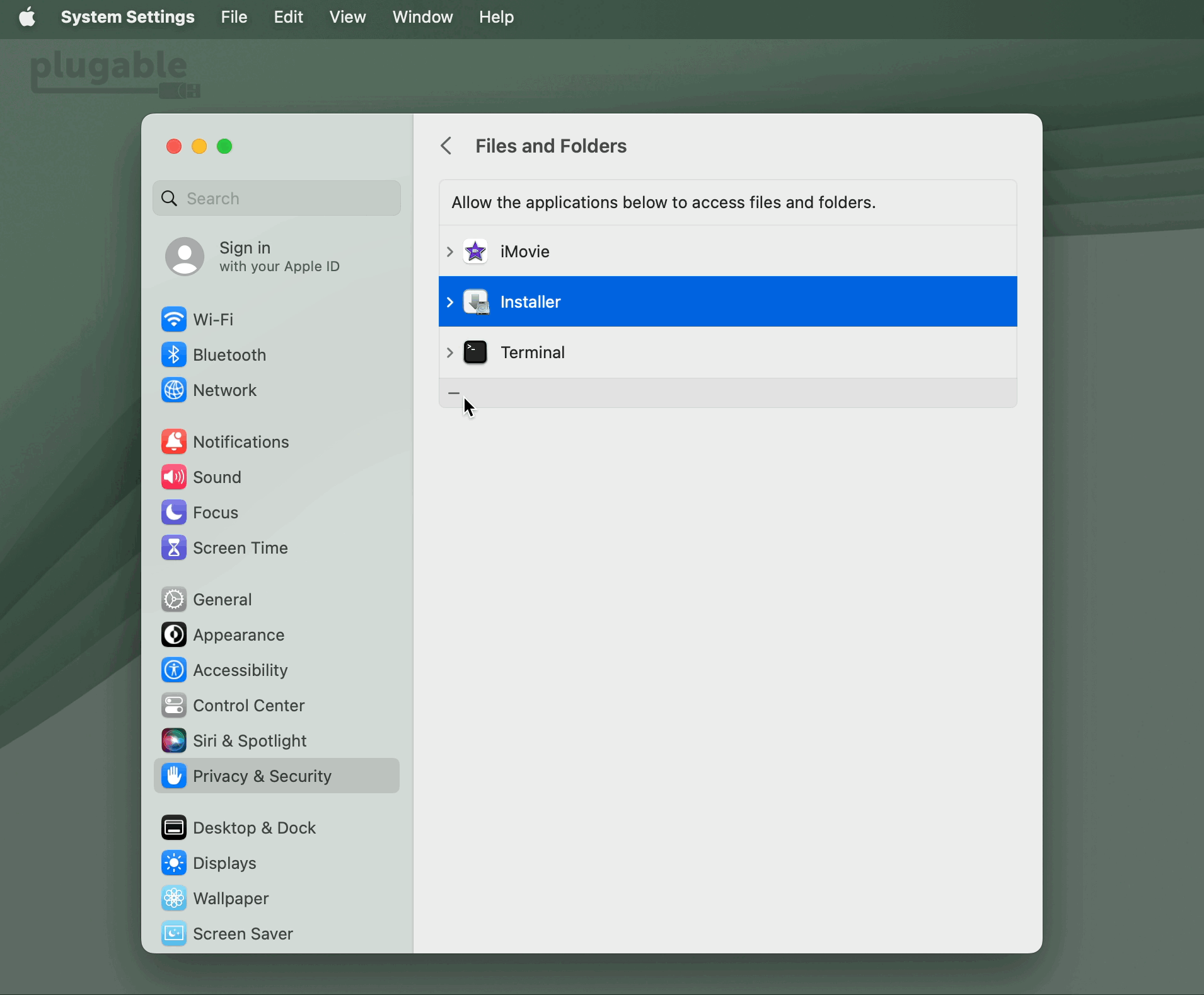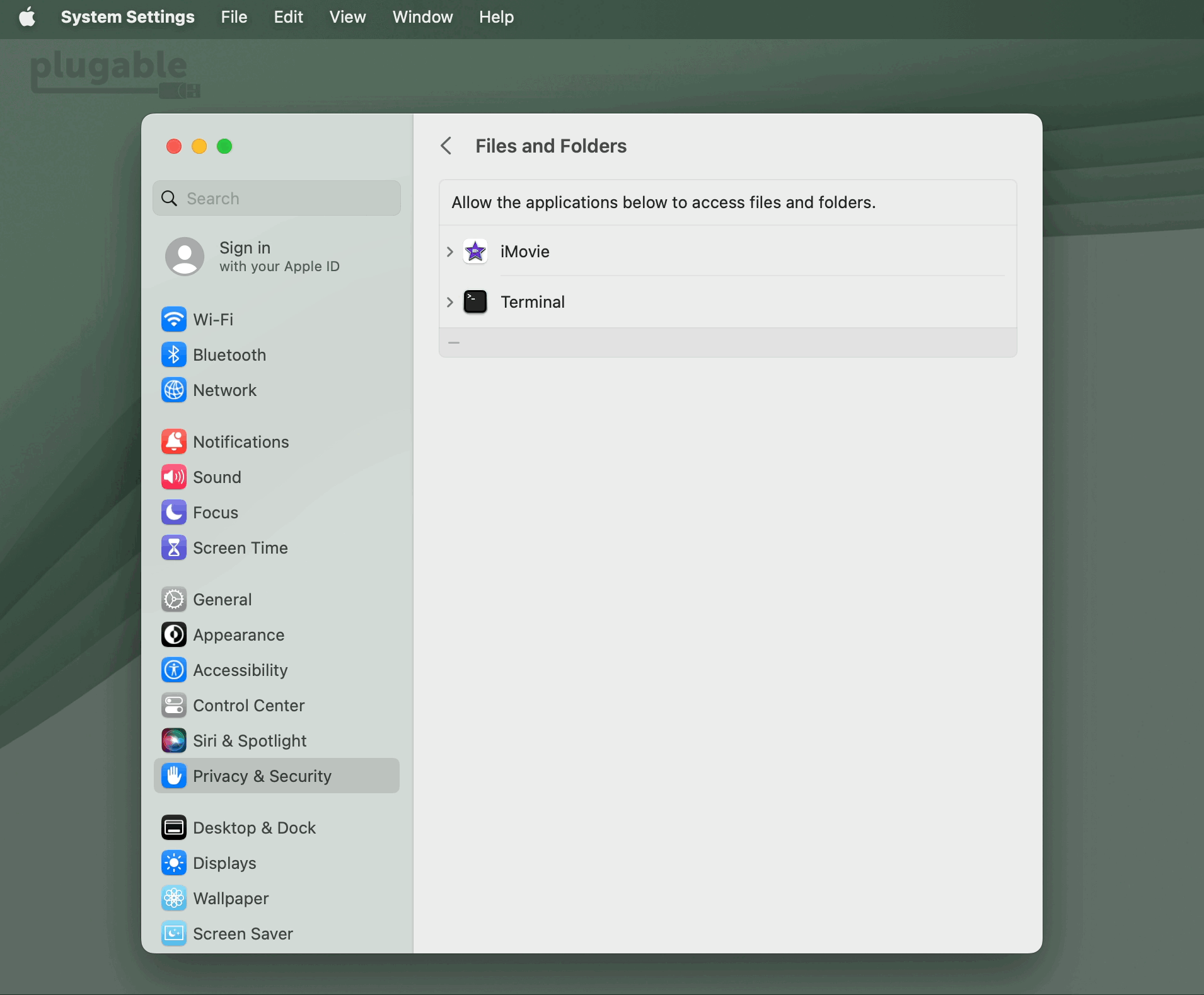
Can I leave my notebook computer connected to a charging dock overnight, or should I discharge and recharge the notebook battery regularly?
We are often asked if it is okay to leave a notebook computer connected to one of our USB-C docking stations with Power Delivery for extended periods of time. The short answer is yes, it is no different from leaving the laptop connected to the manufacturer's original USB-C power supply for the same time. The long answer is yes for modern laptops, and maybe for older (1990s-early 2000s laptops) and involves going into the different battery technologies used in consumer electronics devices.
Another common question is if it is possible to use the docking station but to disable powering and charging the computer. When a modern notebook computer runs on battery power it will often set the system to a reduced power state which may impact performance, or connected devices and we recommend always powering the computer when using a desktop docking station. For all of our docking stations that provide power to the host computer this will not affect the lifespan of the computer's battery.
Modern Laptop Batteries: Lithium-Ion
Lithium-ion (li-ion) batteries are found in a wide range of consumer electronics from notebook computers and cell phones, to electric cars, power tools, and wearable electronics like wireless earbuds. Li-ion offers fast charging, high-current discharging, fairly long service live compared to other rechargeable battery technologies and are relatively inexpensive.
The life-span of a rechargeable battery depends on many factors including age, temperature history, charging patterns, the chemical composition of the specific battery, and usage. For example batteries stored at 100% charge will degrade faster than batteries stored at 50% charge, this is why most consumer electronics devices arrive from the manufacturer with between 25% to 75% charge.
Lithium-ion batteries are consumable components, however in most modern computers, cell phones, and tablets these are not user serviceable components. To help maintain the battery all modern computers and most consumer electronics will include battery charge and protection circuits. These can be fairly simple, charging up the battery at preset rates depending on the charge level to help maintain the battery life, or complex software controlled charging that monitors battery temperature, voltage and current draw to maintain the fastest charging while maintaining the battery longevity.
Modern notebook computers can be left connected to the original power cable or a docking station with charging capability for extended periods, and do not benefit from regular discharge/recharge cycles. Our docking stations with charging capability rely on USB Type-C Power Delivery to power and charge compatible computers. USB Type-C Power Delivery is a negotiated charging protocol between the host computer and the docking station or USB Type-C power supply, this allows the computer to draw only the power it requires, and even select the best voltage level for powering the computer. In combination with a computer's built-in battery charging controller the computer is capable of maintaining the battery's optimal state even when left connected to a power source for an extended period of time.
Legacy Laptop Batteries: NiCad and NiMH
Older laptops, from the 1990s and some early 2000s, as well as some consumer electronics, and most rechargeable AA or AAA battery replacements use Nickel-Cadmium (NiCad) or Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) batteries. These batteries are slower to charge and discharge than li-ion batteries, and require very simple charge controllers, and in some cases can even be trickle-charged ( very low-current continuous charging ) if desired.
These batteries generally don't have smart charging controllers and to prolong the life of the battery required "training" or fully discharging and recharging the battery every so often. Many laptop manufacturers recommended fully charging and discharging a new laptop 2-3 times to train the battery, this is not necessary with modern laptops.
Conclusion
Modern notebook batteries are managed by the computer's built-in battery charging circuit, and require little to no user intervention to maintain optimal battery health. It does not harm the battery to leave the computer connected to an external power supply, so long as the computer is being used regularly. If the computer is to be stored for a prolonged period then discharging the battery to between 50-75% can help to maintain the battery life.
Batteries are consumable components and degrade over time, however modern notebook computers can extend the battery life generally to meet or exceed the life of the computer's other electronic components.
Understanding how adaptive/optimized charging methods have an impact on your smartphone's battery life, performance, and longevity.
With most modern smartphones you may have likely noticed a notification message while charging your phone indicating that your phone has entered "Optimized Battery Charging", this is how Apple refers to its smart charging messaging. With Android devices they will also show this notification message while charging although they refer to it "Adaptive Charging". Through these intelligent charging methods your phone will artificially reduce its charging speeds so that in the long run it will lengthen its overall battery life.
When setting up a new smart phone it may take a few weeks of machine learning to recognize your usage behavior and charging habits. Batteries go through wear and tear to which the more charge cycles it goes through the less healthier the overall battery becomes leading to it holding a lesser charge and other issues.
Your phone will alert you with a notification when it enters into a battery preserving charging state. At night you may notice your phone charging significantly slower along with a message saying “Battery full by 7:00 AM”. Even though it has the ability to fully charge in a much shorter time. If you set an alarm for an even earlier time your phone can adjust to finish charging at your alarm time. This is your phone prolonging the time it takes to charge to 100% in order to preserve battery health.
The reason why your phone will artificially slow its charging rate is to spend less time at 100% battery, and the less time your phone spends at 100% the more it helps with your overall battery health.
It is possible to disable Optimized/Adaptive Charging in your device's battery and charging settings although it is ideal for the majority of users to leave this setting enabled.
How can I rotate the displays connected to my DisplayLink-based USB Docking Station or USB Graphics Adapter in macOS?
Depending on what kind of processor your Mac uses, there's a different method to rotate the displays connected to a DisplayLink-based USB Docking Station or USB Graphics Adapter.
For Apple silicon-based Macs (M1, M1 Pro, M2, etc.)
Starting in macOS 12 (Monterey), DisplayLink-connected displays can be rotated using the DisplayLink Manager application. Display rotation is supported by DisplayLink Manager 1.6 Beta and up.
- Click on the DisplayLink Manager icon in the macOS Menu bar to expand the DisplayLink Manager
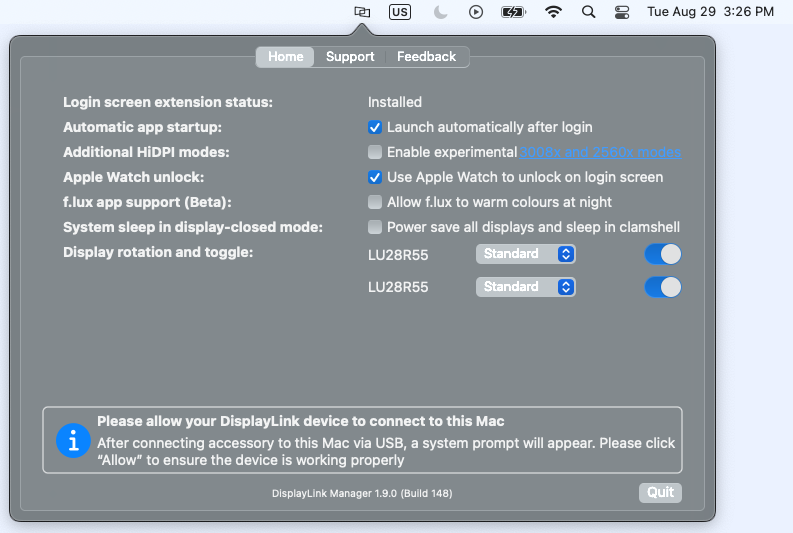
- Identify the display you wish to rotate
- If you're unsure which which display name corresponds with each physical monitor, you can identify the display by moving your cursor over the display's name in the DisplayLink Manager. A red border will be shown on the display when the cursor is over top of the corresponding display's name.
- Click the pop-up menu next to the display you wish to rotate to choose your preferred display rotation value
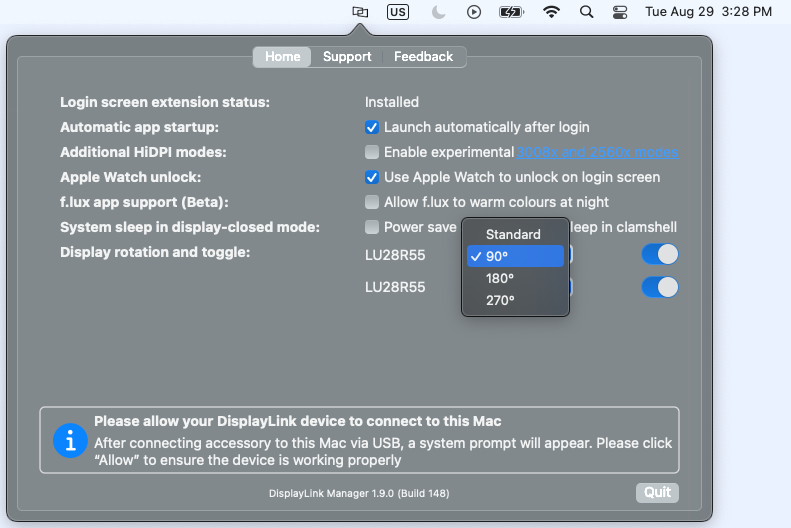
For Intel-based Macs
Starting in macOS 11 Big Sur, DisplayLink-connected displays can be rotated using macOS's built-in Display menu.
For macOS 13 (Ventura)
- Click on the Apple menu in the macOS menu bar at the top of your display
- From the Apple menu, click on “System Settings”
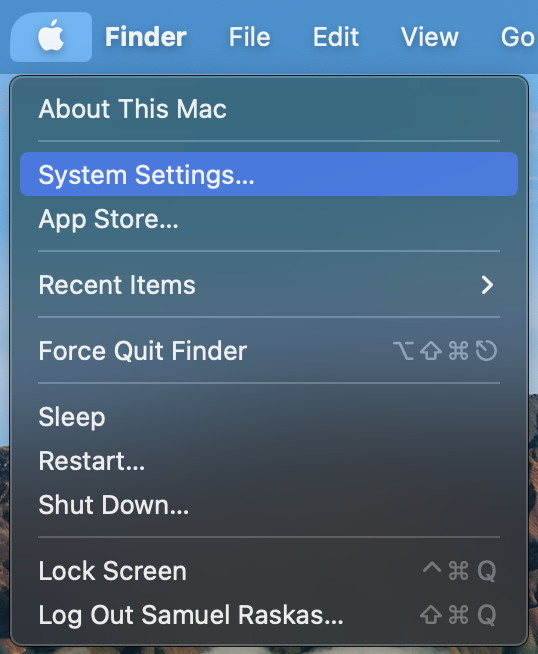
- In the sidebar of the “System Settings” window, click “Displays” (you may need to scroll down to see this)
- Click to select the display you wish to rotate
- Click the pop-up menu next to “Rotation” to choose your preferred display rotation value
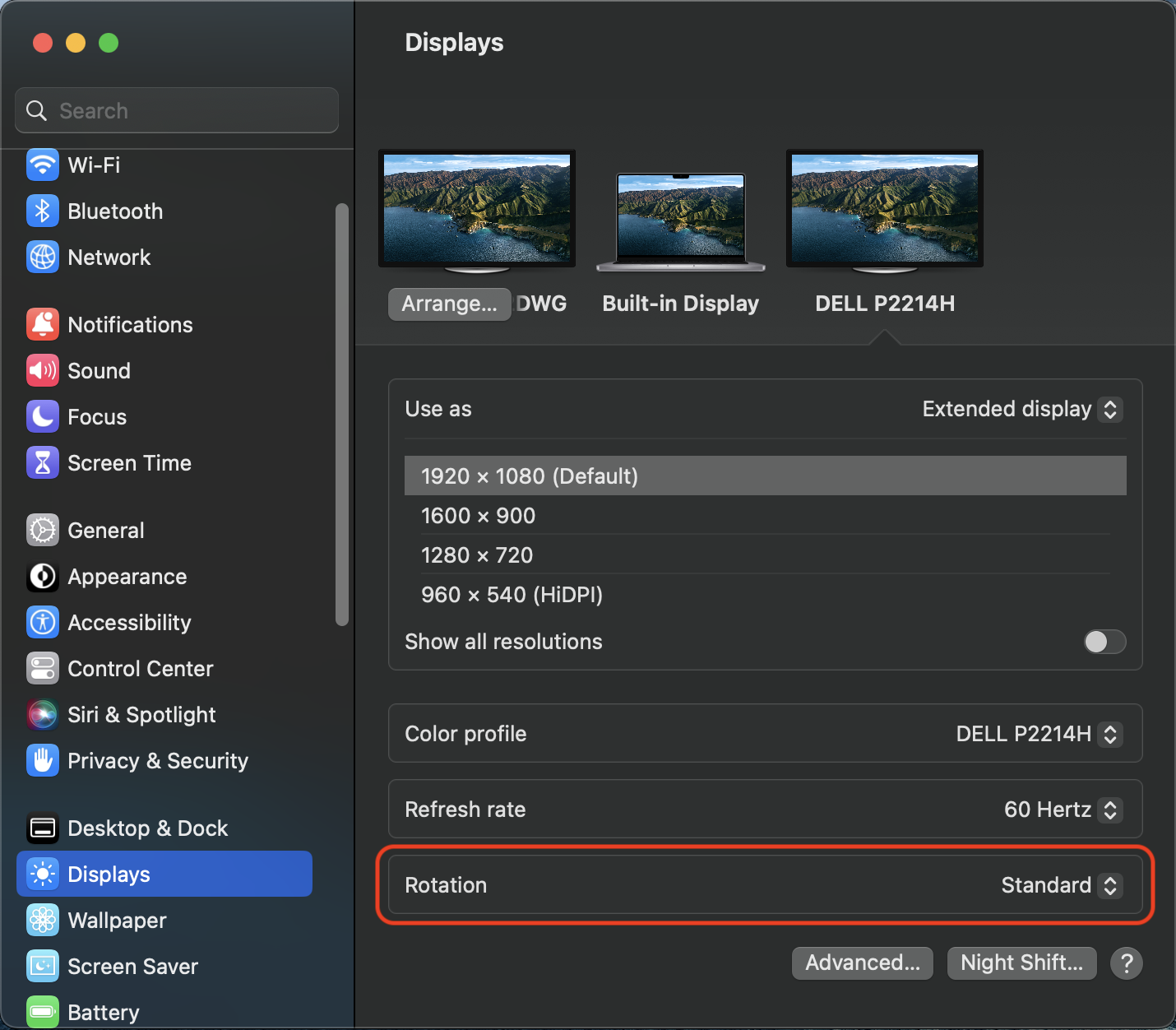
- In the dialog box that appears, select “Confirm” to proceed
For macOS 11 (Big Sur) and macOS 12 (Monterey)
- Click on the Apple menu in the macOS menu bar at the top of your display
- From the Apple menu, click on “System Preferences”
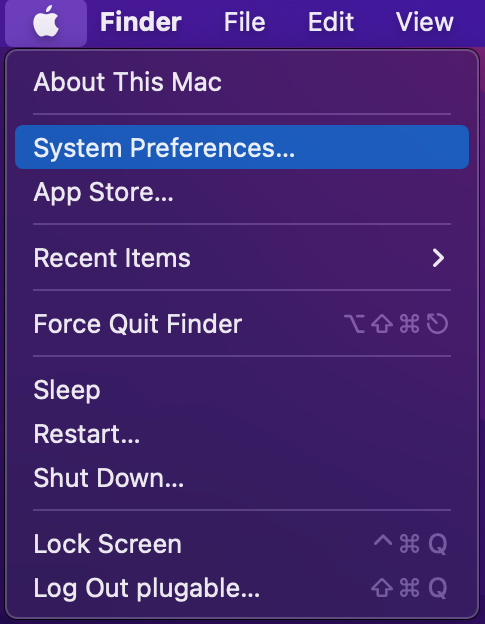
- In the “System Preferences” window, click “Displays”
- From the "Displays" window, select “Display Settings...”
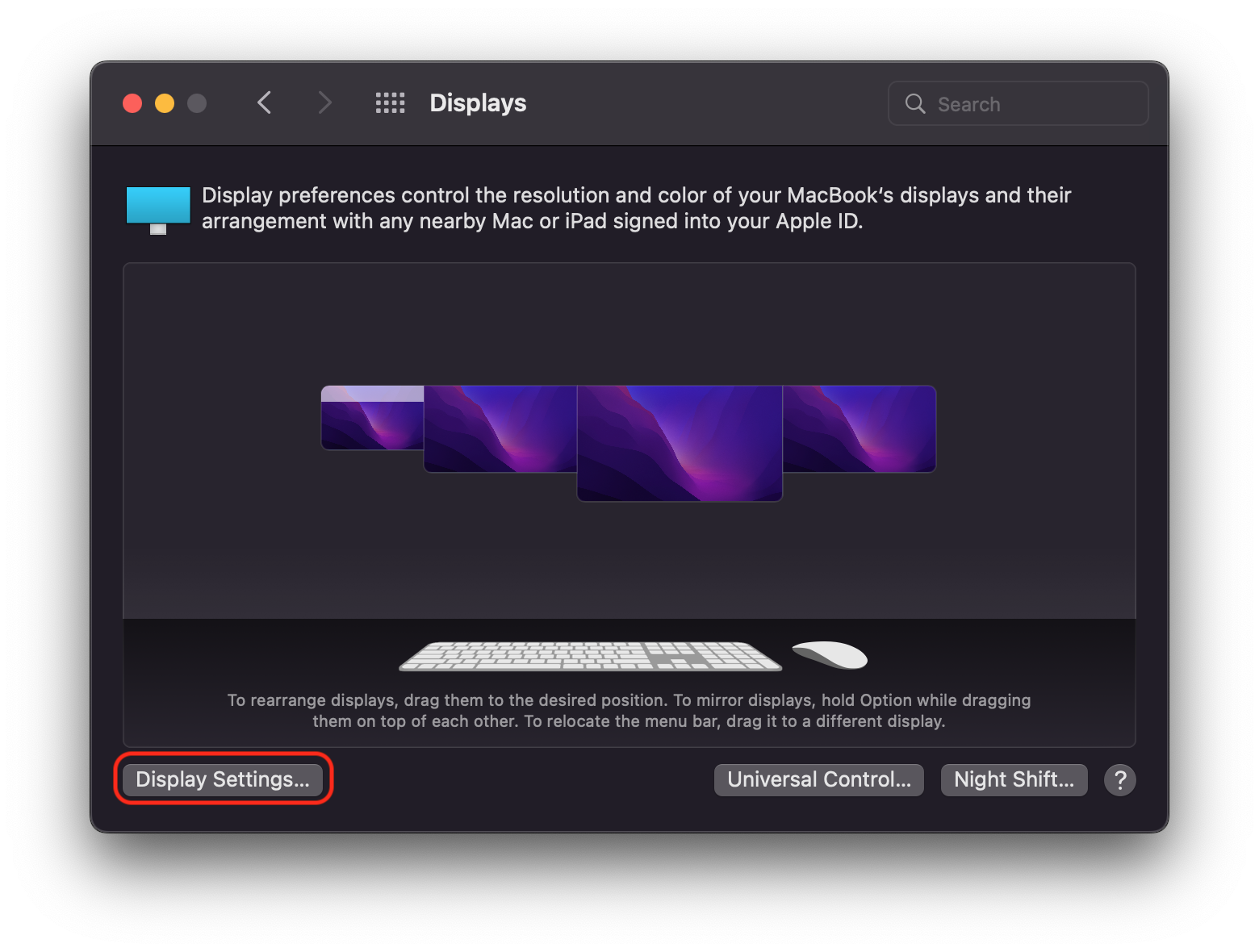
- Click to select the display you wish to rotate
- Click the “Rotate” or “Rotation” pop-up menu to choose your preferred display rotation value
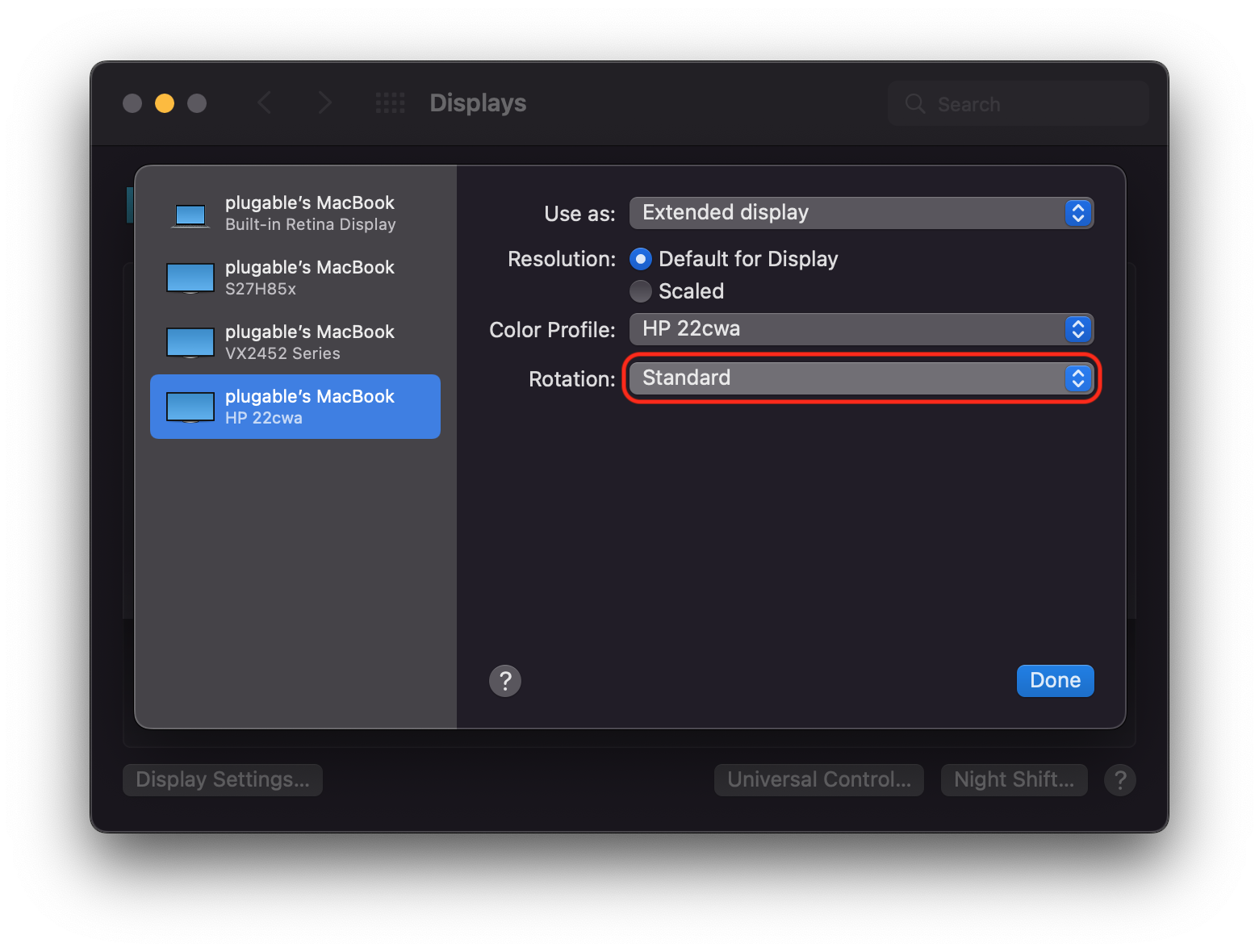
- If you're prompted with an additional dialog box, select “Confirm" to proceed
When my DisplayLink-based product is connected to my Mac running macOS 14 Sonoma, I see a notification within the Apple Menu bar at the top of my screen that states, ‘DisplayLink Manager is capturing your screen.’ Why is this?
The DisplayLink Manager Application requires access to your screen information in order to generate the image shown on the DisplayLink connected displays, and permission to access your screen information is requested during the application’s installation.
Once this permission has been granted, whenever the DisplayLink Manager Application is running you will see a notification within the Apple Menu bar that the DisplayLink Manager Application is capturing your screen. This is both normal and expected behavior.
To be clear, no information is being recorded or stored by the DisplayLink Manager Application. DisplayLink (the separate company that develops the technology and the application software) speak to this in more detail here → LINK
My dock or connected USB devices aren't being detected by my computer. What can I do?
On occasion, the internal USB hub in a docking station may stop working correctly. This can lead to your computer not detecting USB devices connected to the dock, or your computer may not recognize that the dock is plugged in at all.
A common fix for these situations is to perform a power-cycle of the dock to reset its internal hub chipset. We've seen that this can often restore the dock back to a working state when one or more of its functions aren't quite working. It's important that the steps are followed in a specific order to ensure the dock's internal USB hub fully resets. The steps are as follows:
1. Disconnect all USB peripherals connected to the dock
2. Disconnect docking station from host computer, then disconnect the dock's power adapter from power
3. Leave unplugged for at least 1 minute for power to dissipate
4. Connect docking station initially into power only
5. Connect docking station to host computer, then connect USB peripherals and test for functionality
Which USB-C port on this product can be used to connect it to my computer?
For products which have multiple USB-C ports, normally only one port is capable of connecting the product to a computer. USB-C ports capable of connecting the product to a computer are sometimes called “Host” or “Upstream” ports.
On Plugable products with multiple USB-C ports, the dedicated port for connecting to the computer will be marked with a small laptop icon or the words “To host”.
A product may not be able to function if it is connected to a computer through a different USB-C port. These ports are also known as “Hub" or “Downstream” ports.
Why did my displays stop working after my Mac updated or rebooted?
The most common reason a DisplayLink-based product may stop outputting video after rebooting or updating macOS is that the DisplayLink Manager is no longer running. The DisplayLink Manager is the software responsible for allowing DisplayLink-based video ports to output to connected displays. If the DisplayLink Manager is not running then the video will not work correctly.
You can see that the DisplayLink Manager is running by checking if its icon is present in the macOS menu bar at the top of your screen. When the icon isn't present the DisplayLink Manager is not running.
If the DisplayLink Manager isn't running, you can start it by following these steps:
- Open Finder
- Navigate to the Applications folder on the left side of the Finder window
- Within the Applications folder, locate the DisplayLink Manager
- Double-click on the icon for DisplayLink Manager to open it
- Verify that the DisplayLink Manager icon appears in the macOS menu bar, indicating it's running

It's recommended to set the DisplayLink Manager to launch automatically after login as well. This will help ensure the DisplayLink Manager starts automatically if your Mac is rebooted, although in some instances, it may still be necessary to launch the DisplayLink Manager manually.
This can be set by clicking on the DisplayLink Manager's icon when it's running, and checking the box next to Launch automatically after login as shown below
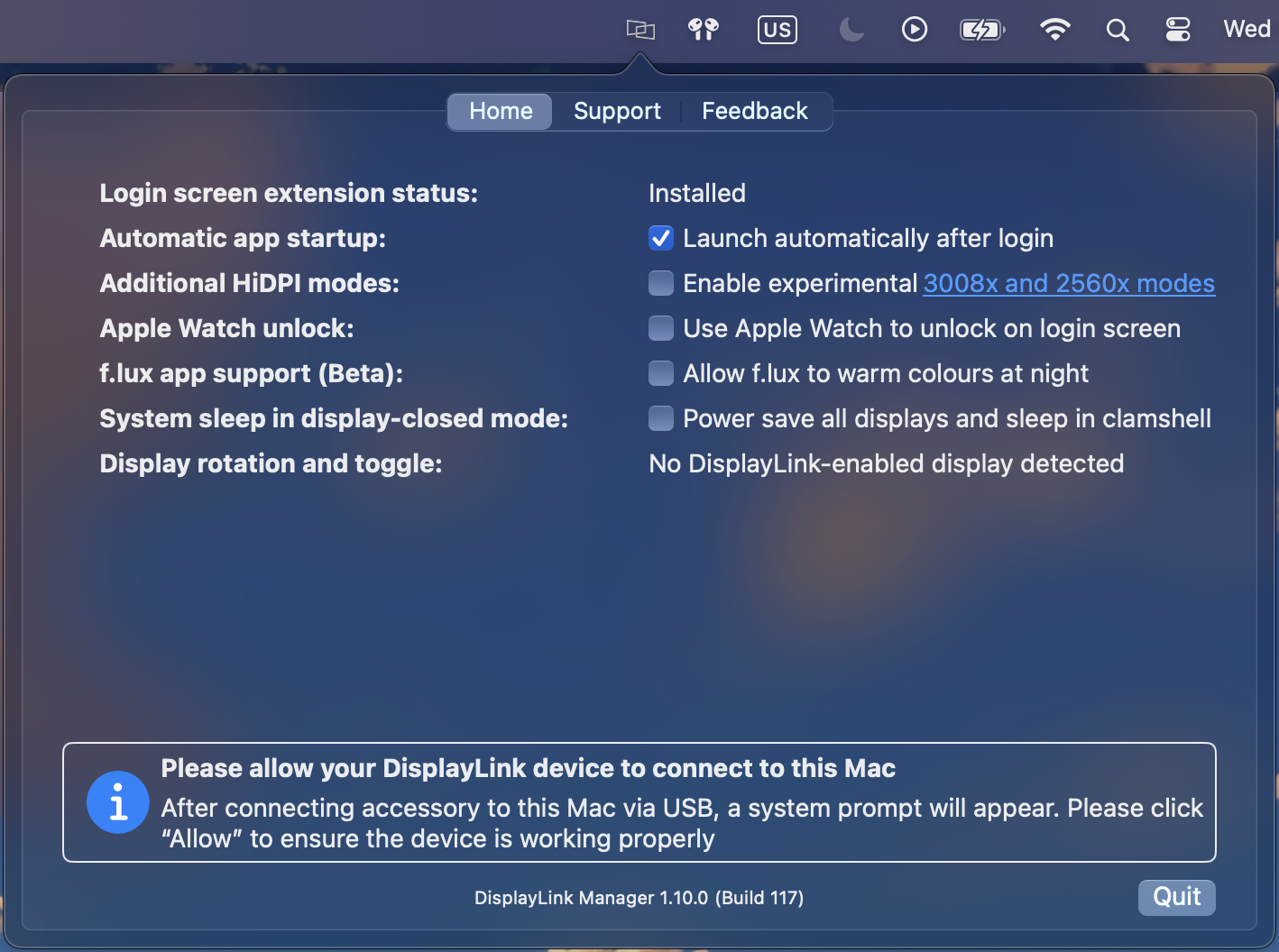
Understanding Heat Generation in Electronics
It's not uncommon for users to notice a certain level of heat generation from electronics and by extension, Plugable products during operation. In this knowledge base article, we'll explore the reasons behind this heat generation and why it is considered a normal experience within reasonable limits.
Electronics, by their nature, generate heat during operation. This is primarily a result of the electrical current flowing through various components, such as integrated circuits, transistors, and other electronic elements. As Plugable products are designed to efficiently process and transfer data (among other functionality), some level of heat generation is inherent.
Factors Influencing Heat Generation:
- Power Consumption: The power consumption of a device directly influences the amount of heat it generates. Higher power usage, especially during data transfer or charging processes, can lead to increased heat.
- Enclosure Design: The design of the product's enclosure and its ability to dissipate heat play a crucial role. Adequate ventilation and heat sinks are often incorporated to manage and disperse generated heat effectively. This is evident in our TBT3-UDZ and TBT4-UDZ designs. The metal case in these docks are designed to function as a heatsink with thermal pads placed throughout the enclosure. This allows heat dissipation from inside to the outside, but will also make it feel as if the device is “too hot”.
- Ambient Temperature: The external environment may also play a role. Higher ambient temperatures can contribute to increased perceived heat from the product. This means that summer temperatures may increase the heat generation of not just Plugable products, but many other electronic devices.
Normal Heat Levels: While it is normal for electronic devices to generate heat, Plugable products are engineered to operate within safe temperature ranges. We conduct rigorous testing to ensure that the heat generated during normal operation falls within industry-standard safety parameters. While not all products are or need to be UL certified, we try to go by UL guidelines for thermal readings. The UL threshold is 77C/170.6F, and we aim for around 71C/160F.
Tips for Users:
- Ventilation: Ensure that Plugable products have sufficient ventilation around them. Avoid placing them in enclosed spaces where heat dissipation may be impeded.
- Usage Patterns: Intensive tasks such as high-speed data transfer or charging multiple devices simultaneously may result in increased heat generation. This is generally normal but may be more noticeable in such scenarios.
- Accessories: A number of our devices will allow for the connection of USB accessories and as such, these will require power. If too many “power-hungry” devices are connected, this will cause the device to run much hotter than expected. Be sure to keep in mind the power limits of your dock/device.
In conclusion, experiencing heat from Plugable products is a normal aspect of their operation. Users can rest assured that we prioritize the safety and efficiency of our devices. By understanding the factors influencing heat generation and following simple usage guidelines, users can make the most of their Plugable products while ensuring a reliable and efficient user experience.
DisplayLink and "Screen Recording" Troubleshooting
If you have installed your DisplayLink-enabled docking station or graphics adapter and downloaded the DisplayLink software, but see that no displays are working properly, you may need to enable “Screen Recording”. In this guide, we will go over a short list of steps to enable this permission, and get your DisplayLink device up and running!
As of macOS Catalina (version 10.15), DisplayLink drivers that are installed require that the “Screen Recording” permission be granted by the user. While this permission, when used in conjunction with DisplayLink is not recording in a traditional sense, it does allow DisplayLink to access the pixels it needs to render images (mirrored or extended). It then sends these pixels over USB from the computer to the display connected to your DisplayLink connected device.
Note: It does not capture or send any data.
During the installation process for the DisplayLink drivers, you will be requested to allow “Screen Recording” for DisplayLink. Additionally, you may see a notification within the DisplayLink application and when a new device is connected. However, we understand sometimes these may get lost in a sea of information and other notifications.
How do I know if the Screen Recording permission hasn’t been set? Reference the image below to check in your “Privacy & Security” settings
If you have not enabled “Screen Recording”, please follow these few instructions to enable it.
- Click on the Apple icon (defaults to the top left corner of your screen) and select “System Preferences
- Navigate to and click “Security & Privacy”
- In this window, select “Privacy”
- A list will be presented, scroll until you find “Screen Recording” and click on it
- Displayed on the bottom left, there is a lock icon, click on this to make changes
- If prompted, login using your computer credentials to make changes
- Check the box next to DisplayLink Manager
- You will be promoted to “Quit & Reopen”, click this button
- Click on the lock icon once more to save your changes
Note: Some of these steps may vary slightly based on your macOS version
You should now be able to see your displays on your docking station or adapter. If you have completed the above steps successfully and still do not see your displays, please be sure to reach out to our support team at support@plugable.com.
My Monitors Are Not Detected When My Mac Wakes from Sleep or Boots. What Can I Do?
Monitors not being detected when a Mac wakes from sleep can sometimes happen when the monitor is using automatic input source detection. Depending on the manufacturer of the monitor, the name of this input source or setting may vary. Some of these include “Auto Select”, “Auto Detect”, “Auto Source”, or other various combinations including “Auto” in the name.
The use of automatic input source detection can be problematic because it causes the monitor to be slower to inform the computer that it's connected when this setting is enabled. The additional delay introduced by automatic input source detection can cause the monitor connection negotiation between macOS and the monitor to time out, leading macOS to think there is no monitor connected to the port. As a result, video will not be sent to the monitor, and the monitor will not be detected by the Mac.
The solution to this problem is to disable automatic input source detection on your monitors. The method of accomplishing this will also vary by monitor model, however there are a few common methods such as:
- Setting the monitor's Input Source to the specific connection being used rather than automatic detection
- Disabling automatic input source detection within the monitor's on-screen display (OSD) settings
For more details on how to disable automatic input source detection, please consult the documentation for your specific monitor model from its manufacturer.
How To - Set a Network to Private or Public in Windows 10 & 11
The Windows Firewall may block some networking features when the local network is not set to Private. This article will describe the process for setting the local network, either wired Ethernet or Wi-Fi to be a Private network.
Windows 11
1 - Connect the computer to the network, either wired or wireless
2 - Open the Windows Settings - right-click on the Start Menu and select “Settings” from the pop-up menu
3 - On the left column select “Network & internet”
For Wired Networks
4 - Select the “Ethernet” option
5 - The connected network should be expanded, if not click on “Network Connected" to expand the section
6 - Select the “Network profile type” either “Public network” or “Private network” to suite your needs
For Wi-Fi Networks
4 - Select the “Wi-Fi” option
5 - Select your Wi-Fi network name “properties”
6 - Select the “Network profile type” either “Public network” or “Private network” to suite your needs
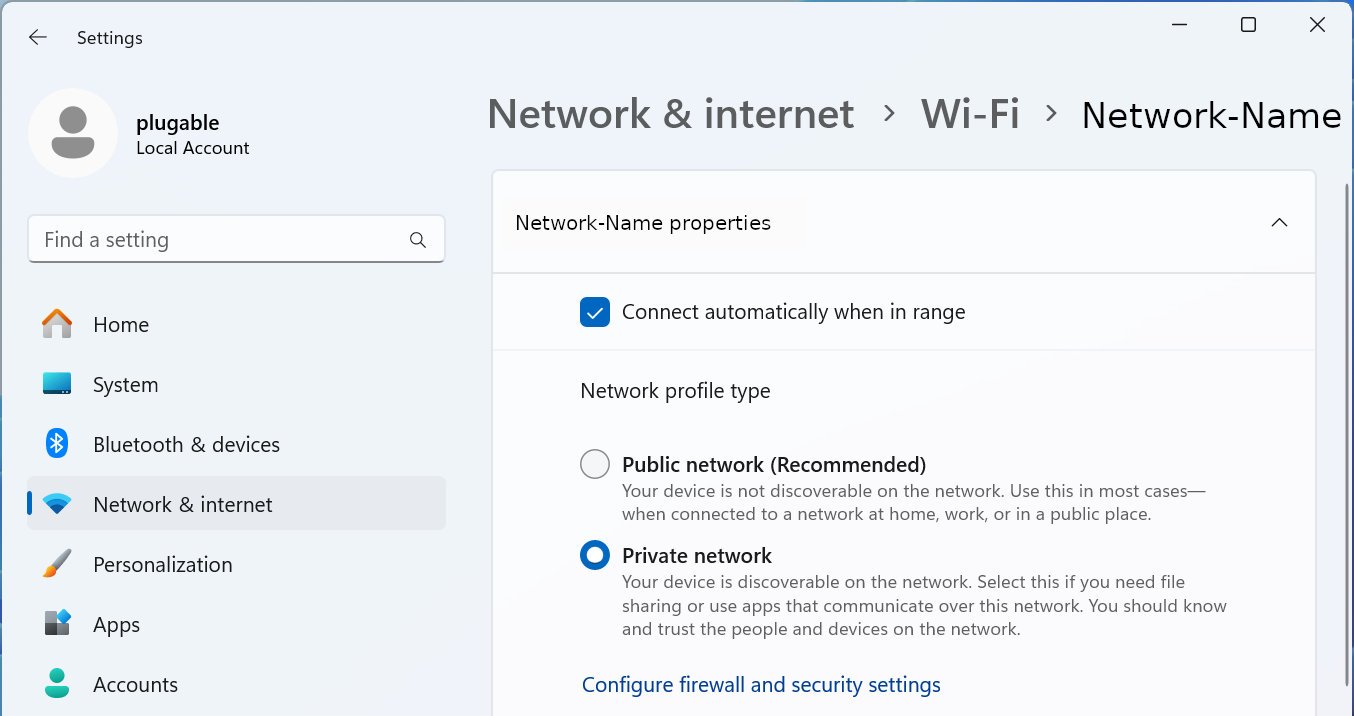
Windows 10
1 - Connect the computer to the network, either wired or wireless
2 - Open the Windows Settings - right-click on the Start Menu and select “Settings” from the pop-up menu
3 - Select “Network & Internet” fro the bottom section
4 - Select the “Ethernet” option from the left pane
5 - Select the “Connected” network from the right pane
6 - Select the “Network profile type” either “Public network” or “Private network” to suite your needs

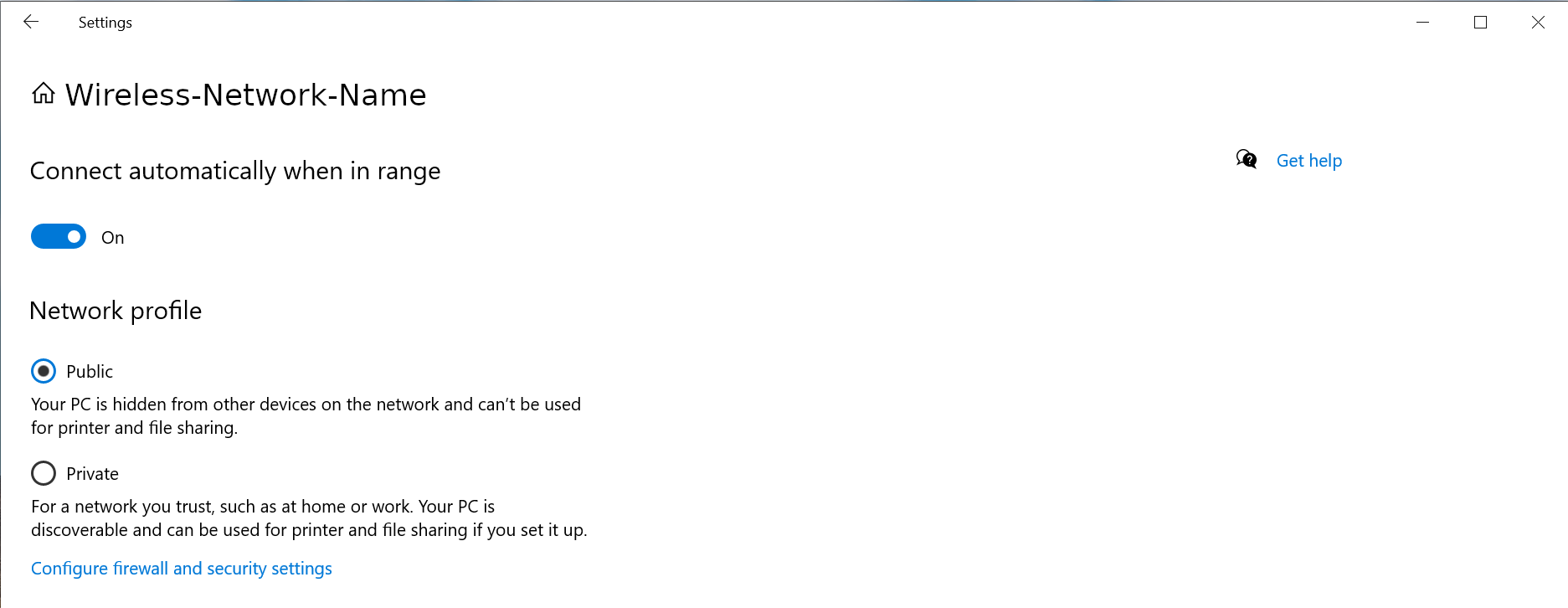
Windows PowerShell
If the option does not show up in the Windows Settings GUI, or if you prefer to use the terminal.
1 - Open a new terminal: Right-click on the Start Menu and select “Terminal”
2 - Run the following command to list the available networks
Get-NetConnectionProfile
PS C:\Users\plugable> Get-NetConnectionProfile Name : Network InterfaceAlias : Ethernet Instance 0 InterfaceIndex : 7 NetworkCategory : Private DomainAuthenticationKind : None IPv4Connectivity : Internet IPv6Connectivity : NoTraffic
3 - Run the following command to set the network to Private
Set-NetConnectionProfile -Name Network -NetworkCategory Private
Where “Network” is the network name from step #2 and “Private” can be either “Public" or “Private”





